Stellar
**Stellar Development Foundation (SDF)**는 스텔라 네트워크를 지원하고 플랫폼 간 거래 및 소액 결제를 처리하는 비영리 단체입니다. 스텔라는 원래 Ripple의 XRP에서 포크되었지만, 2015년 11월에 Stellar Consensus Protocol (SCP)로 코드가 업데이트되어 네트워크를 분산화했습니다.[1][11] 스텔라는 루멘(XLM)이라는 자체 디지털 통화로 구동됩니다.[14]
스텔라 네트워크
스텔라 네트워크는 2014년 스텔라 개발 재단(SDF)에 의해 만들어진 P2P 오픈 소스, 분산형, 커뮤니티 소유 네트워크입니다. 최소한의 비용으로 금융 자원 이전을 용이하게 하도록 설계된 플랫폼입니다. 사람, 은행, 결제 처리업체를 연결하여 사용자가 다양한 유형의 암호화폐를 생성, 전송 및 거래할 수 있도록 합니다. [3][12]
스텔라의 사명은 국경 간 결제 비용을 줄이는 것입니다. 네트워크는 거래당 최소 0.00001 XLM의 수수료를 부과합니다. 여러 거래는 부과되는 수수료 증가로 이어집니다. 스텔라는 더 많은 거래를 포함하는 프로젝트에 우선 순위를 부여합니다. 둘 이상의 프로젝트에 동일한 수수료가 있는 경우, 순서가 섞이고 맨 위에 있는 프로젝트가 블록체인 원장에 들어갑니다. 나머지는 차례를 기다리거나 너무 오래 기다린 경우 삭제됩니다. [2]
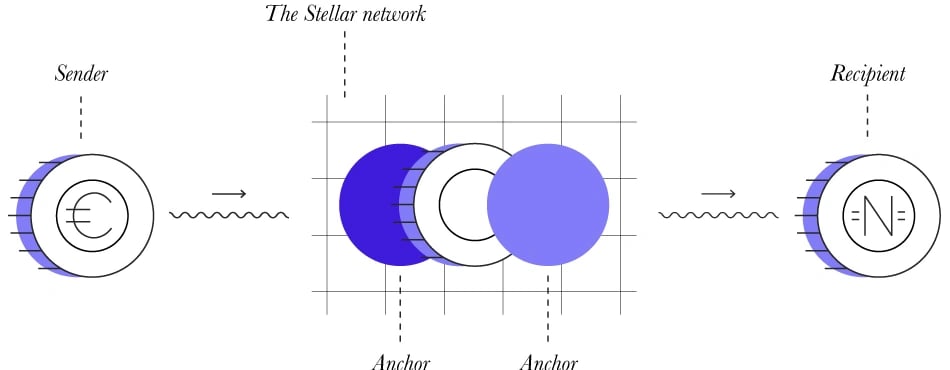
앵커
Stellar의 기능은 앵커라는 개발에 의해 구동됩니다. 앵커는 예금을 보유하고 신용을 발행하는 신뢰할 수 있는 엔터티입니다. 앵커의 기능은 비트코인, USD 및 ICO 토큰과 같은 자산을 발행하는 것입니다. 이러한 자산은 앵커에서 충분한 신용이 발행된 경우 교환됩니다. [1]
앵커는 기존 은행 시스템과 Stellar 간의 가치 이전을 가능하게 하는 데 활용되며 자산 발행, 온/오프 램프 생성, Stellar에서 XLM 또는 USDC에 대한 액세스 제공, 네트워크의 다른 프로젝트와의 통신을 용이하게 하기 위해 Stellar Ecosystem Protocol(SEP) 통합을 포함한 다양한 서비스를 제공할 수 있습니다.
