위키 구독하기
Share wiki
Bookmark
PraSaga
0%
PraSaga
PraSaga는 차세대 레이어 1 블록체인 개발에 주력하는 스위스 기반 재단입니다. 이 기술은 이전 세대 블록체인의 여러 가지 제한 사항을 해결하여 확장성, 효율성 및 전반적인 성능을 향상시키는 것을 목표로 합니다. [1]
개요
PraSaga는 기존 확장성 제한을 극복하도록 설계된 블록체인 플랫폼인 SagaChain을 개발하고 있습니다. 주요 혁신은 Python 프로그래밍 언어의 수정 버전인 SagaPython으로, 개발자가 SagaChain에서 애플리케이션을 쉽게 구축할 수 있도록 합니다. PraSaga는 Python의 인기를 활용하여 광범위한 개발자가 기술에 접근할 수 있도록 하고 기존 엔터프라이즈 인프라와의 원활한 통합을 가능하게 하는 것을 목표로 합니다.
SagaPython은 앱 생성을 단순화하고 보안을 보장하여 블록체인 개발을 향상시키는 PraSaga의 분산 운영 체제인 SagaOS에 통합되었습니다. PraSaga는 오픈 소스 개발 및 커뮤니티 참여에 중점을 두고 플랫폼이 고속으로 수백만 건의 트랜잭션을 용이하게 할 것으로 예상합니다. [5]
PraSaga의 메인넷 출시는 SagaScale 기술 완료, 소프트웨어 개발 환경 출시, 후속 CEX 상장과 함께 12월 랩드 사가코인 런치패드 등 일련의 준비 단계를 거쳐 예상됩니다. [8]
제품
SagaChain
SagaChain은 확장성, 스마트 계약 병렬화 및 암호화폐 유틸리티와 같은 블록체인 기술의 주요 문제를 해결하도록 설계된 PraSaga의 블록체인 인프라입니다. 검증자 수가 증가함에 따라 확장하여 트랜잭션 처리량과 보안을 개선하기 위해 분산 작업 증명(D-POW) 합의 메커니즘을 사용합니다. 또한 이 시스템은 샤딩을 활용하여 블록체인 세그먼트에서 병렬 처리를 가능하게 합니다.
SagaOS
SagaOS는 SagaChain을 기반으로 구축된 객체 기반 운영 체제입니다. 개별 객체와 해당 상태를 관리하는 사용자 계정 모델을 제공하여 병렬 트랜잭션을 허용합니다. 이 시스템은 사용자 계정이 토큰 잔액만 보유하여 직렬화된 트랜잭션으로 이어지는 기존 블록체인 모델과 대조됩니다. [2]
SagaPython
SagaPython은 SagaChain에서 애플리케이션 개발을 위해 설계된 PraSaga의 수정된 Python 프로그래밍 언어 버전입니다. SagaOS의 일부로서 애플리케이션과 블록체인 운영 체제 간의 통신을 용이하게 합니다. 널리 사용되는 언어를 활용함으로써 SagaPython은 기존 리소스의 대규모 풀에 대한 액세스를 제공하여 개발을 더욱 쉽게 만듭니다.
