订阅 wiki
Share wiki
Bookmark
Stempoint
0%
Stempoint
Stempoint 是一个分布式人工智能 (AI) 基础设施平台,旨在通过整合对 AI 模型的访问与 GPU 计算资源的去中心化网络,为 AI 开发提供统一的环境。该项目旨在通过将多模型 API 与按需计算能力相结合,为开发人员和企业提供全面的解决方案。 [1] [2]
概述
Stempoint 的开发旨在解决 AI 行业中的挑战,例如对各种基础 AI 模型的访问分散以及高性能 GPU 计算能力的高成本或稀缺性。该平台的目标是为 AI 模型训练、微调和推理创建一个单一的、面向全球的接口。它试图通过调动来自全球个人和机构提供商的未充分利用的 GPU 资源来实现这一目标,使它们可以按需访问。 [3]
该平台的核心设计结合了两个主要组件:AI 代理聚合层和混合计算基础设施。聚合层充当统一网关,简化了开发人员与各种领先 AI 模型交互的方式。计算基础设施利用去中心化物理基础设施网络 (DePIN)以及集中式弹性云来为密集型 AI 任务提供必要的处理能力。这种混合方法旨在为用户提供灵活性、可扩展性和成本优化。 [4]
生态系统
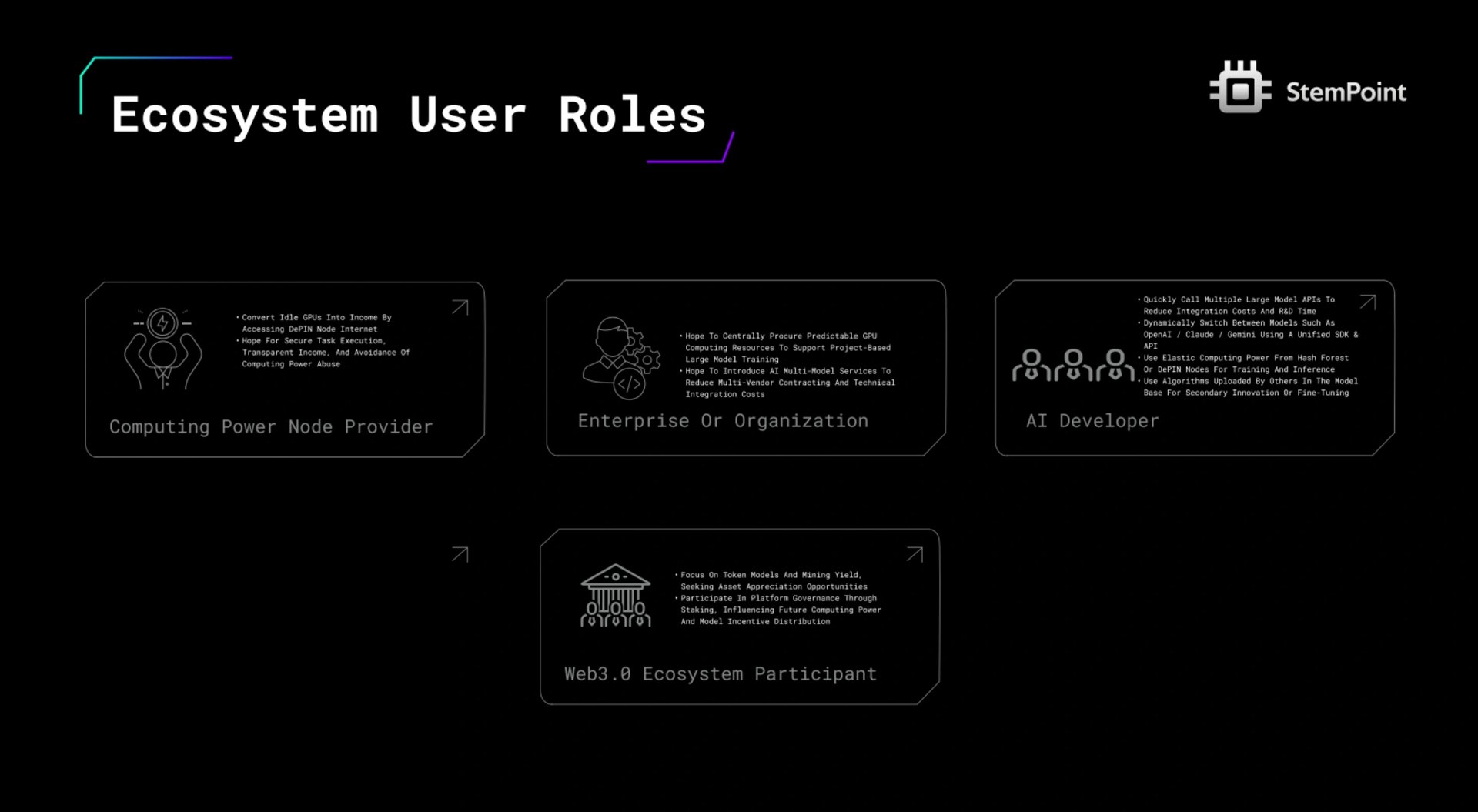
AI 开发人员和个人构建者
以最小的摩擦访问多个基础模型和可扩展的 GPU 资源,从而产生 API 使用和计算需求,从而推动代币效用和网络活动。
企业和 AI 团队
利用大规模计算资源进行模型训练和部署,具有统一的计费和成本控制,提供一致的、高价值的需求,从而加强 Hash Forest 和 DePIN 网络。
算法和模型提供商
将专有 AI 模型转换为可访问的 API 以进行货币化,从而使平台的产品多样化并增加应用程序和模型交互的总体数量。
GPU 计算节点提供商
将空闲或商业 GPU 容量贡献给网络,以换取代币奖励,从而扩展去中心化基础设施并保持低延迟、弹性的计算可用性。
