InfraX
InfraX 是一个分布式计算平台,旨在通过利用来自全球贡献者网络的闲置计算资源来支持开源 AI。该平台旨在普及 AI 计算基础设施的访问,同时为资源提供商提供可持续的经济模式。 [9]
概述
infraX 是一个专注于提供 GPU 和 AI 资源访问的去中心化基础设施平台。它建立在 区块链 技术之上,强调透明度、可访问性和用户参与。infraX 生态系统由 $INFRA 代币提供支持,该代币促进与平台上的各种服务的交互。
主要功能包括 GPU 借贷和租赁,允许用户将闲置的 GPU 资源货币化,或以去中心化的方式访问计算能力。AI 节点 租赁可用于短期和订阅式使用,支持个人和企业需求。其他服务包括用于 AI 功能(如图像和视频处理)的 API 端点、可定制的虚拟机、即时访问 H100 等高性能硬件,以及一种质押机制,用户可以通过锁定 $INFRA 代币来赚取基于 以太坊 的奖励。 [7]
生态系统
infraX 节点
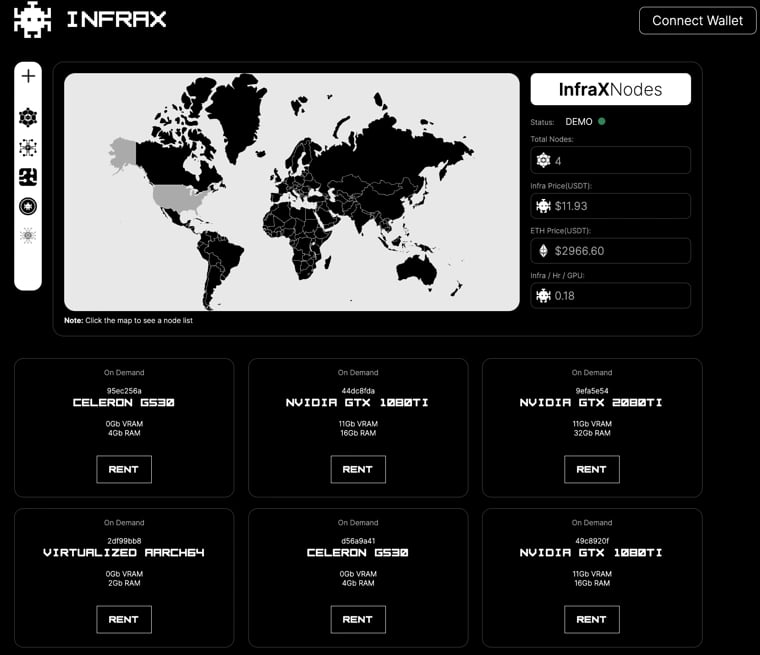
infraX 节点 网络通过将用户与分布式计算资源连接起来,解决了计算供应缺口。通过平台界面,用户可以访问地图,显示按区域划分的 节点 分布,查看总活跃 节点,并监控实时数据,例如每小时运行 GPU 所需的 $INFRA 数量,具有规范的可用按需 节点,以及 $INFRA 和 $ETH 的当前价格。 [3]
产品
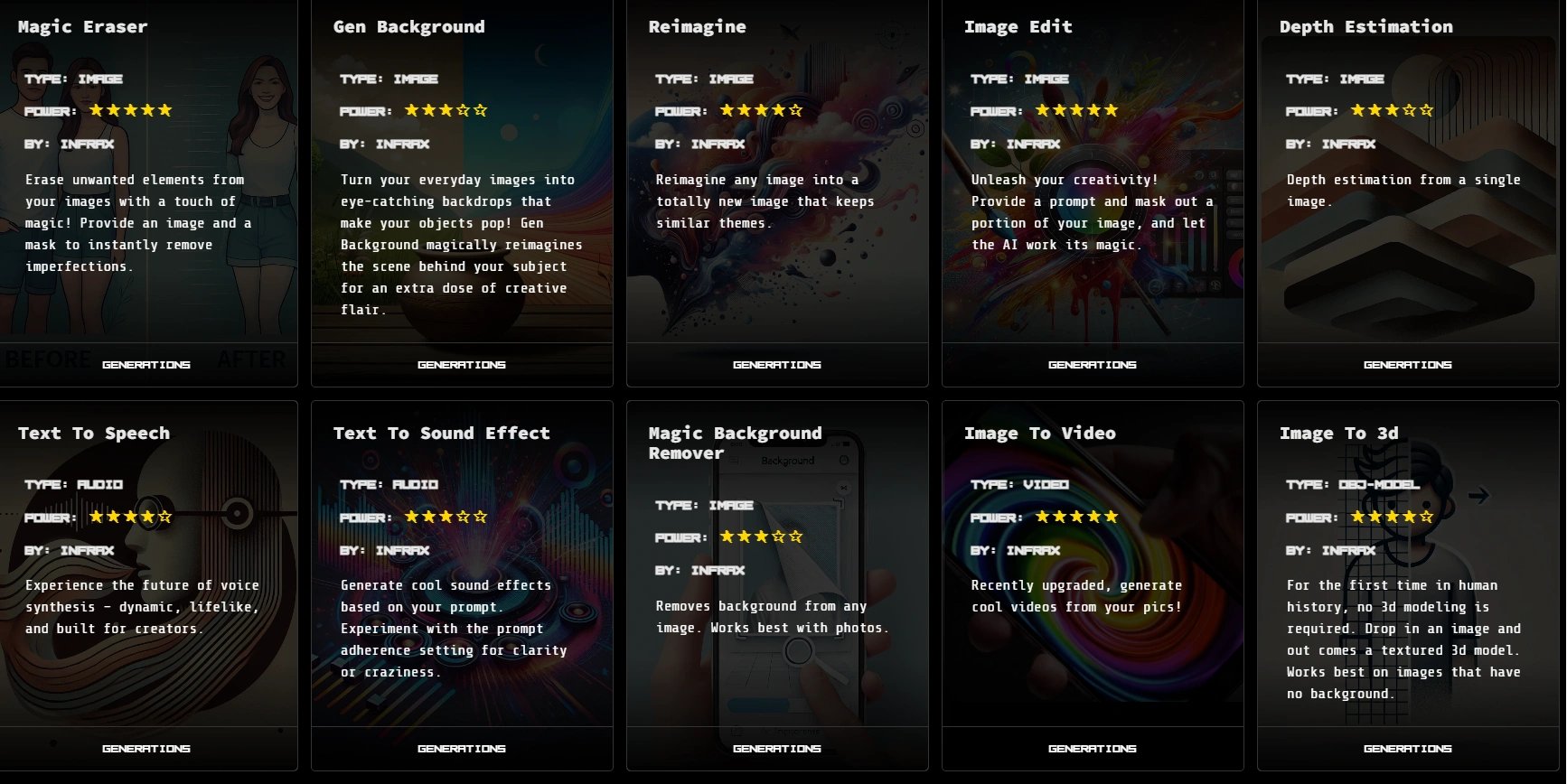
- 魔法橡皮擦 使用遮罩从图像中擦除不需要的元素,以消除瑕疵。
- 生成背景 用富有创意、引人注目的替代方案替换图像背景,以增强视觉吸引力。
- 重新构想 在保留整体主题的同时,根据原始图像生成一个全新的图像。
- 图像编辑 使用提示和遮罩编辑图像的特定部分,以应用 AI 生成的更改。
- 深度估计 从单个图像估计深度,以创建类似 3D 的视觉效果。
- 文本转语音 将文本转换为逼真的人声音频,专为创作者和动态语音合成而设计。
- 文本转音效 根据文本提示生成音效,具有可调节的清晰度或疯狂度。
- 魔法背景移除器 从图像中移除背景,针对照片进行了优化。
- 图像转视频 使用 AI 动画技术将静态图像转换为视频。
- 图像转 3D 将 2D 图像转换为纹理 3D 模型,对于没有背景的图像尤其有效。 [10]
用例
infraX 通过提供对 GPU 和 AI 资源的去中心化访问来支持各种计算工作负载。这种基础设施支持跨多个行业的应用:
- 图形和动画:高性能 GPU 访问支持 3D 渲染和视频编辑等任务,加速工作流程并降低内容创作者的成本。
- 游戏和 VR:开发者可以利用 infraX 进行游戏开发、AI 驱动的测试和渲染虚拟环境,而无需本地高端硬件。
