위키 구독하기
Share wiki
Bookmark
Shardeum
0%
Shardeum
샤르디움은 레이어 1(L1) 블록체인으로, 이더리움 가상 머신(EVM)을 기반으로 구축되었으며, 블록체인 공간에 동적 상태 샤딩을 도입했습니다. 동적 상태 샤딩을 통해 샤르디움은 선형 확장성을 달성하고 샤드 네트워크 전반에서 원자적 구성 가능성을 유지하는 것을 목표로 합니다. 이 접근 방식은 지속적으로 낮은 수수료를 보장하면서 추가 검증자를 수용하여 트랜잭션 처리 용량을 지속적으로 향상시키기 위해 구현되었습니다. [1]
개요
Shardeum은 2022년 2월에 설립되었으며 2024년 1분기에 공식 출시를 목표로 합니다. 목표 중 하나는 확장성, 탈중앙화 및 보안을 동시에 달성하여 블록체인 트릴레마를 해결하는 것입니다. 동적 상태 샤딩 기능을 통해 Shardeum은 새로운 검증인마다 확장할 수 있으며, 개발자는 복잡한 샤딩 고려 사항 없이 Solidity 또는 Vyper로 작성된 스마트 계약을 배포하고 상호 작용할 수 있습니다. 계약은 상호 운용성을 유지하면서 고유한 샤드에 자동으로 배포됩니다. 또 다른 주요 기능은 자동 스케일링 메커니즘으로, 네트워크가 변화하는 작업 부하에 대응하여 샤드 수와 크기를 조정하여 성능을 최적화하고 생태계가 성장함에 따라 지속적인 확장성을 보장합니다. 개방적이고 협력적이며 커뮤니티 중심적인 프로젝트라는 핵심 원칙을 바탕으로 샤딩을 통해 확장성과 구성 가능성에 중점을 둡니다. [2][13][14]
2024년 1월, Shardeum은 Spheron과 파트너십을 맺었습니다. Spheron은 분산형 애플리케이션(Dapp)의 인프라에 혁명을 일으키는 포괄적인 솔루션입니다. Spheron은 Shardeum 검증인 노드에 대한 지원을 추가했으며 사용자는 Spheron UI에서 검증인 노드를 설정할 수 있습니다. [15]
주요 기능
동적 상태 샤딩
동적 상태 샤딩은 Shardeum 아키텍처의 핵심 기능입니다. 샤드 주소 공간을 미리 정의하는 정적 상태 샤딩과 달리 동적 상태 샤딩은 유연성과 적응성을 제공합니다. Shardeum과 같은 동적 시스템의 샤드는 네트워크 조건 변화에 따라 필요에 따라 생성하거나 제거할 수 있습니다. 샤드 분할 또는 병합, 노드 재할당 및 중복 관리와 같은 이러한 적응은 실시간 알고리즘에 의해 조정됩니다. 이러한 동적 접근 방식은 Shardeum이 시스템 부하와 가용 자원 간의 최적 균형을 유지하여 효율적이고 안전한 네트워크 운영을 보장하는 데 도움이 됩니다. Shardeum의 각 검증자는 고유한 주소 범위를 담당하며 할당된 트랜잭션을 실행하고 해당 상태 변경을 저장합니다. 검증자의 중복 커버리지는 각 주소에 최소 128명의 검증자가 중복되도록 보장합니다. 이를 통해 한 검증자에 문제가 발생하더라도 최소 127명의 다른 검증자가 이를 대체할 수 있습니다. [3][4]
트랜잭션 합의
