订阅 wiki
Share wiki
Bookmark
INVINOS
0%
INVINOS
Invinos 是一个 AI 和 区块链 隐私操作系统,旨在将加密的 AI 工具、匿名区块链基础设施和去中心化应用程序集成到一个统一的系统中,专注于用户隐私。它旨在为私密的数字交互和交易提供一个平台。 [35]

概述
Invinos 是一个移动优先、注重隐私的操作系统,支持与人工智能工具、区块链网络和互联网的安全交互。它集成了多种隐私功能——例如跟踪器拦截浏览器、去中心化 VPN、跨链混币器、临时钱包和本地 AI 推理——到一个单一的、有凝聚力的环境中。Invinos 专为 Android 设备构建,默认消除数据暴露,并且在没有中心化依赖或用户识别的情况下运行。它支持私密网页浏览、不可追踪的链上交易以及无需外部记录的 AI 查询。模块化系统允许用户仅激活必要的隐私工具,同时实现分层保护。
Invinos 的创建是为了应对日益增长的数字监控,适用于需要强大隐私保护的个人,例如 DeFi 参与者、开发者和记者。其基础设施强调去中心化、用户自主性和最小数据足迹,这使其与独立的 VPN 或混币器等单一用途工具区分开来。 [1]
架构
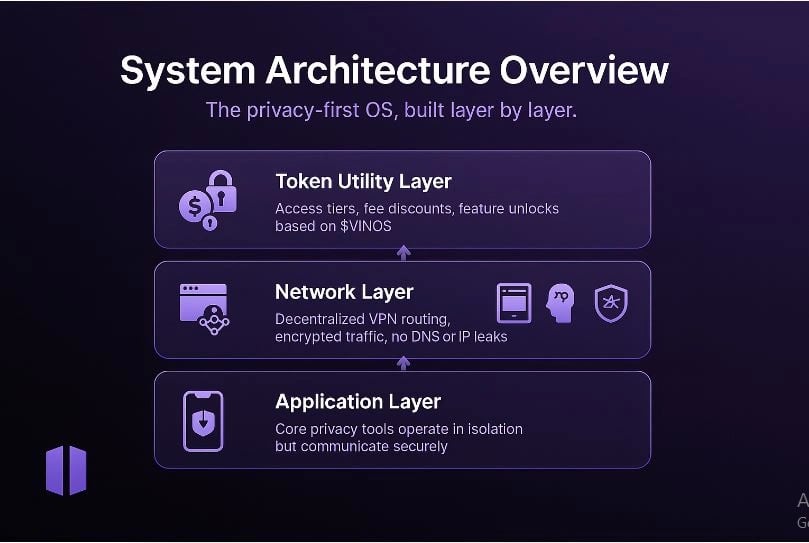
设计层
Invinos 围绕六个不同的设计层构建,每个层负责保护数字交互的不同方面。其架构没有依赖于单一的统一系统,而是将功能分离为专门的模块,以最大限度地降低风险、限制元数据暴露并防止中心故障点。这种模块化结构是故意的,既提供了安全性,又提供了适应性。
每一层都支持三个主要目标:防止可追溯性、消除元数据泄漏以及实现对互联网、金融工具和人工智能系统的私有、无限制使用。无论是处理网络流量、会话数据、钱包活动还是用户身份,每个组件都有助于构建一个更广泛的系统,该系统可以适应不同的隐私需求。
这些层通过集中式仪表板进行管理,以便于访问和协调,但也可以根据用户需求或威胁级别独立运行。这种灵活的框架使 Invinos 能够服务于广泛的用户,从寻求基本保护的个人到在高风险环境中运营的专业人士。 [2]
网络
网络层构成了 Invinos 隐私架构的基础,处理来自用户设备的所有出站和入站通信。与依赖中心化 ISP 或 VPN 提供商的传统系统不同,这些提供商可以监控或存储用户元数据,Invinos 使用去中心化的点对点 VPN 隧道。该系统通过多个匿名中继路由互联网流量,以防止可追溯性。
数据包使用多跳路由在多个阶段进行加密,确保没有单个节点可以查看来源和目的地。 DNS 请求通过匿名通道解析,以防止域级跟踪,并且数据包填充会模糊大小和时间,从而降低流量模式分析的风险。
此层可防止外部服务(网站、应用程序和区块链平台)检测用户位置、设备详细信息或相关活动。 它持续运行并支撑系统中的所有其他模块,作为抵御监视的主要屏障。 [3]
浏览器
