订阅 wiki
Share wiki
Bookmark
Unibase
0%
Unibase
Unibase 是一个去中心化人工智能 (AI) 基础设施项目,旨在为自主代理提供记忆、身份和互操作性层。它使 AI 系统能够持久地存储数据,在不同平台之间安全地通信,并在可验证的链上环境中运行。 [1]
概述
Unibase 是一个去中心化 AI 记忆层,旨在为 AI 代理 提供长期记忆以及跨多个平台运行的能力。该项目声明的目标是为“开放代理互联网”奠定基础,这是一个模块化、可组合的链上生态系统,代理可以在其中交互、共享知识并自主运行。
Unibase 旨在通过提供支持可验证和透明的链上代理操作的基础设施,解决 AI 开发中的关键挑战,包括缺乏持久记忆、系统之间互操作性有限以及与数据主权相关的问题。
该基础设施建立在三个核心组件之上:Membase,一个去中心化记忆和身份系统;代理互操作性协议 (AIP),一个代理通信框架;以及 Unibase DA,一个高性能数据可用性层。该项目已在 BNB Chain 测试网 上线,并为开发人员提供软件开发工具包 (SDK) 和文档。它还与 AI 框架建立了集成,例如多代理通信协议 (MCP)、ElizaOS、Virtuals 和 Swarms。 [2] [3]
架构
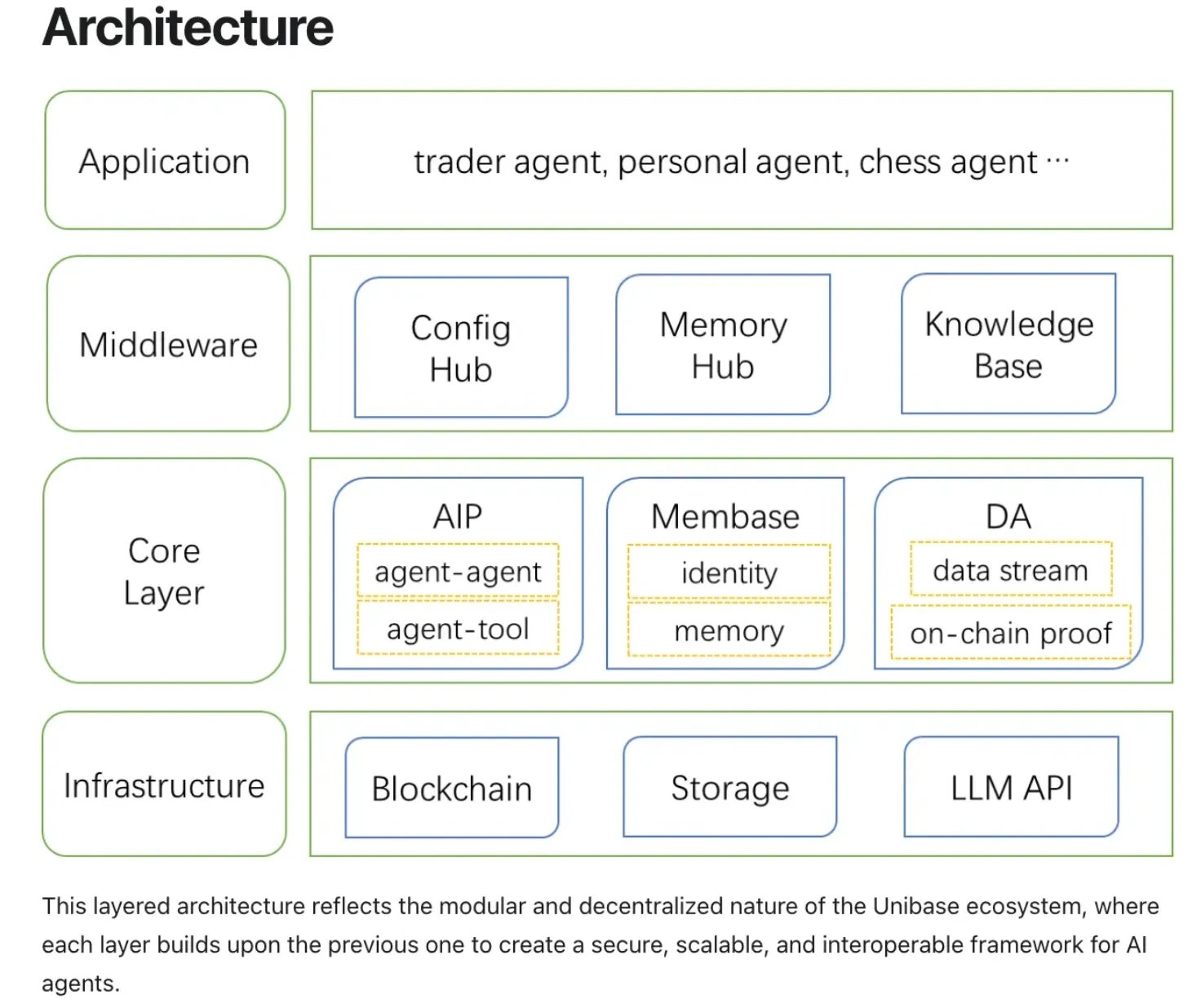
Unibase 的架构分为四个不同的层,以支持模块化、可扩展性和去中心化。每一层都执行特定的功能,从而为可互操作和持久的代理操作创建一个全面的框架。 [9]
- 应用层: 这是顶部的、面向用户的层,由各种 AI 代理 组成,这些代理专为特定任务而设计。示例包括交易代理、个人助理和直接与用户或其他应用程序交互的游戏代理。