Shardeum은 트랜잭션 유효성 검사를 위해 지분 증명(PoS)과 쿼럼 증명(PoQ)으로 구성된 하이브리드 합의 메커니즘을 사용합니다. PoS 구성 요소에서 모든 검증자 노드는 네트워크에 참여하기 위해 최소 SHM(Shardeum의 기본 토큰)을 스테이킹해야 합니다. 검증자 노드는 SHM 보상으로 트랜잭션을 정직하게 검증하도록 장려되며, 악의적인 행동은 스테이킹된 SHM의 삭감으로 이어져 네트워크 보안을 강화합니다. [7]
PoQ 측면은 다른 네트워크에서 흔히 볼 수 있는 블록 수준 합의에서 벗어나 트랜잭션 수준 합의를 도입합니다. 트랜잭션 수준 합의는 즉각적인 완결성과 낮은 대기 시간을 보장하여 네트워크 혼잡을 최소화합니다. 트랜잭션은 수신 즉시 개별적으로 검증되고 이중 지출을 방지하기 위해 타임스탬프가 찍힙니다. 트랜잭션 정보는 가십을 통해 샤드 내의 노드 간에 공유되어 영수증 형태로 신뢰할 수 없고 리더가 없는 전자 투표 또는 쿼럼을 설정합니다. 트랜잭션은 전자 투표를 통해 디지털 서명되며 쿼럼(영수증의 50% 이상)에 도달하면 네트워크에 커밋됩니다. 합의 알고리즘은 검증자 노드의 자동 회전을 통합하여 악의적인 행위자에 대한 네트워크 보안을 더욱 강화합니다. [7]
EVM 호환성
Shardeum은 이더리움 가상 머신(EVM) 호환성을 제공합니다. 이더리움 및 이더리움 기반 개발자에게 이는 애플리케이션 코드를 변경하지 않고도 Shardeum으로 간단하게 전환할 수 있음을 의미합니다. EVM용으로 Solidity 또는 Vyper로 작성된 스마트 계약은 Shardeum으로 쉽게 포팅할 수 있어 가스 요금 상승에 대한 우려를 해소합니다. [8]
Shardeum Opcode
Shardeum은 블록 단위가 아닌 개별적으로 트랜잭션을 처리하지만, JSON RPC 사양과 호환되는 기존 스마트 계약을 지원하기 위해 주기적으로 블록을 생성합니다. 블록은 주기적으로 예약되며, 각 주기는 일반적으로 60초 동안 지속되고 10개의 블록을 생성합니다. 트랜잭션의 타임스탬프는 타임스탬프를 블록 번호에 매핑하여 적절한 블록을 선택합니다. 트랜잭션에 타임스탬프가 없는 경우 네트워크는 타임스탬프를 할당하고 해당 블록을 선택합니다. Shardeum은 블록 관련 공개 API 엔드포인트를 노출하여 JSON RPC 서버가 네트워크에서 사용하는 것과 동일한 블록 정보에 액세스하여 호환성 및 상호 운용성을 향상시킬 수 있도록 합니다. [9]
SHM 토큰
SHM은 Shardeum 생태계 내에서 네이티브, 유틸리티 및 거버넌스 토큰 역할을 합니다. 네트워크의 필수 요소이며 다양한 기능을 제공하고 네트워크 운영에서 중요한 역할을 합니다. [10]
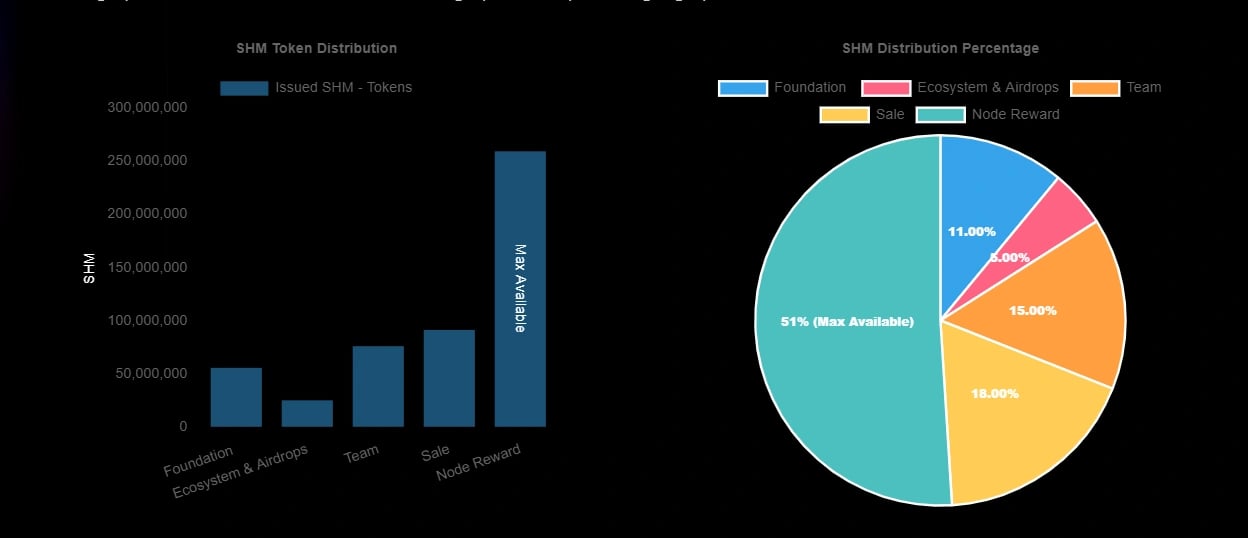
공급 및 분배
최대 공급량: 5억 8백만 SHM 분배:
- 커뮤니티 (51%): 검증자, 아카이브 노드 및 대기 서버를 포함한 노드에 대한 지불.