통합 및 개발자 지원
SagaPython은 기존 아키텍처와의 호환성 덕분에 프로젝트를 처음부터 시작할 필요 없이 쉽게 통합할 수 있습니다. PraSaga는 또한 다양한 온라인 리소스와 튜토리얼로 개발자를 지원하여 SagaChain에서 혁신을 주도하는 협업 커뮤니티를 장려합니다. [3]

토큰노믹스
SagaChain의 기본 암호화폐인 SagaCoin은 분산 거버넌스를 통해 토큰 순환을 조정하여 디플레이션 및 인플레이션 측면의 균형을 맞추는 것을 목표로 합니다. 이 금융 모델은 블록체인 내에서 경제적 안정성을 유지하여 트랜잭션 사용에 적합하게 만들면서 장기적인 블록체인 보안을 보장하는 것을 목표로 합니다. [2]
SagaCoin 관리 모델
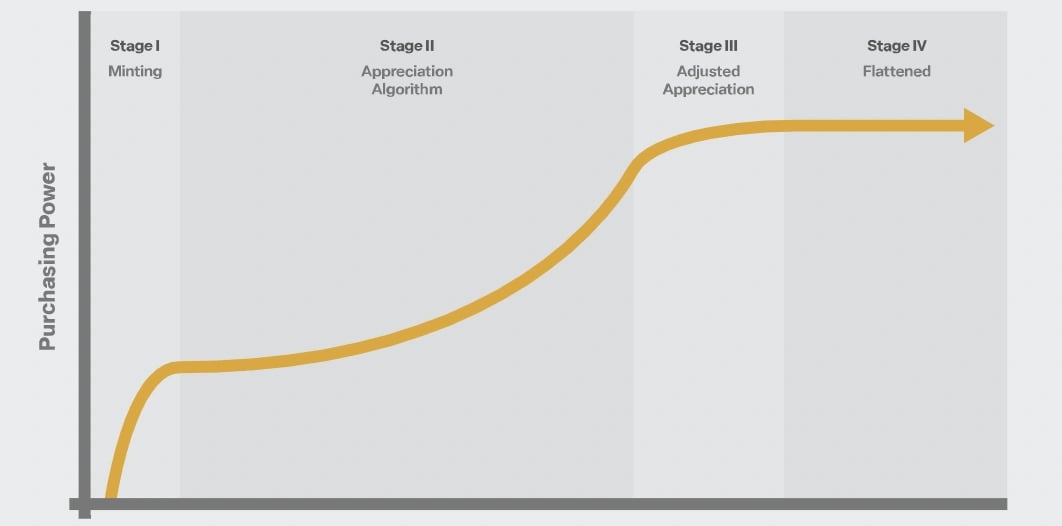
SagaCoin 관리 모델은 트랜잭션 활동을 기반으로 코인 공급을 동적으로 규제하기 위해 수요 대응 알고리즘을 사용하여 변동성을 해결합니다. 비트코인과 같은 고정 공급 암호화폐에서 볼 수 있습니다. SagaCoin의 공급은 수요 변화에 맞춰 조정되며 시간이 지남에 따라 구매력을 안정화하는 것을 목표로 합니다. [7] 처음에는 구매력이 소비자 물가 지수(CPI) 및 GDP 디플레이터와 같은 전통적인 경제 지표를 사용하여 측정됩니다. [6]
관리 모델은 4단계로 구성됩니다. 처음 두 단계는 시장 진입 및 가치 상승에 중점을 두고 후반 단계는 코인의 가치를 안정화하여 교환 매체로서의 유용성을 높이는 것을 목표로 합니다.
- 1단계:
- 공급에 제한이 없는 초기 출시 단계입니다.
- 2단계:
- 목표 가치 상승 경로가 설정됩니다.
- 가치 상승 목표에 맞추기 위해 분기별로 확장률이 조정됩니다.
- 3단계:
- SagaCoin의 구매력을 안정화하는 데 중점을 둡니다.
- 4단계:
- 블록체인 데이터를 기반으로 내부 가격 책정 모델로 전환합니다.
- 공급은 암호화된 비즈니스 보고서를 사용하여 개인 정보 보호를 보장하고 장기적인 안정성과 결제 매체로서의 광범위한 사용을 목표로 조정됩니다.
역사
1993년에 출시된 모자이크 브라우저는 인터넷 붐을 일으켰고, 넷스케이프 내비게이터가 그 뒤를 이었습니다. 1994년 AT&T는 클라우드 서비스 개념을 도입했습니다. 2006년까지 AWS S3는 주요 클라우드 스토리지 제공업체가 되었습니다.
2008년 비트코인의 백서는 최초의 분산 통화로 이어졌습니다. 이더리움의 2015년 스마트 계약 출시는 분산 애플리케이션 및 금융을 가능하게 하여 피어 투 피어 트랜잭션에 혁명을 일으켰습니다.
2018-2021: 확장 및 PraSaga의 혁신
샤딩은 2018년에 블록체인 확장을 위한 솔루션으로 주목을 받았습니다. 2021년 PraSaga는 SagaChain™ 및 SagaOS™를 도입하여 스마트 계약 제한 사항을 해결하고 웹 3.0을 위한 확장 가능한 블록체인 아키텍처를 만들었습니다. [4]
잘못된 내용이 있나요?
