Subscribe to wiki
Share wiki
Bookmark
Lightning Network
The Agent Tokenization Platform (ATP):Build autonomous agents with the Agent Development Kit (ADK)
0%
Lightning Network
The Lightning Network is a Layer 2 solution designed to enable faster and cheaper transactions on the Bitcoin blockchain by allowing off-chain payment channels. This decentralized network facilitates instant micropayments and enhances the scalability of Bitcoin, making it more suitable for everyday use. [1][2]
Overview
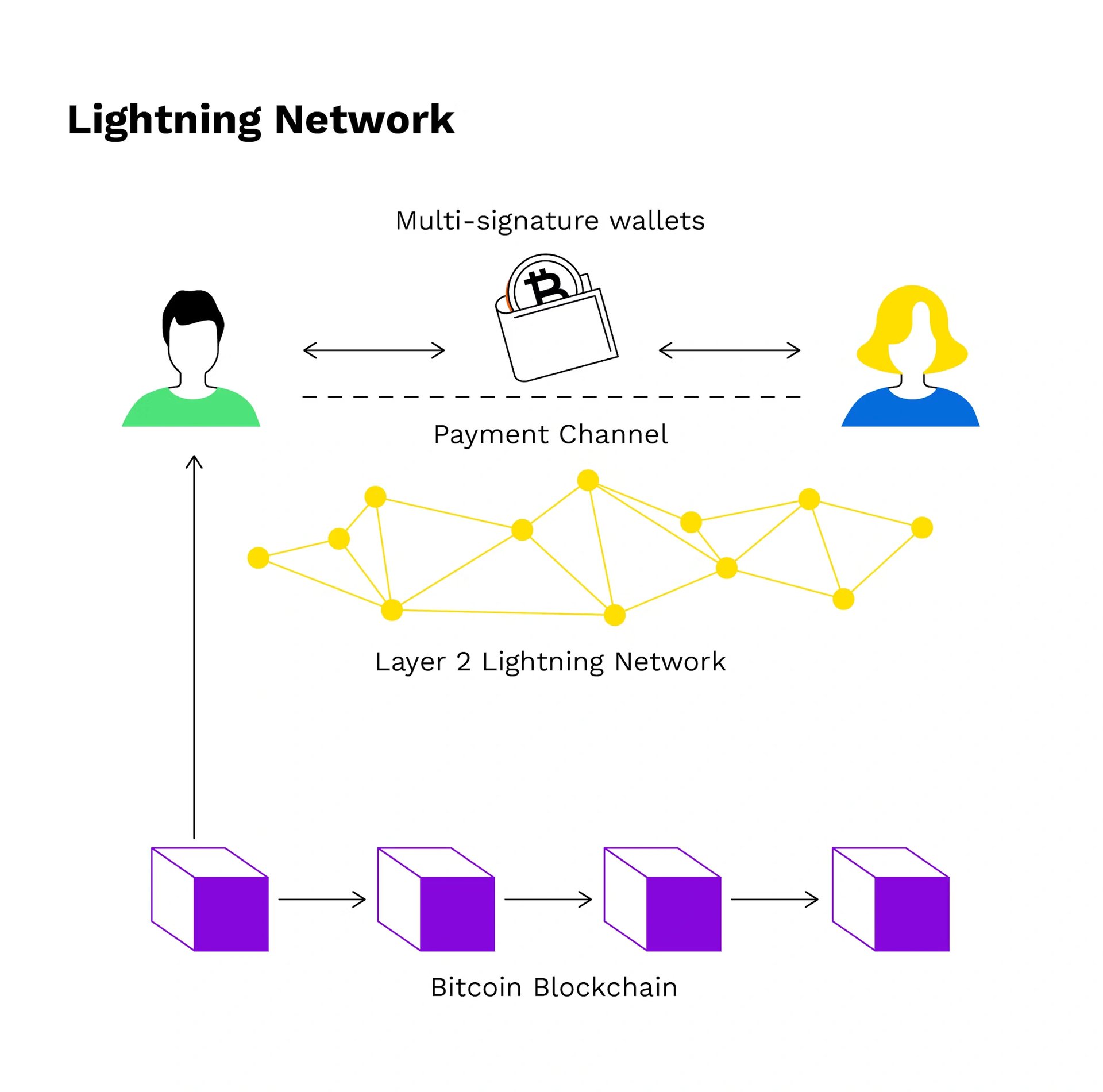
The Lightning Network is a peer-to-peer payment system enabling fast, low-cost Bitcoin transactions by linking payment channels on the blockchain. These channels are connected, allowing payments across the network without needing trust between participants. Transactions require a route from the sender's node to the recipient, which may involve multiple attempts due to limited visibility into liquidity availability at each node. Payments are atomic, using Hash Timelock Contracts (HTLC) to ensure completion or failure, even if nodes become unresponsive. Routing nodes earn fees by strategically managing liquidity to support reliable transactions. [2][3]
Lightning Labs

Founded by Elizabeth Stark and Olaoluwa Osuntokun, Lightning Labs develops software to power the Lightning Network, facilitating fast, low-cost, and globally accessible layer-two Bitcoin transactions. Their open-source, secure, and scalable Lightning systems streamline sending and receiving money. Additionally, Lightning Labs offers verifiable, non-custodial financial services on the Lightning Network, bridging open-source technology with the next generation of Bitcoin-based financial software. [1]
Features
Lightning Loop
Lightning Loop enables users to manage Lightning channel liquidity by facilitating transactions to and from on-chain Bitcoin addresses. Loop Out allows sending a Lightning transaction to an on-chain address, creating inbound capacity, while Loop In sends on-chain Bitcoin into a Lightning channel, adding outbound liquidity. Using trustless submarine swaps, Loop operates non-custodial, allowing secure, independent transactions. Loop Out transactions are batched to minimize fees. Authentication for Loop services uses L402, combining Macaroons with Lightning payment verification to secure access. [4]
Lightning Pool
Lightning Pool is a non-custodial auction platform for leasing Lightning Channel Liquidity (LCL). Participants can buy or sell liquidity as time-bound assets with a maturity date secured through Bitcoin contracts. These leases enable participants to gain inbound or outbound liquidity and earn interest. They are enforced with Bitcoin contracts, ensuring makers’ funds are locked until maturity. [3]
Cleared orders are processed in a batched, on-chain transaction, creating a stable income source for participants beyond routing fees. The open auction format lets the market signal where liquidity is most needed, reducing dormant channels and optimizing liquidity distribution. Pool supports newcomers by letting them acquire inbound funds at a percentage needed, with market-driven pricing based on liquidity demand. [3]
Payment Channels
The Lightning Network comprises payment channels, each representing a 2-of-2 multi-signature contract between two peers, where they can make repeated Bitcoin transactions. A commitment transaction records each transaction update in the channel, and either party can use the latest transaction to close the channel unilaterally, reclaiming funds on-chain without the other’s consent—a process known as a force close. The protocol uses a penalty system to prevent breaches (publishing outdated commitment transactions to gain a higher balance), where the breaching party’s funds are penalized if they act maliciously. [5][6]