最终应用程序消费者 (B2B/B2C)
参与 AI 驱动的产品和服务——例如聊天机器人、生成工具和分析平台——创建现实世界的用例,从而加强生态系统的技术和经济基础。
Web3 投资者和治理参与者
质押或持有代币以参与治理决策并赚取收益,从而为生态系统的经济和决策框架增加流动性和长期稳定性。 [13]
主要特点
公共和私有 AI 基础设施
提供具有托管运营、站点优化和完全可观察性的可定制本地和混合云集群。该系统支持高效的能源使用、成本控制和 AI 工作负载的可靠性。 [6]
Hash Forest
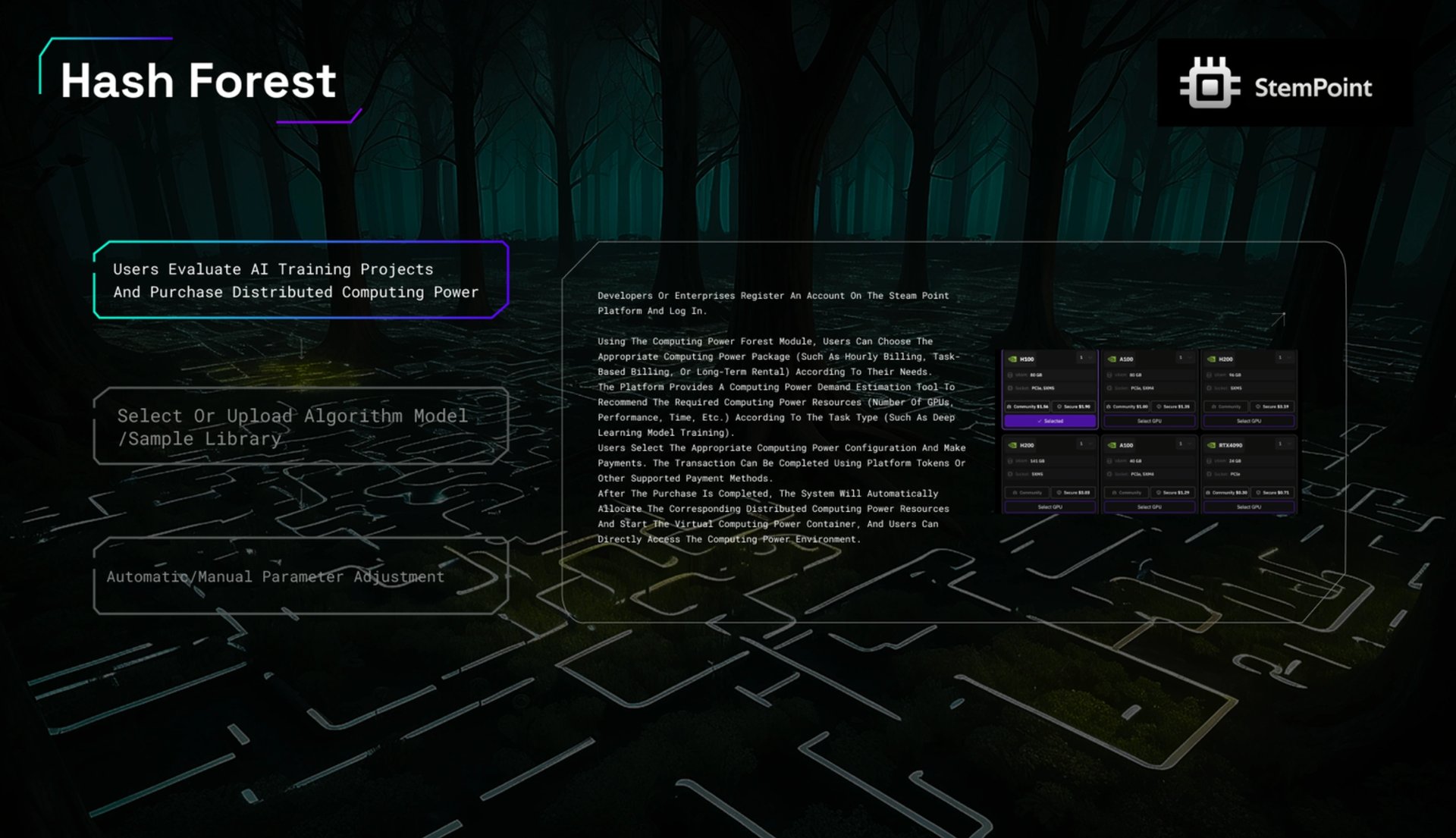
一个弹性 GPU 云网络,聚合全球空闲 GPU 用于 AI 训练和推理。它提供预配置的环境,其中包含主要的 AI 框架和自动化调度,以优化性能、延迟和成本。 [7]
AI 计算能力市场
将计算资源标准化为模块化单元,以实现灵活的租赁。它包括用于计费、性能报告和基于延迟、成本或主权要求的战略路由的工具。 [8]
AI 代理聚合层

一个统一的 API,它将多个基础模型(例如,OpenAI、Claude、Gemini)与动态路由、翻译和内存功能连接起来。它使开发人员能够通过单个 SDK 高效地构建 AI 应用程序。 [9]
AI 计算 RWA(现实世界资产)
将 GPU 集群所有权和收入权在链上进行代币化,从而实现透明的会计、收入分配和二级市场流动性。 [10]
DePIN 节点网络

一个去中心化的计算网络,参与者通过容器化客户端贡献 GPU 资源。节点安全地执行 AI 任务并获得代币化奖励,从而确保可扩展、可验证和分布式计算。 [11]
边缘 AI 硬件共享挖矿
连接机器人和 NPU 等边缘设备,以在保护隐私的条件下执行轻量级 AI 计算,从而扩展网络边缘的数据和计算能力。 [12]
用例