- 中间件层: 这一层充当应用层和核心层之间的桥梁,管理代理配置、记忆和共享知识。它包含三个主要中心:配置中心,用于管理设置和权限;记忆中心,允许代理在交互过程中保留上下文和数据;以及知识库,一个共享存储库,代理可以在其中访问和贡献集体智能池。
- 核心层: 这一层包含管理代理通信、数据存储和身份的基本协议。其组件包括用于通信的代理互操作性协议 (AIP)、用于去中心化身份和记忆的 Membase 以及用于数据完整性和可用性的 Unibase DA。
- 基础设施层: 这一基础层提供支持整个网络的底层技术。它包括用于保护交易和验证代理身份的 区块链、用于可扩展数据检索的分布式存储系统以及用于集成高级 AI 功能的大型语言模型 (LLM) API。 [9]
核心组件
Unibase 的基础设施由三个主要技术支柱组成,它们协同工作以实现自主 AI 代理。 [1]
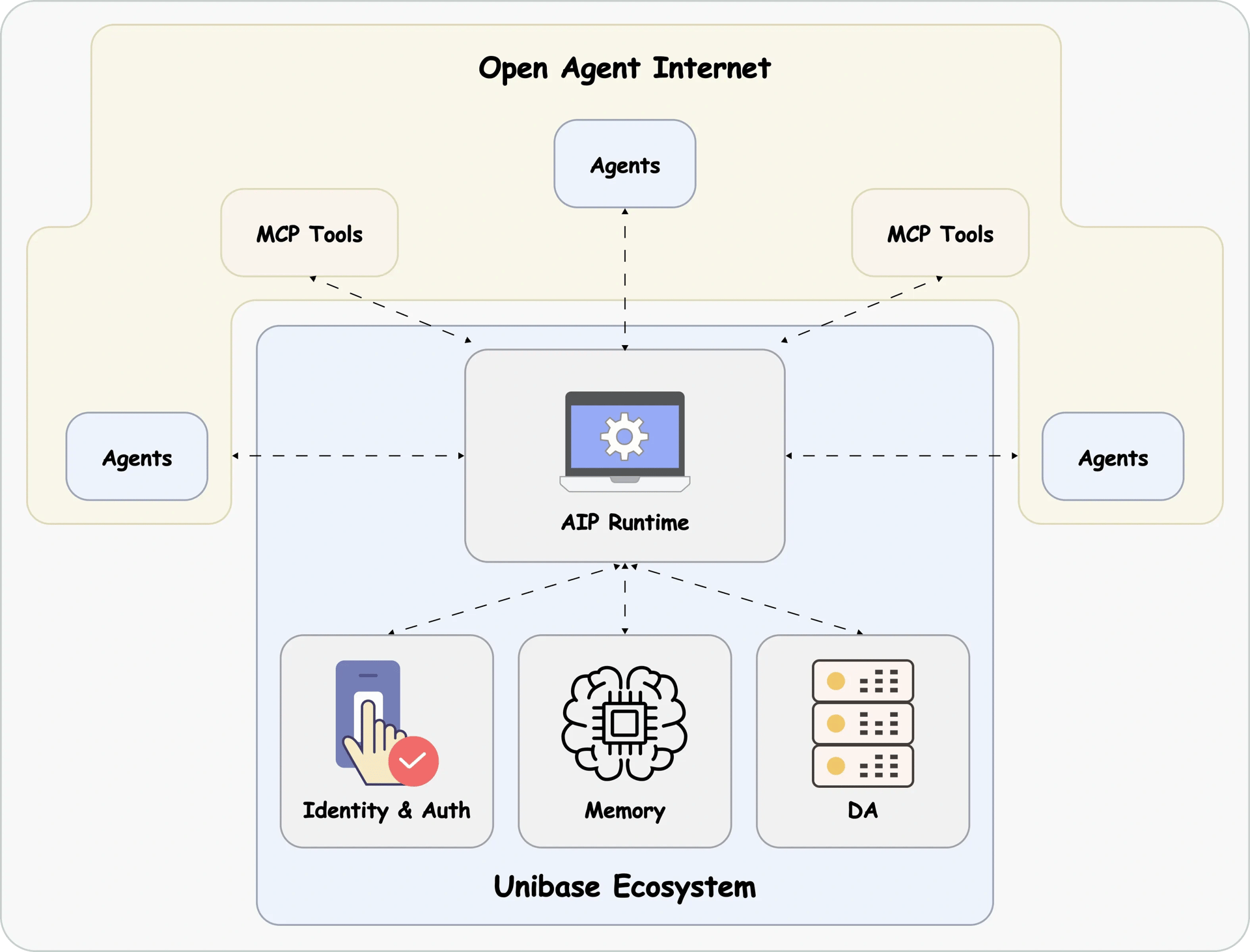
Membase
Membase 是 Unibase 生态系统的去中心化身份和记忆层。它负责管理代理注册、配置和持久记忆存储,通过将基于 区块链 的身份与去中心化数据可用性相结合,为安全和可验证的代理操作提供基础。
其核心是代理中心,它通过三个子模块协调 代理 的完整生命周期和交互:
- 链接中心: 促进远程交互服务,允许代理连接到外部服务或其他 代理。
- 配置中心: 管理代理配置,包括身份、权限和操作参数,同时支持代理发现。
- 记忆中心: 存储持久数据,例如对话历史记录和交互记录,以确保跨会话的数据连续性。
