Subscribe to wiki
Share wiki
Bookmark
Sei
The Agent Tokenization Platform (ATP):Build autonomous agents with the Agent Development Kit (ADK)
0%
Sei
Sei is a Layer 1 that combines the advantages of Ethereum and Solana: the dominant development standard of Ethereum with the performance of Solana. The V2 update for Sei makes it the first parallelized EVM. Serving as a new scaling approach for the Ethereum ecosystem. Sei launched its mainnet in 2022 and has a growing ecosystem with key teams from Ethereum, Solana, Polygon, Arbitrum, and others. The team is backed by Multicoin, Jump, Coinbase Ventures, etc. Jayendra Jog and Jeff Feng are Sei's co-founders. [1][2]
Overview
Launched in 2022, Sei has one core thesis: the fundamental use case for blockchains is the ability to exchange digital assets. Thus, the problem of how to scale exchanges is instrumental to unlocking the next stage of growth for Web3 adoption. Sei is an open-source, general-purpose Layer 1 blockchain built for trading, optimized at every level of the stack to offer the best infrastructure for the exchange of digital assets. [1][3]
Sei launched its public mainnet on August 16, 2023, and its public devnet on February 13, 2024. [10][11]
Sei V2 EVM
The Sei v2 is introducing a variety of new features, such as high-performance parallelized EVM. It can result in a chain that combines the best parts of both Solana and Ethereum; improving the user experience and unlocking a new design space for developers, with improvements in throughput when compared with current offerings in the Ethereum ecosystem.
- Interoperable EVM: This allows existing developers in the Ethereum ecosystem to deploy their applications, tooling, and infrastructure to Sei with no changes, while benefiting from the 100x performance improvements offered by Sei. Sei will still support Cosmwasm, as a second execution environment on the same blockchain.
- Optimistic Parallelization: This feature allows developers to unlock parallel processing for their applications, with no additional work. This is similar to how Solana has scaled its throughput; Ethereum developers can now also build out parallelized workflows for the first time.
- SeiDB: This major upgrade allows Sei to handle a much higher rate of data storage, reads, and writes which become important for a high-performance blockchain. Not only does this facilitate huge performance improvements, for developers and specifically node operators, it means rapid state sync, and reduced hardware requirements through reducing state bloat.
- Twin Turbo Consensus: This feature allows Sei to reach the fastest time to finality of any blockchain at 390ms, unlocking web2-like experiences for applications.
- The Parallel Stack: This emerges as a robust, open-source framework designed for crafting Layer 2s and rollups that harness the power of parallel processing, this architectural innovation is tailored to significantly enhance the Ethereum ecosystem, targeting the performance bottlenecks that Layer 2 blockchains currently face. [1]
2025 SIP-3 Update
Sei has begun transitioning to an EVM-only architecture following the initial approval of SIP-3 through community governance. This proposal outlines the deprecation of CosmWasm and native Cosmos transactions in favor of a streamlined, Ethereum Virtual Machine-based design. The change is intended to simplify the developer experience and enhance Sei’s alignment with the broader EVM ecosystem while preserving its high-performance characteristics.