Watchtowers, separate network nodes, help monitor breaches by watching for specific transaction IDs on the Bitcoin blockchain. Although they monitor for breaches, watchtowers cannot view commitment details, maintaining user privacy. Upon detecting a breach, the watchtower can decrypt and publish a revocation transaction to enforce penalties, preventing the attacker from accessing funds and forfeiting their channel balance as punishment. [5][6]
The Gossip Network
The Lightning Network uses a gossip network for nodes to share information about themselves, including public channels, routing fees, and network access details. Each node assembles a network graph based on this shared data to determine transaction routes, though some routing nodes may bypass this requirement. The gossip network, often busy with frequent fee updates from nodes, lacks a strict consensus on the network graph, as nodes may remove inactive peers or miss certain updates. Through the graph data, nodes can analyze network metrics, including total nodes, channels, and each node's centrality—a measure of how often routes pass. However, centrality doesn’t necessarily indicate optimal routing fees. To prevent spam, nodes only relay gossip messages from those with at least one public channel, ensuring participation with a Bitcoin stake and transaction fees. [7]
Pathfinding
In the Lightning Network, the payer selects the route for their payment, aiming for a direct and low-cost path but often needing to try multiple routes with different fees. Nodes may use various strategies to optimize pathfinding; some may outsource this process. Each route is onion-encrypted, so only the sender knows the full path, intermediate nodes see only the previous and next channels, and the recipient knows only the final hop without witnessing the origin of the payment. [8]
Lightning Protocol (L402)
L402, previously LSAT, is a protocol that combines Lightning payments with Macaroon-based authentication to enable secure and efficient paid API access in decentralized networks. Aperture, which implements this protocol, operates as a reverse HTTP proxy for gRPC and REST, enabling paid APIs to separate payment, permission, and request handling. Lightning Loop and Pool, services for non-custodial swaps and channel liquidity, currently use Aperture to handle these processes. L402, a Lightning API key, combines Macaroons with a payment hash to facilitate authentication and verification in distributed systems without central user databases. For an L402 to be valid, a Macaroon containing the payment hash and the preimage obtained by paying a Lightning invoice is required. This allows for metered, machine-to-machine API access without the need for traditional login methods, enabling verification of payment and authority for API requests. [9][10]
Macaroons
Macaroons are bearer tokens designed for secure authentication in distributed systems. They include permissions and can be verified using only a root key, eliminating the need for a central database lookup and enhancing system resilience and efficiency. Unlike cookies, Macaroons can be restricted and safely delegated, allowing users to control permissions. However, they are challenging to revoke, requiring the deletion of the root key, which invalidates all related tokens. [11]
Taproot Assets