- 增强现实和媒体:infraX 能够跨娱乐、建筑、营销和教育等行业高效创建和渲染 AR 内容。它还通过 GPU 加速处理来增强媒体流。
- 金融:在交易和风险管理中,infraX 支持对算法策略和风险评估进行实时数据分析,减少人为错误并加快决策速度。 [4]
代币经济学

infraX 代币 ($INFRA)
$INFRA 是 infraX 平台的原生实用代币,是生态系统中访问和交互的主要手段。它促进跨服务的交易,例如 GPU 租赁、节点 使用和 质押,同时激励用户参与。
该代币的固定最大供应量为 1,000,000 INFRA。截至最新数据,有超过 5,000 名持有者和超过 74,000 次记录的转账。$INFRA 在去中心化交易所积极交易,Uniswap V2 (以太坊) 是主要的市场,它最常与 WETH 配对。链上市值约为 398 万美元。 [5] [6] [8]

创始人
InfraX 由 Illia Polosukhin 创立,他也是 NEAR 协议 的联合创始人。Polosukhin 为该项目带来了 区块链 技术和分布式系统方面的丰富经验。他的背景包括在 Google Research 工作,在那里他为 Transformer 架构的开发做出了贡献,Transformer 架构是现代 AI 系统中的一项基础技术。 [1]
平台功能
InfraX 的平台围绕几个核心功能构建,这些功能使其能够实现分布式计算模型:
- 分布式计算网络:由 节点 运营商贡献的计算资源的全球网络,创建了集中式云服务的去中心化替代方案
- 资源市场:一个将计算资源提供商与需要计算能力来处理 AI 工作负载的用户相匹配的系统
- 经济激励:一种基于代币的经济模型,奖励 节点 运营商将其计算资源贡献给网络
- 开源重点:优先支持开源 AI 开发和研究,使高级 AI 功能更易于访问 [2]
未来服务
InfraX 概述了计划在未来实施的几项服务:
- AI 推理:支持在分布式网络上部署和运行经过训练的 AI 模型
- AI 训练:提供训练新 AI 模型所需的计算资源
- 数据存储:为 AI 开发所需的大型数据集提供去中心化存储解决方案
- 专用计算:支持专用计算需求,例如用于深度学习的 GPU 密集型工作负载 [2]
技术架构
虽然可用来源中提供的具体技术细节有限,但 InfraX 可能采用 区块链 技术进行协调和激励机制,以及用于分配和管理计算工作负载的专用协议。该系统需要解决几个技术挑战:
- 跨 计算节点的异构网络进行资源分配和调度
- 保护计算资源和 AI 工作负载的安全措施
- 用于数据密集型 AI 任务的高效数据传输和管理
- 满足时间敏感型计算需求的质量服务保证
技术架构需要在去中心化与 AI 计算任务的性能要求之间取得平衡,AI 计算任务通常需要低延迟和高带宽连接。