订阅 wiki
Share wiki
Bookmark
opML
0%
opML
简介
OpML(Optimistic Machine Learning,乐观机器学习)是由 ORA 发明和开发的,它引入了一种将机器学习与区块链技术集成的突破性方法。通过利用与乐观 Rollup 相似的原理,opML 确保了计算的有效性,以去中心化的方式进行。该框架通过允许对 AI 计算进行链上验证,从而增强了机器学习推理的透明度并促进了信任。[1]
架构
OpML 由以下关键组件组成:
- 欺诈证明虚拟机(链下 VM):一个强大的链下引擎,负责执行机器学习推理。此组件执行机器学习推理,生成新的 VM 状态作为输出。当出现差异(表现为不同的 VM 状态)时,MIPS VM 采用二分法来精确定位发散开始的确切步骤或指令。
- opML 智能合约(链上 VM):用于验证计算结果,确保链下计算的准确性。这些合约允许执行单个 MIPS 指令,使链上环境能够验证计算过程中的特定步骤。此功能对于解决争议和确保链下计算的完整性至关重要。
- 欺诈证明:如果发生争议,验证者生成的欺诈证明将作为确凿的证据,说明计算中的差异,并通过 opML 智能合约促进解决过程。
验证游戏
验证游戏是假定两个或多个参与方执行相同程序的过程。然后,参与方可以采用精确定位的方式相互挑战,以找到有争议的步骤。此步骤将发送到智能合约进行验证。 为了使系统按预期工作,确保以下几点非常重要:
- 确定性 ML 执行 opML 通过使用定点算术和基于软件的浮点数来确保一致的 ML 执行,从而消除随机性并通过状态转换函数实现确定性结果。
- 将执行与证明分离 opML 采用双重编译方法:一种用于优化的本机执行,另一种用于欺诈证明 VM 指令,以实现安全验证。这确保了快速执行和可靠的、与机器无关的证明。
- VM 中 AI 模型推理的效率 乐观 Rollup 系统中广泛采用的现有欺诈证明系统需要将整个计算交叉编译为欺诈证明 VM 指令,这将导致执行效率低下和巨大的内存消耗。opML 提出了一种新颖的多阶段协议,该协议允许半本机执行和延迟加载,从而大大加快了欺诈证明过程。
整个 opML 过程包括以下步骤:
- 请求者首先启动 ML 服务任务。
- 然后,服务器完成 ML 服务任务并将结果提交到链上。
- 验证者将验证结果。假设存在一个验证者声明结果是错误的。它与服务器启动验证游戏(二分法协议),并尝试通过精确定位一个具体的错误步骤来反驳该声明。
- 最后,将在智能合约上进行关于单个步骤的仲裁。
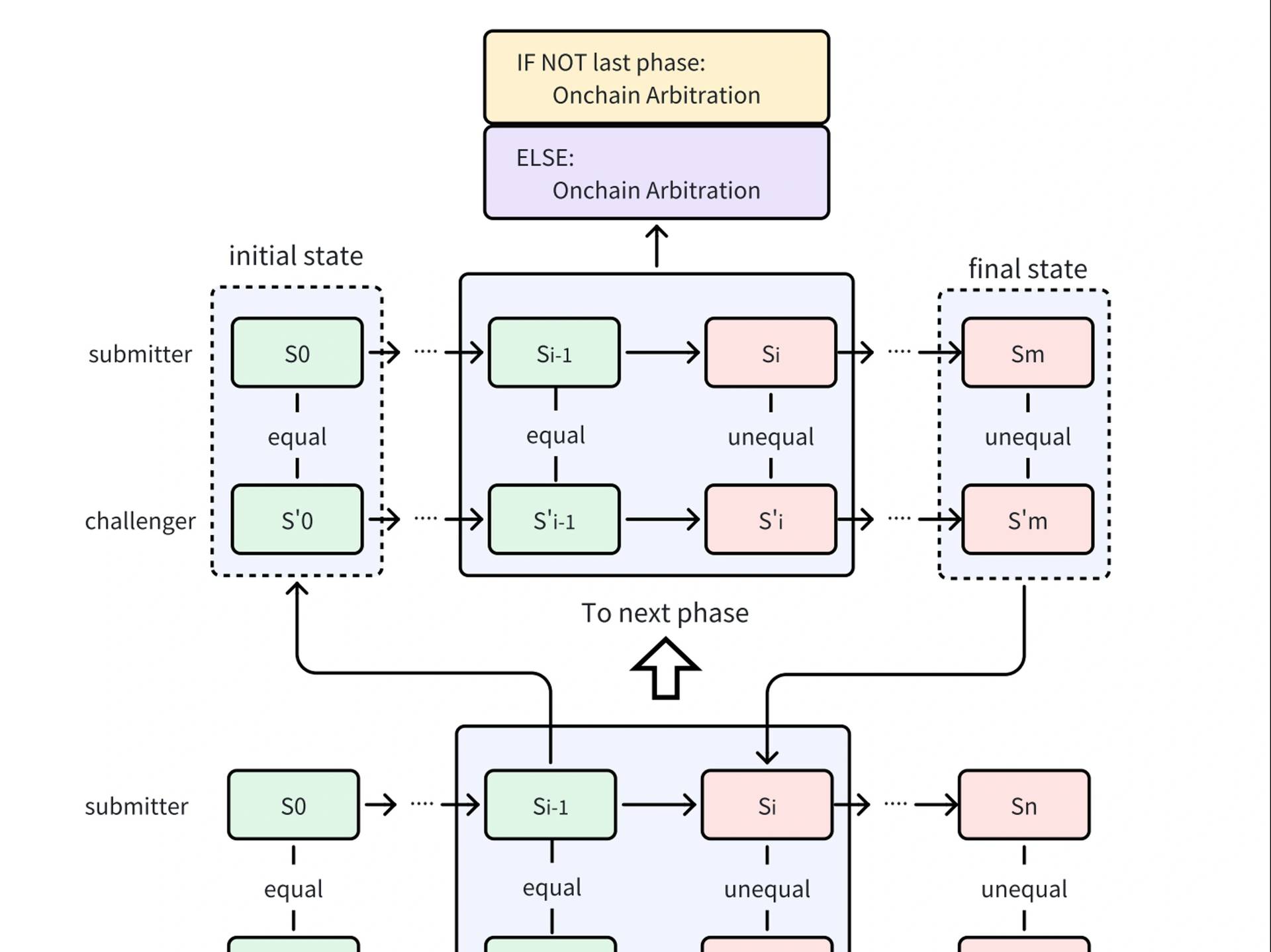