Membase 按照同步的六步工作流程运行:代理首先在 区块链 上注册其身份,然后由代理中心同步。代理通过链接中心连接以进行远程交互,通过配置中心管理其设置,并将生成的数据上传到记忆中心。最后,此数据同步到 Unibase DA 层以进行去中心化、持久存储。 [10]
代理互操作性协议 (AIP)
代理互操作性协议 (AIP) 是 Unibase 的去中心化通信框架,该项目将其描述为 Web3 原生的多代理通信标准。它定义了标准化的格式和工作流程,供 AI 代理 识别、交互和跨不同平台协作,而无需依赖中心化中介。
AIP 的主要功能包括链上身份验证,其中每个代理都拥有一个可验证的 区块链 身份,并具有可编程的权限以进行受控访问。它还结合了使用加密签名和多层信任机制(例如 零知识证明 (ZKP))的去中心化授权,以确保隐私和真实性。该协议旨在与 MCP 和 gRPC 等现有标准兼容。通过与 Membase 和 Unibase DA 集成,AIP 统一了通信、身份和存储,允许 代理 在跨生态系统自主运行的同时保持持久记忆。 [8] [11]
Unibase DA
Unibase DA 是去中心化数据可用性和存储层,是 Unibase 基础设施的基础,旨在为 AI 应用程序提供可验证、可扩展和低延迟的数据访问。它支持 代理 的持久存储,同时通过链上验证保持透明度和安全性。该系统使用纠删码将数据分布在多个节点上,从而确保持久性和抗审查性。
该层对所有数据交互使用基于 ZK 的链上验证,从而实现安全且可审计的操作。它通过内置的欺诈证明机制具有“诚实一人”安全模型,该机制不依赖于诚实多数假设。技术规范表明数据吞吐量高达 100 GB/s,访问延迟低于 100 毫秒。