订阅 wiki
Share wiki
Bookmark
Frax Bonds (FXB)
0%
Frax Bonds (FXB)
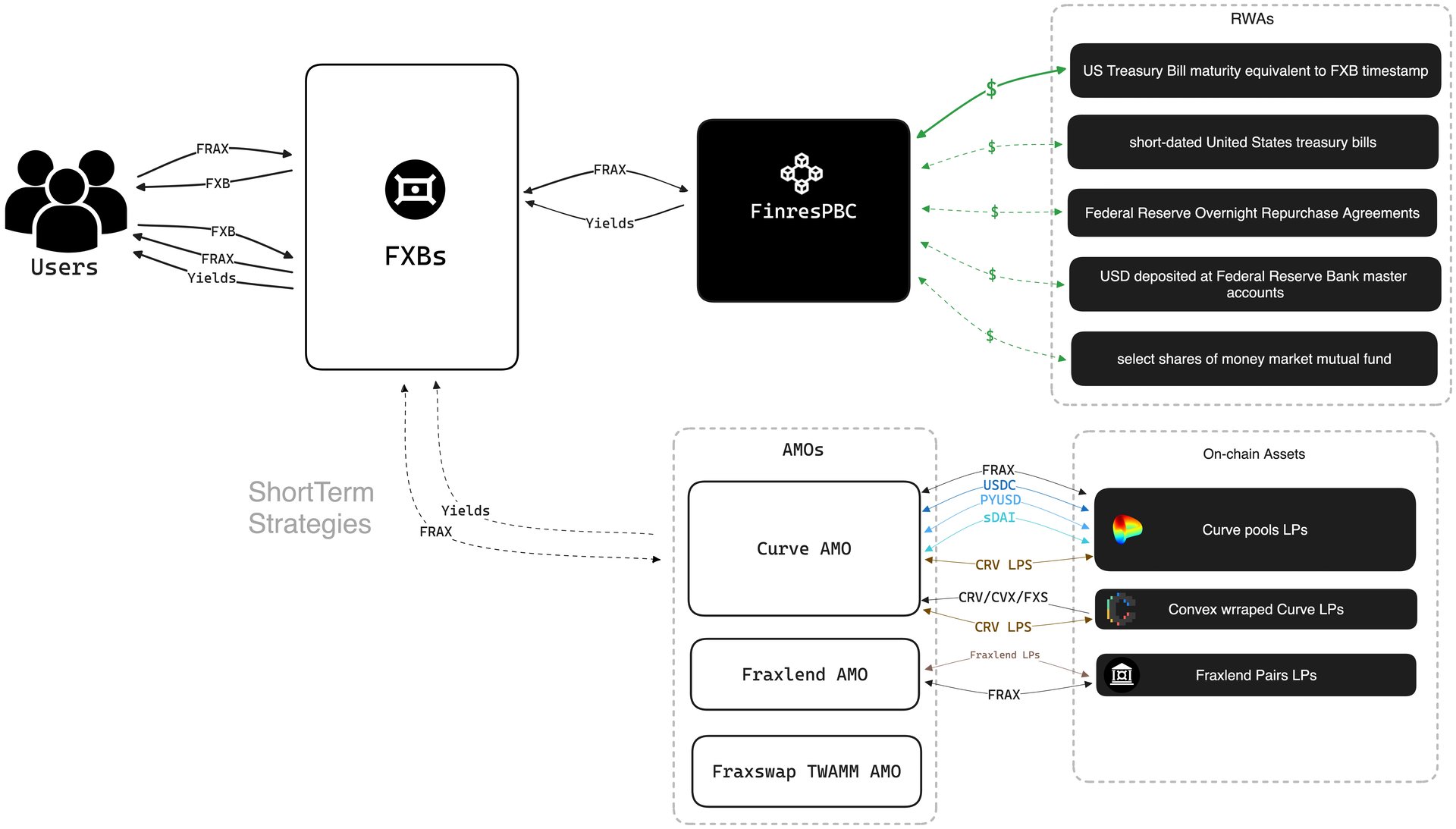
Frax Bonds (FXBs) 是一种链上工具,其设计功能类似于零息债券。每个 FXB 代币在到期时都会按面值转换为 FRAX 稳定币。FXB 以折扣价通过 FXB 算法市场运营 (AMO) 管理的拍卖机制发行。折扣定价提供类似收益的回报,而无需直接承担现实世界资产 (RWA) 风险。[1][2]
概述
Frax Bonds (FXB) 是完全以 FRAX 稳定币计价的 ERC-20 债务代币。它们不是对任何抵押品或外部资产的索赔,也不提供除 FRAX 之外的任何货币的收益或赎回。FXB 的设计目的是在达到发行时预定的到期日时,以固定的 1:1 比例转换为 FRAX。它们不受现实世界资产(包括美国国库券)的支持或赎回,并且除了其编程转换为 FRAX 之外,不提供其他功能。
每个 FXB 都是通过工厂合约铸造的,该合约会锁定相应的 FRAX 金额直至到期,从而确保该过程完全在链上且无需信任。FXB 通过允许基于市场的时锁定 FRAX 定价来支持收益率曲线的开发,并且对 FXB 系列的数量或其各自的到期日没有任何限制。[2][3] [4]
系列拍卖
FXB 系列的价格发现通过连续渐进式荷兰式拍卖 (GDA) 拍卖系统进行,该系统具有由 frxGov 设置的数量和价格限制。这保证了 FXB 代币的出售价格不会低于最低限额。拍卖通过 FXB AMO 合约进行,并且是无需信任、无需许可和非托管的。可以通过 frxGov 和 FXB AMO Timelock 发起的交易随时进行新的拍卖。[2]
铸造与赎回
Frax Bonds (FXB) 分为 Origin 或 Bridged,具体取决于它们最初发行的链。在 Fraxtal 等链上铸造的 FXB 被指定为 Origin FXB,并由发行时存入的 FRAX 支持。这些 FXB 只能在达到到期日后在其原始链上兑换为 FRAX。
如果 Origin FXB 被转移到另一条链,它将成为 Bridged FXB。在这种情况下,基础 FRAX 仍保留在原始链上,并且必须通过将 FXB 桥接回该链来进行赎回。这是因为用于在原始链上铸造的 FXBFactory 合约嵌入了销毁和赎回 FXB 的功能。相比之下,桥接的 FXB 通过桥的 ERC20Factory 实例化,并依赖于桥进行铸造和赎回,而无法直接访问基础 FRAX。[2]
发现错误了吗?