- **AI 模型训练:**使用 Hash Forest 和 DePIN 网络的组合能力对大规模 AI 模型进行高性能、分布式训练。
- **AI 模型推理:**为需要实时或批量处理的已部署 AI 应用程序运行可扩展且经济高效的推理任务。
- **AI 代理开发:**构建复杂的 AI 代理,这些代理需要持久的上下文内存,并通过单个统一界面访问多个基础模型。
- **算法货币化:**将自定义或专有算法包装到可调用的、按次付费的 API 中,这些 API 可以提供给平台上的其他开发人员。
- **GPU 硬件货币化:**使个人和数据中心能够通过将其未充分利用的 GPU 硬件贡献给 DePIN 节点互联网来赚取被动收入。
- **研究与开发:**为研究人员和开发人员提供按需访问强大的计算资源,以用于试验和微调自定义 AI 模型。 [1] [2]
代币经济学
Stempoint 生态系统由其原生实用和治理代币 $SPT 提供支持,总供应量为 100 亿。该代币是平台运营不可或缺的一部分,它创造了将计算资源提供商与 AI 应用程序开发人员联系起来的经济激励。
- 挖矿:50%
- 基金会:15%
- 团队:10%
- 社区:5%
- 筹款:20%
代币实用程序
- **计算支付:**开发人员和企业使用 SPT 来支付在 Hash Forest 和 DePIN 网络上进行 AI 模型训练和推理期间消耗的 GPU 资源,以及对 AI 代理聚合层的 API 调用。
- **节点奖励:**将 GPU 硬件贡献给 DePIN 节点互联网的计算提供商因成功完成任务而获得 SPT 代币奖励。这是扩大网络容量的主要激励。
治理
Stempoint 的治理模型旨在允许利益相关者影响平台的战略方向。通过质押 SPT 代币,持有者可以获得对关键提案的投票权。这种机制旨在指导与计算能力激励、模型集成优先级和其他平台参数相关的决策。目标是创建一个去中心化和参与性的生态系统,让社区在项目的长期发展中拥有发言权。 [4] [2]
发现错误了吗?