其模块化架构包括并行数据通道,以支持大规模 AI 工作负载和 Exabyte 级存储。该系统在 以太坊 上结算并支持数据可用性采样 (DAS)。该架构是该项目“DA++”概念的一部分,该概念旨在从技术和经济角度创建一个全面的链上 DA 解决方案。 [5] [12]
生态系统
BitAgent
BitAgent 是一个建立在 Unibase 基础设施之上的去中心化多代理协作平台。它允许用户和组织部署具有持久记忆、可验证的链上身份和跨平台交互能力的自主 AI 代理。BitAgent 平台上的代理使用 Unibase 的 Membase 进行长期记忆,并使用 AIP 协议进行通信和协作,跨各种平台,包括社交媒体、交易所和 去中心化自治组织 (DAO)。该平台还集成了基于代币的激励和治理机制,以鼓励生态系统参与。 [13]
UB
UB 代币充当 Unibase 生态系统中的 实用 和 治理 资产,支持其去中心化 AI 基础设施。它促进协议级操作、网络参与以及用户和开发人员的激励机制。 UB 用于支付记忆存储、代理部署和互操作性服务的费用。持有者还可以质押代币以激活或推广代理,通过 veUB 投票参与治理,并因向系统贡献有用的提示、数据或可重用知识而获得奖励。 [3]
代币经济学
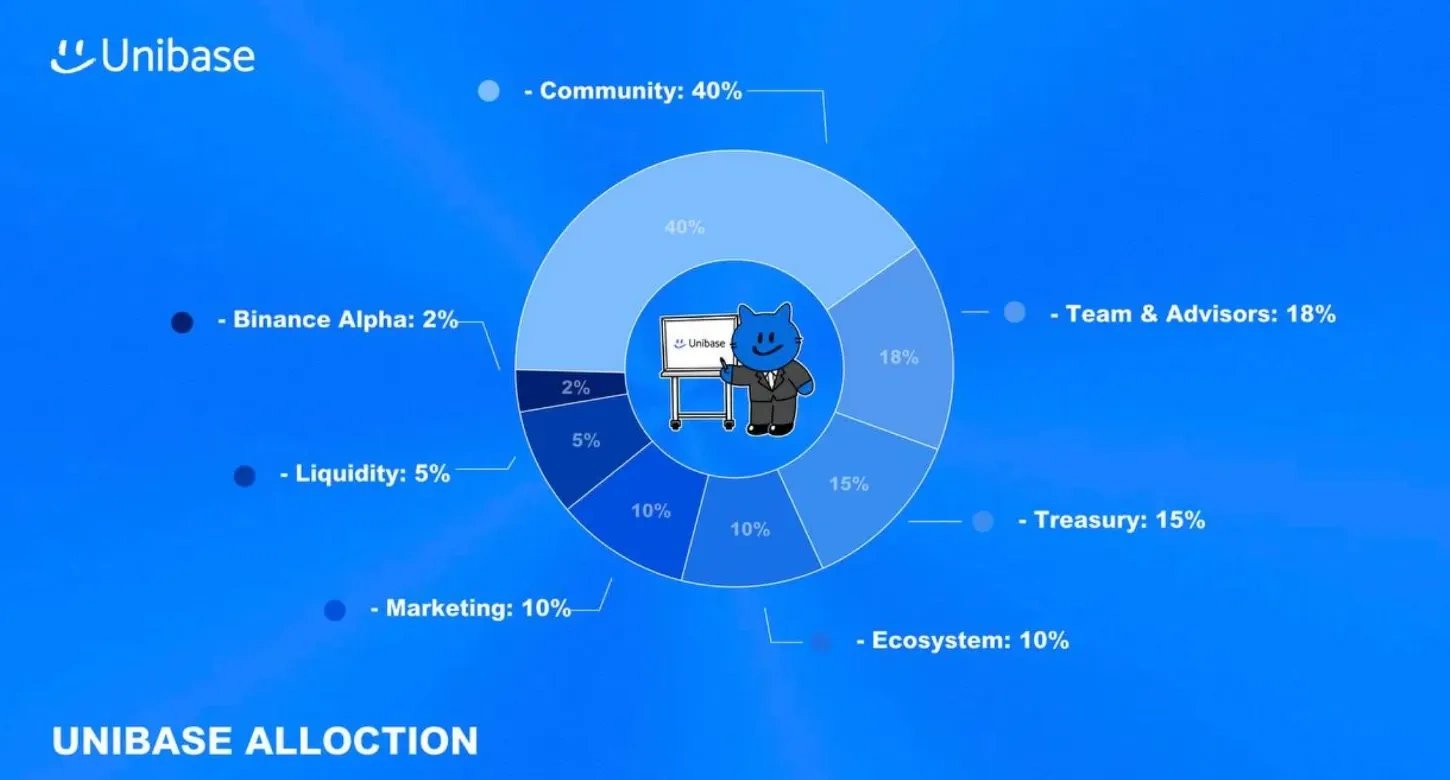
UB 的总供应量为 10,000,000,000 个代币,根据以下分配模型进行分配: [3]
- 社区: 40%
- 团队和顾问: 18%
- 国库: 15%
- 生态系统: 10%
- 营销: 10%
- 流动性: 5%
- 币安 Alpha: 2%
合作伙伴
发现错误了吗?