Key considerations identified during the community feedback period include migration support for existing CosmWasm projects, mechanisms for asset transfers, updated technical specifications for EVM precompiles, infrastructure requirements for RPC and indexing services, and clearer communication around asset impacts. Notably, only CosmWasm assets will require migration; EVM assets will remain unaffected. The transition will proceed in multiple phases, with additional checkpoints to guide implementation. [13]
Main Features
Sei incorporates several essential features to enhance its functionality. Security is key, with Sei collaborating with global institutions and validators to ensure robust security measures for digital asset transactions. Its architecture prioritizes scalability, catering to the growing demand for decentralized applications (dApps) and supporting major global applications seamlessly. The platform's adaptability allows it to evolve alongside industry trends, with community governance guiding innovations. Speed is emphasized to enable swift transactions while maintaining security and stability. Sei also focuses on eco-friendliness by leveraging proof of stake consensus to minimize its environmental impact, contributing to a more sustainable digital assets industry through carbon neutrality initiatives by the Sei Foundation. [4]
Technology
Twin-Turbo Consensus
Sei employs the Twin-Turbo Consensus mechanism to enhance transaction efficiency. This method optimizes the process of transaction propagation, disseminating user-initiated transactions across the network. Validators integrate these transactions into their local mempools, and block proposers create block proposals with unique transaction identifiers and full block references. This approach reduces latency, expedites validator wait times, and contributes to Sei's overall operational efficiency. [5]
Optimistic Block Processing
Sei introduces Optimistic Block Processing, a distinctive feature that improves transaction efficiency. Unlike conventional methods where transaction processing is deferred until the pre-commit step, Sei concurrently processes transactions upon receiving the block proposal. This generates a candidate state in a cache committed upon successful block acceptance. This parallel process reduces latency and accelerates data processing, enhancing Sei's block processing efficiency. [5]
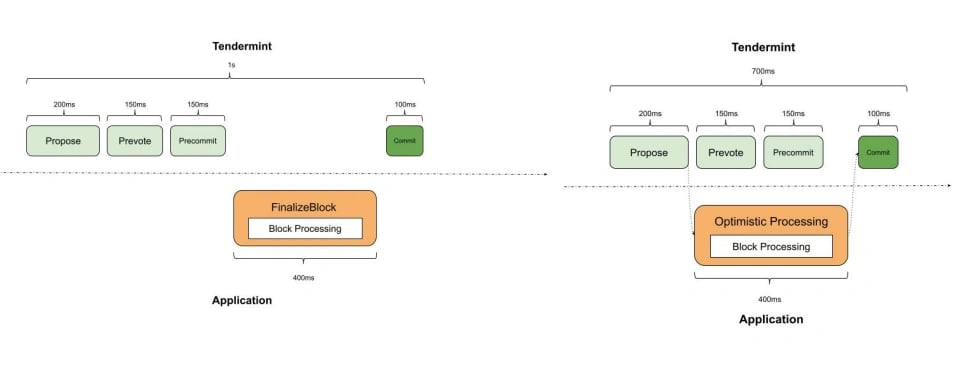
Parallelization
Parallelization is a fundamental strategy in Sei's block processing optimization. During the DeliverTx phase, transactions are processed in parallel, increasing transaction throughput. Sei also implements Market-Based Parallelization, allowing the simultaneous processing of independent Central Limit Order Book (CLOB) orders through its native order matching engine. This approach enhances transaction efficiency by enabling the parallel handling of orders that don't impact the same market within a block. Sei's tailored parallelization approach ensures efficient management of diverse transaction types. [5][7]
Oracles
Sei has both Pyth and native oracle modules to support asset exchange rate pricing for use by other modules and contracts. When validating for the network, participation as an Oracle is expected and required to ensure reliable and accurate pricing for assets. [5][8]
Native Order Matching Engine
The Native Order Matching Engine is a tool for decentralized exchanges building on the Sei blockchain. This engine enables the creation and management of Central Limit Order Books (CLOBs) within the Sei ecosystem. By maintaining order books at the chain level, decentralized exchanges can efficiently deploy and manage markets, offering users an enhanced trading experience. [5]
On April 4, 2024, the Sei Foundation, a non-profit committed to the Sei ecosystem's growth, launched the Sei Creator Fund, a $10m grants fund for both the creation of new projects and growth of existing NFT and Social projects on Sei. [12]
This fund is deployed in recognition of the community growth on Sei, designed to help scale Sei’s NFT and Social ecosystems. [10]
The Sei Creator Fund is designed to empower creators and builders across the spectrum of NFTs and Social: collections, applications, infrastructure, content creation, and even In-Real-Life (IRL) events.
Beneficiaries of the fund include a wide array of projects and teams contributing to the Sei NFT ecosystem. The Sei Creator Fund is designed to support various projects and creators at varying stages of their development journey. [10]
Community Directed Funding
In a move towards enhanced decentralization within the Sei ecosystem, the second phase of grants involves the community's votes. This section is to be facilitated through a collaboration with Gitcoin, a platform known for its commitment to funding open-source development and public goods. Through this, the Sei community has a say in how the grants are distributed, empowering the ecosystem. [10]
See something wrong?
The Agent Tokenization Platform (ATP):Build autonomous agents with the Agent Development Kit (ADK)