Invinos中的浏览器层旨在消除最常见的监视来源之一:浏览器指纹识别和行为跟踪。传统浏览器,即使在隐私模式下,也会暴露字体、分辨率、语言设置和输入模式等数据点,所有这些都可用于构建持久的用户配置文件。Invinos通过创建一个隐形浏览器来解决这个问题,该浏览器在完全隔离、可丢弃的环境中启动每个会话。
每个浏览会话都是沙盒化的,没有持久的cookie、缓存或标识符。屏幕尺寸、时区和键盘行为等可识别属性在每个会话中都是随机的。JavaScript执行受到限制和监控,以阻止指纹识别尝试,并且跟踪脚本在网络和应用程序级别都被主动过滤掉。
不保存会话历史记录,并且浏览器不依赖于对第三方供应商或上游服务的信任。每个页面视图都包含在内,与之前的活动无关,并在会话结束时被擦除。这种方法确保用户可以在不暴露于分析、定位或长期数据收集的情况下浏览网络。 [4]
钱包与资产
Invinos 中的钱包和资产层侧重于通过幽灵钱包保护链上隐私——幽灵钱包是临时的、一次性使用的地址,为每个金融会话自动生成。这些钱包不与任何中心账户或身份相关联,并且永不重复使用,从而防止创建可追踪的交易历史。
为了进一步模糊资产转移,Invinos 集成了一个名为 zkMixer 的交易混合器。该系统允许用户在一个链上存入资产,并在另一个链上使用单独的地址提取不同的资产,从而打破两个点之间的可追溯性。通过这样做,钱包层可以保护用户免受集群分析、抢先交易以及基于身份的针对性攻击,这些攻击可能发生在去中心化金融和基于区块链的应用程序中。 [5]
计算 (AI)
Invinos中的计算层通过确保所有处理都在本地设备上进行,而不是在云端进行,从而解决了人工智能使用中的隐私问题。与大多数记录用户提示和响应的人工智能工具不同,Invinos使用量化权重和GPU加速,直接在移动硬件上运行优化的语言模型,从而消除了外部数据暴露。
提示在运行时加密,处理后不保存任何推理数据,从而保护用户输入的机密性。这种设置允许用户私下与人工智能模型交互。未来的更新计划包括支持加密提示序列、协作代理和去中心化智能合约执行。 [6]
身份
Invinos中的身份层通过使用加密方法创建匿名且可验证的身份,消除了对传统帐户、电子邮件或社交登录的需求。用户通过保持隐私的加密证明进行交互,而不是将身份与个人信息联系起来。
借助zk-Identity,个人可以证明凭证、治理权或声誉的所有权,而无需暴露钱包地址或个人详细信息。这些可移植的身份可以通过密钥备份恢复,并支持零知识证明和Merkle树证明,以实现安全、私密的验证。 [7]
界面 & 仪表盘
界面和仪表盘层是Invinos中用户的本地控制中心。它显示活动隐私模块的状态,提供实时隐私指标,并允许用户根据当前需求调整设置。诸如zkMixer之类的功能可以在不损害隐私的情况下有选择地启用或禁用。
所有仪表盘功能都在本地运行,没有外部通信或数据存储。这种设计确保用户界面不会成为监视或信息泄漏的来源。 [9]
无服务器