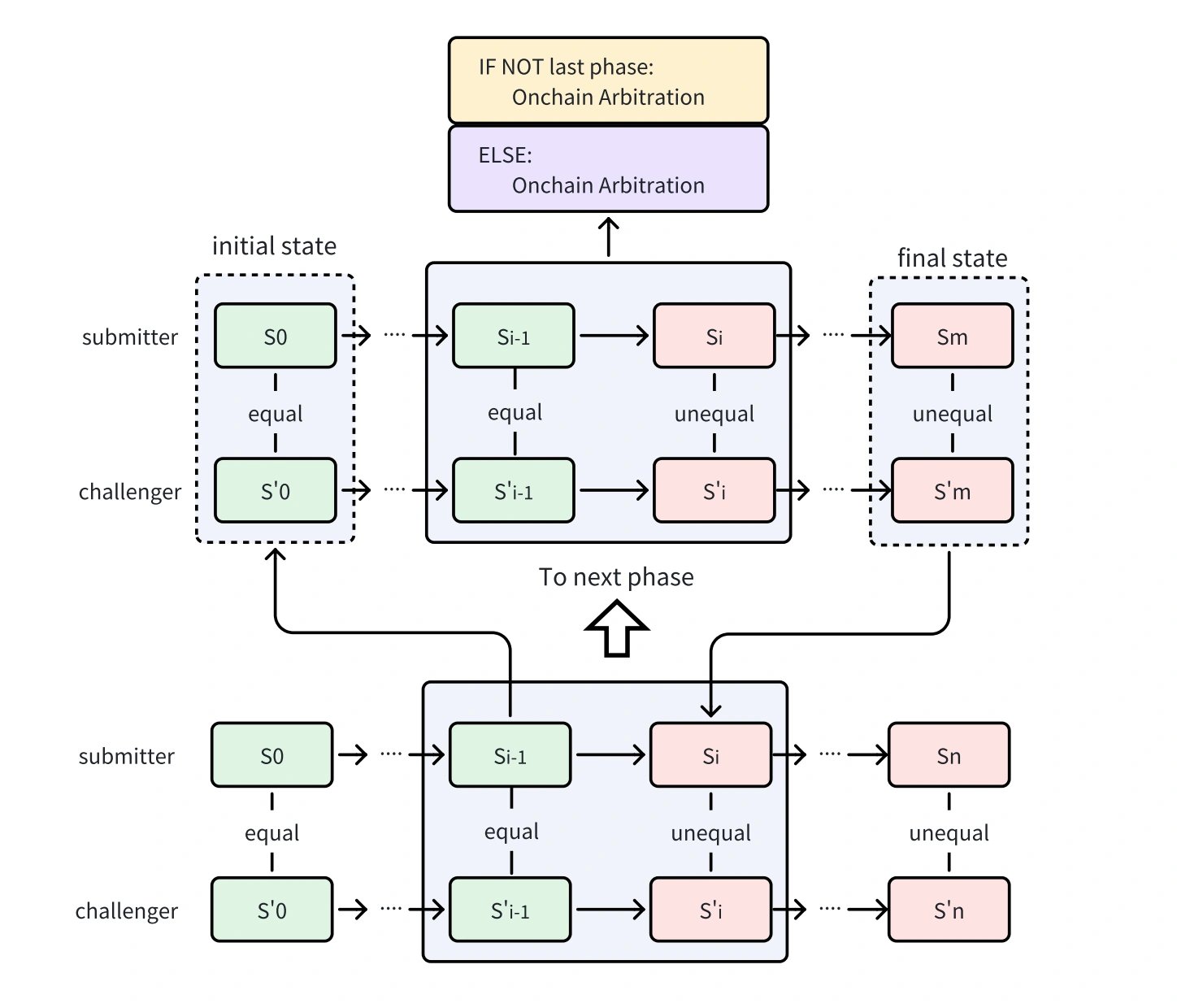
多阶段验证游戏
表示单阶段验证游戏的扩展,从而可以更好地利用计算资源。 单阶段验证游戏将整个 ML 推理代码交叉编译为欺诈证明 VM 指令。此方法不如本机执行有效(无法充分利用 GPU/TPU 加速和并行处理)。欺诈证明 VM 的内存也有限,这会阻止将大型模型直接加载到内存中。 为了解决上述问题,多阶段验证游戏引入了以下属性:
- 半本机执行 通过多阶段设计,我们只需要在最后阶段在 VM 中进行计算,类似于单阶段协议。对于其他阶段,我们可以灵活地执行导致本机环境中状态转换的计算,从而利用 CPU、GPU 甚至 TPU 中的并行处理能力。通过减少对 VM 的依赖,我们显着降低了开销,从而显着提高了 opML 的执行性能,几乎与本机环境的执行性能相似
- 延迟加载设计 为了优化欺诈证明 VM 的内存使用和性能,我们实施了一种延迟加载技术。这意味着我们不会一次将所有数据加载到 VM 内存中,而只会加载标识每个数据项的键。当 VM 需要访问特定数据项时,它会使用该键从外部源获取该数据项并将其加载到内存中。一旦不再需要该数据项,它就会从内存中换出,以释放空间供其他数据项使用。这样,我们就可以处理大量数据,而不会超出内存容量或影响 VM 的效率。
进一步阅读
发现错误了吗?