앵커는 은행이나 PayPal과 유사하게 작동하여 자금을 보유하고 지갑에 신용을 발행합니다. 수신 측의 가상 지갑은 신용을 받을 수 있으며, 이는 EUR, USD, AUD 등과 같은 지원되는 모든 법정 통화로 변환됩니다. [4]
역사
Jed McCaleb은 Ripple의 창립자 중 한 명으로, 2013년에 변호사 Joyce Kim과 함께 Stellar를 설립했습니다. [13] Jed McCaleb은 회사의 미래 방향에 대한 의견 불일치로 2013년에 Ripple을 떠나 Stellar를 구축했습니다. Stellar의 배후에 있는 논리를 설명하면서 McCaleb은 CoinMarketCap에 다음과 같이 말했습니다.
“Stellar의 원래 디자인은 법정 통화와 다른 종류의 가치 형태가 암호화 자산과 병행하여 실행될 수 있다는 것입니다. 이것은 이러한 것들을 주류로 이끄는 데 매우 중요합니다.” [3]
2016년에는 공동 창립자 Joyce Kim이 Stellar에서 사임하면서 공동 창립자인 Jed McCaleb에게 전무 이사직을 넘기겠다고 밝혔습니다. [5]
2019년 3월, 전 Mozilla 임원인 Denelle Dixon이 Jed McCaleb이 최고 설계자 역할로 이동하면서 Stellar Development Foundation(SDF)의 CEO로 합류했습니다. [9]
논란
2015년, 스텔라는 리플, 비트스탬프와 함께 제드 맥칼렙과 디지털 통화 거래소 비트스탬프에 보관된 1,038,172달러를 두고 법적 다툼을 벌였습니다.
비트스탬프는 원래 소장에서 리플 랩스와 피고인 제이콥 스티븐슨(맥칼렙의 사촌) 중 누가 분쟁 자금의 정당한 소유자인지 판단할 수 없다고 주장했습니다. 스티븐슨은 리플 네트워크의 기본 통화인 XRP를 비트스탬프에서 리플에 판매했는데, 리플은 이 행위가 합의 계약을 위반하여 맥칼렙을 대신하여 이루어졌다고 주장했습니다. [6] 리플은 맥칼렙이 당시 90억 개의 토큰에 달하는 XRP 보유량 판매를 규율하는 계약을 위반했다고 주장했습니다. 리플은 또한 맥칼렙이 가족 구성원과 공모하여 계약상 통제를 넘어 XRP를 판매하기 위해 계약을 우회하려고 했다고 주장했습니다. [7]
또한 스텔라 개발 기금(SDF)은 소송에 개입 피고인으로 참여할 것을 요청했습니다. 변호인 측은 또한 비트스탬프의 원래 상호 제소 청구의 근거에 대해서도 의문을 제기했습니다. 스텔라는 5월 22일 개입 신청에서 리플이 애초에 해당 자금에 대한 권리가 없었다는 과거 변호인 측의 주장을 되풀이했으며, 이는 리플과 비트스탬프의 자체 서류에 의해 뒷받침된다고 밝혔습니다.
“비트스탬프는 리플의 자체 진술에서 명확히 알 수 있었듯이, 소장에 주장된 바와 같이 리플은 r3Q 및 rPQ 계정(총 1,038,172달러)에 포함된 특정 자금이 리플에 속한다고 주장하지 않았습니다. 오히려 비트스탬프는 리플이 맥칼렙이 리플과의 계약을 위반했으며 리플이 거래에서 리플이 지불한 금액에 해당하는 손해 배상을 받을 자격이 있을 수 있다고 주장하고 있다는 것을 알고 있었습니다.” [6]
합의
2016년, 리플은 맥칼렙과의 1백만 달러 소송을 합의하고 분쟁 XRP에 대한 모든 청구를 포기했습니다. 재판 기간 동안 캘리포니아 북부 지방 법원에 예치된 분쟁 자금은 스텔라에 반환되었습니다.