- 판매 (18%): 3개월의 대기 기간 후 2년에 걸쳐 선형 베스팅 일정.
- 팀 (15%): 3개월의 초기 대기 기간 후 2년에 걸쳐 2년에 걸친 선형 베스팅 기간.
- 재단 (11%): 토큰 생성 이벤트 (TGE)에서 잠금 해제됨
- 생태계 및 에어드랍 (5%): TGE에서 잠금 해제됨
유틸리티
채굴 및 보상
SHM 토큰은 Shardeum 네트워크에 대한 기여에 대한 보상으로 검증인과 아카이브 노드에 의해 채굴됩니다. 이러한 기여에는 네트워크 리소스 제공 및 네트워크의 효율적인 운영 보장이 포함됩니다. 이 메커니즘은 생태계 내에서 참여와 리소스 제공을 장려합니다. [10]
가스 수수료 및 스마트 컨트랙트
SHM 토큰은 Shardeum 네트워크에서 전송 트랜잭션을 실행하고 스마트 컨트랙트와 상호 작용하는 데 관련된 가스 수수료를 지불하는 데 사용됩니다. 이러한 가스 수수료는 네트워크 운영의 필수적인 부분이며 트랜잭션 실행 및 스마트 컨트랙트 배포를 용이하게 합니다. [10]
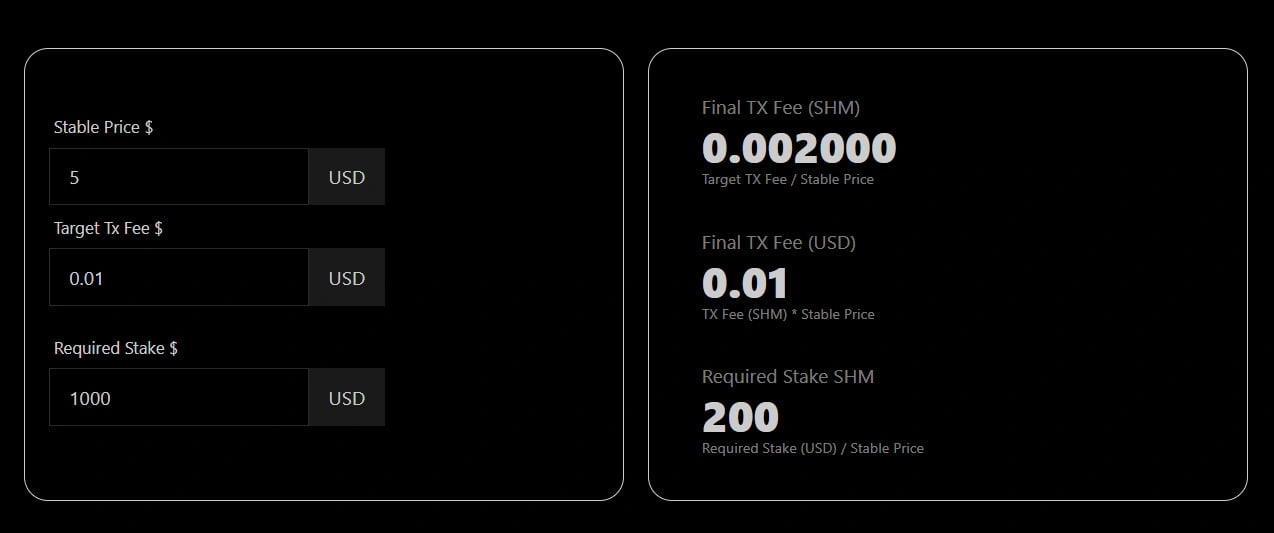
안정적인 가격 및 거래 수수료
Shardeum은 최근 SHM 가격의 평균으로 계산되는 안정적인 가격을 유지하며, 이는 매일 업데이트됩니다. 이 안정적인 가격은 거래 수수료, 검증인 스테이킹 금액 및 기타 네트워크 관련 값을 결정하는 기준으로 사용됩니다. 이는 SHM 가격 변동성과 관계없이 거래 수수료와 보상이 USD 기준으로 안정적으로 유지되도록 보장합니다. [10]
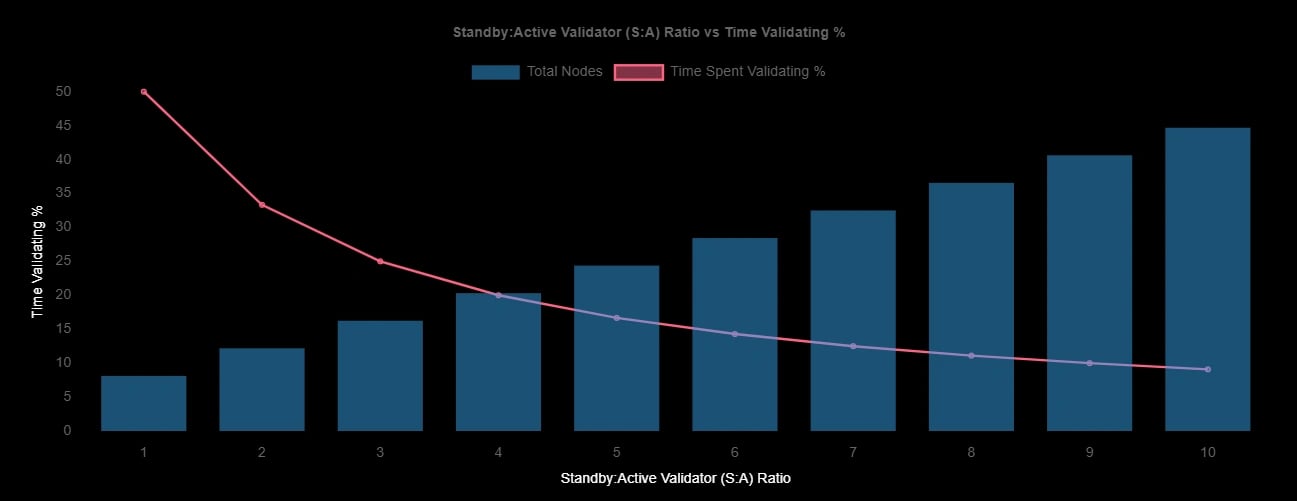
S:A 비율
S:A 비율은 네트워크에서 활성 노드에 대한 대기 노드의 비율을 의미합니다. 대기 노드는 무작위로 선택되어 네트워크에 참여하며, 장기간 활성 상태였던 노드는 주기적으로 교체됩니다. 이 로테이션은 트래픽이 많은 기간 동안 확장성을 향상시키고, 네트워크 분산화를 촉진하며, 과반수 점유 또는 시빌 공격에 대한 복원력을 강화하는 것을 목표로 합니다. [10]
재단에서 DAO로
Shardeum은 탈중앙화 경로를 따라 재단 주도의 네트워크에서 탈중앙화 자율 조직(DAO)으로 전환합니다. 초기에는 제안 또는 투표에 필요한 임계값보다 더 많은 SHM을 보유한 재단에 통제권이 있습니다. 그러나 시간이 지남에 따라 이 임계값은 커뮤니티 주도의 투표를 통해 감소하여 더 많은 커뮤니티 구성원이 거버넌스에 참여할 수 있습니다. 중앙 집중식 통제에서 완전한 기능을 갖춘 DAO로의 이러한 점진적인 전환은 네트워크 거버넌스가 탈중앙화를 향해 점진적으로 전환되도록 보장합니다.
스핑크스 베타넷