Taproot Assets, a protocol leveraging Bitcoin’s Taproot upgrade, enables issuing assets on the Bitcoin blockchain, which can be transferred over the Lightning Network for fast, high-volume, and low-cost transactions. By utilizing Taproot's advanced tree structure and Schnorr signatures, Taproot Assets enhance privacy and scalability, supporting multi-hop transactions and integration with the broader Lightning Network. Verification costs are decentralized as participants store asset data off-chain in local " Universes " repositories and validate assets by tracing transaction history from their genesis, verified via a dedicated gossip layer. [12][13]
Edge Nodes
Edge Nodes are specialized Taproot Assets-aware Lightning nodes facilitating transactions between Taproot Assets and Bitcoin channels. Operating as service providers, they maintain private Taproot Assets channels with clients while staying connected to the public Lightning Network. Edge nodes enable Taproot Assets wallets to interact seamlessly with standard Lightning services by supporting asset-to-Bitcoin swaps, allowing payments to any Lightning invoice. Clients can also receive real-time quotes for Taproot-to-Bitcoin conversions, while the Edge node earns fees through atomic routing of payments. Edge nodes may hedge positions to mitigate exchange rate volatility, providing stable swaps across asset types. [14]
Lightning Terminal
Lightning Terminal is a web-based dashboard for managing Lightning Labs products, providing a remote interface for node observation, channel management, and liquidity solutions. Secured with Lightning Node Connect (LNC), it ensures end-to-end encrypted connections where all node data remains private from Lightning Labs. Users can view node rankings, centrality, and performance stats and leverage Lightning Loop to manage channel liquidity, allowing funds to be moved on-chain or into Lightning channels. With Lightning Pool, users can buy and sell channel liquidity, track orders, and monitor channels. The terminal also supports Taproot Assets integration, enabling asset transfers over the Lightning Network. The terminal is accessible via a browser, while self-hosted setups (litd) lack web-based recommendations, payment features, and transaction tracking. [15]
Lightning Node Connect
Lightning Node Connect (LNC) enables a secure, end-to-end encrypted connection to a Lightning node, even if it’s behind Tor or NAT, simplifying remote node management. Lightning Terminal uses this open-source tool to connect applications to nodes through a browser or app. LNC relies on LND’s gRPC interface, with the node making an outbound connection to a web proxy for user access. A password-authenticated key exchange (PAKE) ensures the encrypted session between the user and the node. [16]
The LNC system includes three main components: [16]
- Lightning Node Connect, running on the Lightning Terminal Daemon (litd), facilitates requests, data transfer, and macaroons for authentication.
- Proxy (TURN), which supports network traversal for nodes behind NAT or firewalls, creating synchronous communication channels.
- Application, such as Lightning Terminal, accessed through a web server, with potential for standalone use on various devices.
LNC supports browser extensions, mobile wallets, and network explorers to connect and manage nodes, send payments, and more. [16]
Partnerships
- Binance
- Coinbase
- SimpleSwap
- Kraken
- Bitfinex
- Bithumb
- Bitstamp
- Kucoin
- OKEx
- OKCoin
- NiceHash
- CoinCorner
- BitMex
- Buda
- Strike
- Mt Pelerin
- Paxful
- BullBitcoin
- Bitaroo
- River Financial
- VBTC Vietnam
- FixedFloat
- LOFT
- PrimeBit
- SimpleFX
- BitcoinVN
- Bipa
- Boltz
- Kollider
- LN Markets
- Tauros
- Coinfinity
- Ripio
- StealthEX
- SecureShift
- Rhino Bitcoin
See something wrong?
The Agent Tokenization Platform (ATP):Build autonomous agents with the Agent Development Kit (ADK)