합의의 일환으로 맥칼렙은 리플의 지분을 매각하고 자신과 자녀가 소유한 53억 XRP에 대한 판매 통제에 동의했습니다. 추가로 20억 XRP가 비공개 자선 기금에 기부되었습니다. [7]
스텔라 루멘 (XLM)
루멘(XLM)은 스텔라 네트워크의 기본 디지털 통화입니다. XLM은 운영을 위한 중간 통화 역할을 하며 네트워크에서 거래 수수료를 지불하는 데에도 사용됩니다.
2014년 네트워크 출시 당시 1,000억 XLM이 발행되었으며 스텔라가 존재한 처음 5년 동안 루멘 공급량은 설계상 매년 1%씩 증가했습니다. 인플레이션 메커니즘은 2019년 10월 커뮤니티 투표에 의해 종료되어 2019년 11월 총 루멘 공급량이 감소했습니다. [10]
암호화폐 공급량의 절반 이상을 소각한 후 SDF는 다음과 같이 설명했습니다.
“SDF는 더 적은 루멘을 사용하여 더 효율적으로 운영하고 만들어진 목적을 달성할 수 있습니다… 555억 루멘은 스텔라 채택을 증가시키지 못할 것입니다.” [3][8]
스텔라는 XLM 채굴을 지원하지 않습니다. 스텔라 합의 프로토콜(SCP)이라는 합의 시스템을 채택하여 네트워크의 일부를 사용하여 트랜잭션을 승인합니다. 이는 지분 증명 모델을 기반으로 구축되었습니다. [4]
활성 스텔라 계정을 가지려면 최소 1 XLM이 필요합니다.
유틸리티
스팸 방지
루멘은 거래 수수료 비용을 충당하고 스텔라 네트워크에서 최소 계정 잔액을 유지하는 데 사용됩니다. 이는 네트워크에서 스팸 거래 수를 줄이기 위한 것입니다. 각 거래에는 0.00001 루멘의 수수료가 필요합니다.
다중 통화 거래
루멘은 충분히 큰 직접 시장이 없을 때 두 개의 분리된 통화 간의 거래를 용이하게 합니다.
탈중앙화
스텔라의 데이터베이스는 오픈 소스이며, 단일 기관이 루멘 이동을 통제하지 않습니다. 트랜잭션은 커뮤니티에 의해 승인되며, 데이터는 블록체인에 저장되어 모든 사람이 액세스할 수 있습니다.
전송 속도
스텔라 합의 메커니즘에 의해 촉진되는 거래 시간은 약 3~5초입니다. 스텔라 블록체인은 초당 수천 건의 거래를 지원하여 스마트 계약 및 다중 서명을 사용할 수 있습니다.
저렴한 번역 비용
스텔라 블록체인은 다른 방법에 비해 번역 비용이 저렴합니다. 연간 인플레이션율은 1%로 고정되어 있습니다. [3][1]
메리디안 컨퍼런스
제4회 연례 메리디안 컨퍼런스 2022는 10월 11일부터 13일까지 이탈리아 로마에서 대면 컨퍼런스로 개최되었습니다. 컨퍼런스의 주제는 다빈치의 행동 촉구에서 영감을 받은 '실행의 긴급성'이었습니다. 컨퍼런스에는 기조 연설, 패널 토론, Fireside Chat, 토론, 네트워킹 기회, 인터랙티브 세션 등을 포함한 40개 이상의 세션이 있었습니다. [21]
2023년 메리디안 컨퍼런스는 9월 26일부터 28일까지 스페인 마드리드에서 개최될 예정입니다. 배우이자 UN 친선대사인 이드리스 엘바가 행사의 개막을 맡을 예정입니다. [24]
Soroban
SDF는 2022년 3월 튜링 완전 스마트 컨트랙트를 스텔라에 도입할 계획을 발표했습니다. 제4회 연례 Meridian 컨퍼런스에서 스텔라는 스텔라 네트워크의 기본 스마트 컨트랙트 플랫폼인 Soroban이 현재 초기 개발자를 위한 인센티브 테스트 환경인 Futurenet에서 라이브로 제공된다고 발표했습니다. [17][16]
스텔라 개발 재단의 기술 전략 부사장이며 Soroban의 수석 개발자인 Tomer Weller는 다음과 같이 말했습니다.