샤르디움의 스핑크스 베타넷은 샤르디움 리버티로 알려진 알파넷에 대한 광범위한 테스트를 거쳐 2023년 2월 2일에 출시되었습니다. 이 테스트에는 이더리움 가상 머신(EVM) 호환성 및 샤딩 기능과 같은 기능 평가가 포함됩니다. 스핑크스 베타넷은 샤르디움의 공식 메인넷 출시 전 최종 테스트 단계 역할을 합니다. [5][6]
주요 내용
- 노드 운영자를 위한 사용자 친화적인 GUI/대시보드 생성
- 투명성 증진을 위해 Shardeum 검증기 및 검증기 대시보드 코드 오픈 소싱
- 블록체인에서 상태 샤딩 데모를 통해 크로스 샤드 원자성 구성 가능성 잠재력 입증
- 개발자 친화적인 경험을 위한 EIP-2930 액세스 목록 자동화
- 베타넷에서 35,000명 이상의 검증자를 확보하여 가장 큰 분산형 테스트넷 중 하나가 됨
- 초당 평균 180건의 트랜잭션 네트워크 용량 유지[6]
커뮤니티 증명
커뮤니티 증명(PoC) 이니셔티브는 Web3 기술과 관련된 인식을 높이고 교육 기회를 제공하기 위해 설계된 일련의 커뮤니티 이벤트를 포함합니다. [15]
이벤트 종류
밋업
이러한 모임은 네트워킹, 학습 및 새로운 산업 트렌드 탐색을 위한 플랫폼을 제공합니다. 전문가들은 지식과 통찰력을 공유하며, 잠재적 협력자, 자문위원 및 Web3 애호가에게 제품 프레젠테이션 기회를 제공하기도 합니다. [15]
워크숍
워크숍은 참가자들이 기술적 배경에 관계없이 ERC-20 토큰을 생성하거나 NFT 프로젝트를 개발하는 방법을 배울 수 있는 실용적인 핸즈온 세션입니다. 업계 전문가가 지침을 제공하여 참석자들이 귀중한 기술을 습득할 수 있도록 합니다. [15]
캠퍼스
캠퍼스 행사는 학습 자료, 바운티, 멘토링 기회를 제공하여 학생들의 역량 강화에 중점을 둡니다. 업계 전문가들이 캠퍼스를 방문하여 학생들이 Shardeum 리소스를 사용하여 스마트 계약을 배포하고 애플리케이션을 구축하도록 안내합니다. 또한 학생들은 바운티 프로그램, 멘토링, 홍보대사 이니셔티브에 참여하여 Web3 지식과 기술을 향상시킬 수 있습니다. [15]
자금 조달
시드 펀딩 라운드
2022년 10월 18일, Shardeum은 전 세계 50명 이상의 ECA(Early Community and Angel) 참가자들의 참여로 1,820만 달러의 시드 펀딩을 확보했습니다. 주목할 만한 기여자로는 Jane Street, Big Brain Holdings, Struck Crypto, The Spartan Group, Ghaf Capital, DFG, CoinGecko Ventures, Foresight Ventures, Jsquare, Cogitent Ventures, WeMade, Veris Ventures, ZebPay, Tupix Capital 및 MapleBlock Capital과 같은 다양한 벤처 캐피털 회사가 있습니다. 