Invinos 的运作无需集中式服务器,而是依赖于去中心化和本地系统。它使用 IPFS 分发应用程序和元数据,使用去中心化 VPN 中继器进行网络路由,并使用 以太坊 和 Polygon 等公共 区块链 作为其 zkMixer。身份、证明和钱包功能通过开源加密库处理,而 AI 任务完全在设备上使用优化的推理工具运行。
这种架构使 Invinos 具有抗审查性,并且不依赖于单一故障点。即使更广泛的基础设施的某些部分不可用,其核心功能仍然可以访问。 [9]
移动优先
Invinos主要为移动设备使用而构建,所有组件都经过优化,可在Android设备上高效运行。本地AI模型经过量化以提高性能,浏览器使用GPU加速和每个选项卡隔离的内存,VPN层在基于WireGuard的轻量级中继上运行,以减少电池使用。
该系统无需依赖后台服务或应用商店分发即可运行。用户通过去中心化的APK链接安装它,并通过IPFS清单管理更新。这种方法确保了移动设备上提供全面的隐私保护,不限于桌面环境。 [36]
应用程序模块
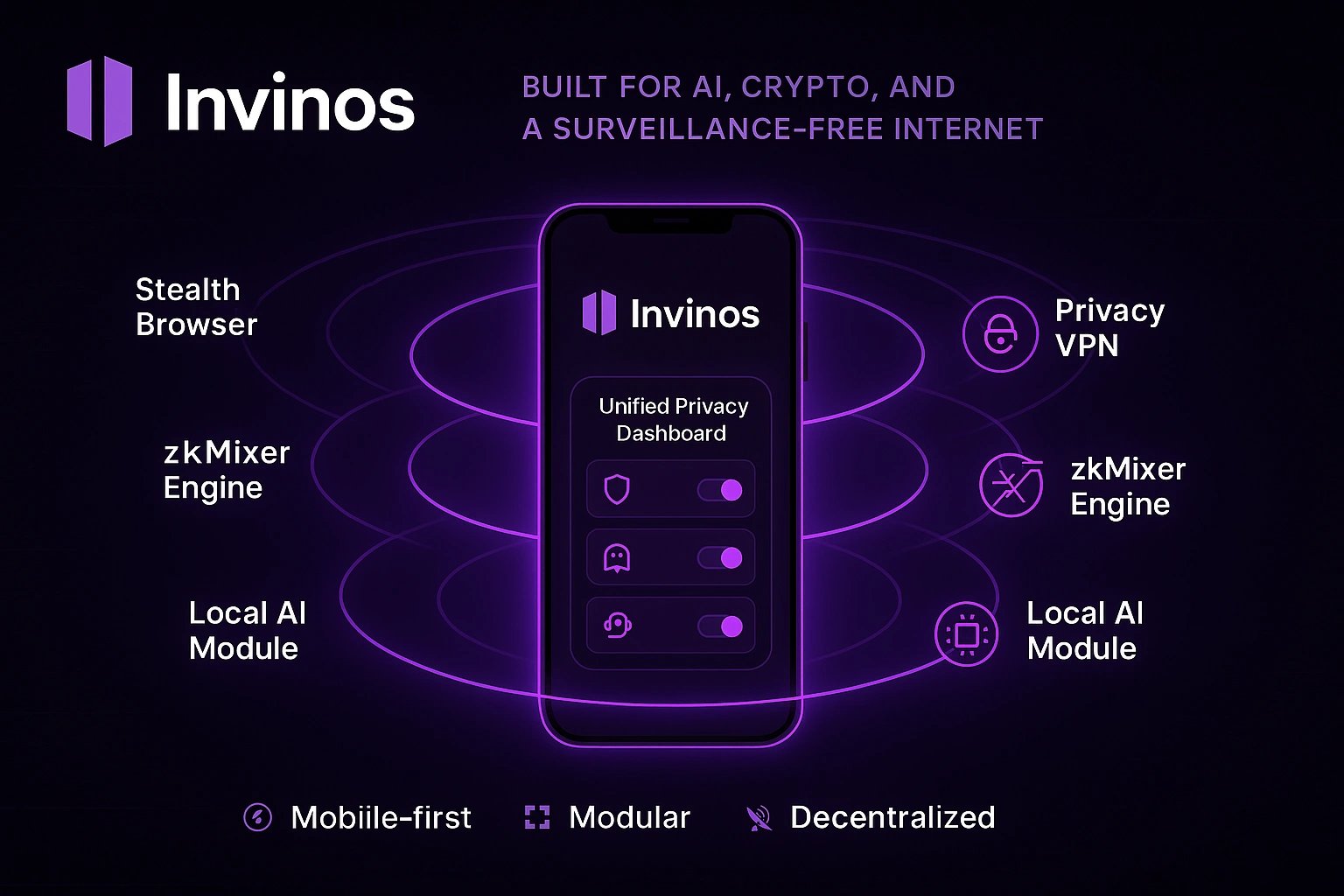
隐身浏览器
Invinos中的隐身浏览器提供互联网访问,而不会暴露用户行为或设备详细信息。每个会话都在一个独立的容器中运行,没有持久存储,确保在会话结束时清除cookie、缓存和日志。
为了阻止跟踪,浏览器会随机化设备属性(如屏幕大小和字体),对JavaScript进行沙盒处理以避免分析,并在DNS级别过滤掉第三方脚本和跟踪器。这种设置提供了标准的浏览体验,防止网站收集识别数据。 [10] [11]
隐私 VPN
Invinos 的 VPN 通过去中心化的多跳中继网络运行,加密所有流量,无需依赖中心化服务器。每个数据包都经过多层加密,并通过旋转中继路由,防止任何节点将其来源与其目的地联系起来。
加密的 DNS 处理和动态 IP 掩蔽进一步隐藏浏览活动和位置。VPN 自动运行,无需设置,允许用户访问在线服务,而无需透露其 IP 地址或物理位置,包括 Invinos。 [12]
zkMixer
zkMixer是Invinos的系统,通过打破存款和取款活动之间的联系来模糊资产转移。用户可以存入一种代币,稍后将另一种代币提取到不同的地址和链上,而没有可追踪的连接。
该过程包括批量处理交易、随机延迟以及通过临时钱包进行路由。它提供了强大的实际隐私,并计划添加零知识证明以实现正式的不可链接性。使用无需帐户、登录或持久状态——每个会话都保持完全加密和匿名。 [13]
幽灵钱包
幽灵钱包是为单次交互而本地生成的临时区块链钱包。与具有持久历史记录的传统钱包不同,这些钱包是即时创建并在使用后丢弃的,不留下任何长期痕迹。
幽灵钱包依赖于基于设备的熵来生成密钥,并且永远不会链接到用户身份或集中式存储。它们支持私有dApp使用、资产转移和治理参与,并且可以与zkMixer配对以确保交易保持不可链接。 [14]
匿名 DEX