"저희는 개발자로서 시장에서 함께 작업하고 싶은 스마트 컨트랙트 플랫폼을 보지 못했고 다른 네트워크에서 마찰을 확인했기 때문에 Soroban을 구축했습니다. 저희의 대응은 Soroban입니다. Soroban은 배터리가 포함된 개발자 경험, 확장성 및 스텔라 네트워크를 통한 안정적인 금융 레일에 대한 액세스를 위해 설계된 스마트 컨트랙트입니다.
Soroban이 Futurenet에서 라이브로 제공됨에 따라 개발자는 이제 테스트 환경에서 스마트 컨트랙트를 작성하고 배포하기 시작하여 그에 대한 보상을 받을 수 있습니다. [16]
SDF는 또한 Soroban에서 빌드하는 개발자를 지원하기 위해 1억 달러의 채택 기금을 조성했습니다. [16][17]
Stellar Enterprise Fund
Stellar Enterprise Fund는 2020년에 시작되었으며, 오픈 소스 Stellar 네트워크를 성장시키기 위한 벤처 스타일 펀드입니다. 그 목적은 전 세계 핀테크 또는 블록체인 기업에 대한 시리즈 E 단계까지의 직접 투자 또는 인수를 하는 것입니다. [18]
2022년에는 Enterprise Fund가 5개 회사에 투자했으며 총 2,352만 5천 달러를 투자했는데, 이 중 325만 달러는 아프리카 및 라틴 아메리카와 같은 주요 시장에서 스타트업 구축에 집중하는 액셀러레이터에 할당되었습니다. Enterprise Fund의 최신 투자 트랙인 Matching Fund는 Stellar 기반 구축에 관심 있는 초기 단계 회사(시리즈 B 이전)를 지원하며, 2022년에 Stax, Stablecorp 및 Afriex의 세 회사에 120만 달러를 할당했습니다. [19]
파트너십
MoneyGram Access
2022년 6월, 글로벌 결제 플랫폼인 MoneyGram은 SDF와의 파트너십을 발표하여 MoneyGram Access를 출시했습니다. 이는 현금과 암호화폐 간의 다리를 만들어 디지털 자산의 유용성을 높이기 위한 디지털 지갑용 글로벌 온-오프 램프 서비스입니다. [19]
Stellar Aid Assist
MoneyGram Access를 통해 Stellar Aid Assist가 구축되었습니다. 이는 구호 단체가 취약 계층에게 현금 지원을 제공할 수 있도록 하는 도구입니다. Stellar Aid Assist는 또한 구호 단체나 정부로부터 구호금을 받는 개인이 디지털 달러를 원격으로 수령하여 휴대폰의 디지털 지갑에 안전하게 보관할 수 있도록 합니다. [20]
2023년 상반기에 Stellar Aid Assist는 디지털 통화 컨퍼런스에서 '디지털 통화 부문 최고의 혁신상'을 수상했으며, CoinDesk에서 주목해야 할 프로젝트로 인정받았습니다. [22]
Stellar x Bitso
2023년 7월 19일, 라틴 아메리카의 암호화폐 거래소인 Bitso는 Stellar의 앵커 네트워크를 통합하여 라틴 아메리카와 세계 간의 결제 통로를 확장했습니다. Bitso는 성명에서 Stellar 개발 재단과의 협력을 통해 전 세계 기업이 USDC로 아르헨티나, 콜롬비아, 멕시코에서 거래할 수 있도록 솔루션을 개발했다고 밝혔습니다. Bitso는 이 지역의 은행 시스템과 직접 연결되어 있습니다. [23]
기타 파트너십
- Binance
- Bitfinex
- Coinbase
- Crypto.com
- Dinaro
- Flutterwave
- Interstellar.Exchange
- MoonPay
- Mobius
- Upbit
- Yellow Card
- Circle
- Coinme