이 자금은 Shardeum의 기술, 생태계 개발 및 연구 확장을 강화하기 위해 마케팅 및 개발 팀을 성장시키는 데 사용될 예정입니다. [16]
엔젤 투자자 또한 Balaji Srinivasan, Mayur Gupta(Kraken의 CMO) 등과 같은 개인들과 함께 이 펀딩 라운드에서 중요한 역할을 했습니다. 이 라운드는 많은 수의 ECA 참가자를 참여시키는 데 중점을 두었으며, 그 중 40% 이상이 엔젤 투자자였습니다. 목표는 SHM 토큰의 광범위한 분배를 보장하여 소수의 주체에 과도하게 집중되는 것을 방지하는 것이었습니다. [16]
전략적 모금 라운드
2023년 7월 8일, 샤르디움은 Amber Group, Galxe, J17 Capital, TRGC, Jsquare 등을 포함한 다양한 투자자들의 기여로 540만 달러의 전략적 모금 라운드를 완료했다고 발표했습니다. 추가 자본은 메인넷 출시를 앞두고 생태계 성장을 더욱 지원하는 데 사용될 것입니다. 샤르디움의 최고 성장 책임자인 Kelsey McGuire는 글로벌하고 다양한 커뮤니티를 육성하려는 그들의 사명을 발전시키는 데 있어 이번 전략적 모금의 중요성을 강조했습니다. 이 자금 지원을 통해 그들은 분산화를 계속 우선시하고 교육 이니셔티브를 통해 전 세계 참가자 커뮤니티를 확장할 수 있습니다. [17]
"주요 참가자들의 이번 전략적 모금 완료로 샤르디움은 글로벌하고 다양한 커뮤니티를 육성하려는 우리의 사명을 확장할 수 있는 위치에 놓였습니다. 샤르디움의 합의 설계와 동적 상태 샤딩 사용을 고려할 때, 검증인 참여는 사용자 컴퓨팅 리소스 접근성과 관계없이 매우 접근성이 높습니다. 이번 모금을 통해 우리는 교육 및 기타 주요 이니셔티브를 통해 전 세계 참가자 커뮤니티를 성장시켜 분산화를 계속 우선시할 수 있습니다." - Kelsey McGuire, 최고 성장 책임자
Shardeum Atomium
Shardeum 커뮤니티는 Shardeum의 인센티브 테스트넷 이름을 Atomium으로 결정했습니다. [18]
104,000명이 넘는 커뮤니티 구성원의 적극적인 참여로 이 투표 과정은 가장 큰 참여를 기록했습니다. 진위성을 보장하기 위해 유권자는 지갑을 연결해야 했고 봇을 방지하기 위해 캡차가 구현되었습니다. 이 응답은 ~7,000표를 받은 이전 Betanet 명명 투표를 능가합니다. [18]
잘못된 내용이 있나요?