Invinos中的匿名去中心化交易所(DEX)允许跨链资产交换,而不会暴露用户身份或交易模式。它使用会话钱包、交易中继和跨链混合器,避免了公共订单簿、内存池和持久钱包历史记录。
该系统可防止抢先交易、地址聚类和流动性跟踪,同时支持高效交易并与DeFi工具集成。所有交换都在保护隐私的环境中进行,让用户完全控制披露。 [15]
本地 LLM
Invinos 集成了完全离线运行的本地语言模型,消除了与基于云的 AI 工具相关的隐私风险。提示和响应永远不会被记录、存储或传输,确保用户活动保持机密。这些模型在沙盒环境中运行,所有会话数据在应用程序关闭后都会被删除。这种设置允许用户安全地与 AI 交互,无需外部暴露即可执行翻译、摘要和文本生成等任务。 [16]
Context Lock
Context Lock是Invinos本地语言模型的临时记忆系统。它支持多轮对话,而无需持久保存数据。它仅在活动会话期间维护上下文,从而实现更连贯的交互,而无需在会话结束后保留提示或响应。这种设计支持自然的对话和推理,同时确保用户意图和思维模式保持私密且不被保存。 [17]
隐私仪表盘
隐私仪表盘是 Invinos 的本地界面,用于管理隐私功能。它显示哪些模块处于活动状态,提供实时的隐私指标,并允许用户根据自己的需求启用或禁用功能。所有操作都在设备上进行,无需外部通信或数据保留,确保界面不会成为跟踪或数据暴露的来源。 [18]
zk-Identity
zk-Identity 使⽤户能够在不泄露身份的情况下验证属性,例如 NFT 所有权、代币余额或 DAO 成员资格。它采⽤ 零知识证明 来创建可验证的证明,这些证明不链接到钱包地址或个⼈数据。
证明在本地⽣成,链上验证通过智能合约进⾏,旨在在投票、访问控制和选择性披露过程中保持⽤户匿名性。 [37]
治理
治理模块使VINOS代币持有者能够提交提案、投票和表达偏好,而不会暴露钱包活动或个人数据。投票使用zk-Identity的隐私保护凭证,确保不创建参与记录或选民登记。
这种方法支持去中心化、保密的治理,允许社区指导平台,同时保护隐私并防止操纵或胁迫。 [19]
VINOS
VINOS代币是Invinos平台的核心经济层,实现去中心化、注重隐私的功能访问,如加密的AI代理和zkMixers,无需依赖广告或第三方控制。与纯粹的投机代币不同,VINOS在所有平台层都具有嵌入式实用性,并支持保护隐私的经济模式,取代了传统的货币化方法。
代币使用量随着隐私模块中的交互而自然增加,促进平台增长,并通过实际效用奖励持有者。VINOS支持基于用户自由而非数据货币化的经济模式,为注重隐私的用户强化可持续的生态系统,并支持由个人而非公司拥有的数字环境[26]。
代币经济学
VINOS的总供应量为1亿枚代币,分配如下:
- 流动性池: 65%
- 生态系统发展: 20%
- 市场营销与社区: 10%
- 团队: 5%
合作伙伴关系
发现错误了吗?
