订阅 wiki
Share wiki
Bookmark
Chromia
0%
Chromia
Chromia 是一个去中心化平台,旨在支持去中心化应用程序 (dApp) 的创建和运行。Chromia 由瑞典科技公司 ChromaWay 开发,于 2018 年推出,它将分布式账本技术与关系数据库系统相结合。这种方法旨在解决早期去中心化系统中观察到的可扩展性、可用性和灵活性挑战,其应用领域涵盖游戏、去中心化金融 (DeFi) 和数字资产管理。[1] [4] [5]
概述
Chromia 作为一个区块链平台运行,它将去中心化网络原则与关系数据库结构相结合。这种方法允许开发人员创建能够处理复杂数据交互的 dApp。
主要运营特点包括:
- 可扩展性:该平台通过分片支持水平扩展,使多个应用程序能够同时运行。
- 定价结构:费用根据资源消耗而非单个交易计算。
- 开发框架:Chromia 使用 Rell,这是一种专为区块链环境设计的编程语言,它结合了类似 SQL 的语法用于数据库查询。
- 互操作性:该平台促进与 Ethereum 等网络的跨链交互。
Chromia 的架构经常用于需要高交易量的领域,包括游戏生态系统、NFT 平台和供应链管理系统。[1] [4] [8] [5] [9]
历史
Chromia 起源于 ChromaWay,这是一家于 2014 年在瑞典成立的 区块链 技术公司。ChromaWay 之前开发的 Postchain(一个将区块链协议与传统数据库合并的开源框架)为 Chromia 的技术基础提供了信息。
2018 年,ChromaWay 宣布计划建立一个专注于 dApp 开发的区块链平台。9 月发布的白皮书概述了 Chromia 的“关系区块链”模型,该模型提出将去中心化网络与关系数据库效率相结合。
第一个 测试网 于 2020 年启动,允许开发人员部署基本的 dApp。随后于 2021 年发布的测试网引入了 质押 机制、治理功能以及与 以太坊虚拟机 (EVM) 的兼容性。
从 2022 年到 2023 年,Chromia 与 Mineplex(游戏)和 Hedera Hashgraph(互操作性)等项目建立了合作伙伴关系。该平台还组织了以开发者为中心的活动,包括黑客马拉松和资助计划。截至 2023 年,Chromia 仍在开发中,主网 发布计划待定。
主网启动
Chromia 的 主网 于 2024 年 7 月 16 日从开发过渡到运营状态,首先是最小可行产品 (MVP) 阶段。MVP 引入了核心功能,例如基于集群的架构,其中独立的子网络(集群)托管具有可自定义共识规则的 dApp。这种分阶段的推出优先考虑稳定性,最初的集群由 ChromaWay 和选定的合作伙伴运营。
主网启动期间激活的关键技术特性包括:
- EVM 兼容侧链:实现与基于以太坊的应用程序的互操作性。
- 费用模型实施:以 CHR 代币支付的交易费用,部分被销毁以管理供应。
- 质押激活:代币持有者可以将 CHR 委托给节点运营商,以参与网络安全和治理。
2024 年 9 月的发布后更新将集群可访问性扩展到外部开发人员,同时增强了跨链通信协议。[8] [11] [12] [13] [14] [15] [16]
技术
Chromia 的架构包含以下组件:
- 数据以关系结构组织,从而可以进行基于查询的检索。每个 dApp 都在一个独立的侧链上运行,称为集群,可以使用特定的 共识 参数进行配置。
- 交易使用 拜占庭容错 (BFT) 派生的算法进行验证。网络参与者可以质押 CHR 代币来影响治理决策。
- Rell 专为区块链开发而定制,其语法类似于 SQL,并具有用于 智能合约 验证的自动化工具。
- 开发人员承担用户的交易成本,费用以 CHR 代币支付。这些代币的一部分将永久从流通中移除。
CHR 代币
CHR 代币用作该平台的原生 加密货币。其主要用途包括:
- 支付交易和 dApp 部署费用。
- 通过 质押 参与网络治理。
- 通过质押机制赚取奖励。
代币经济学
- 最大供应量:1,000,000,000 CHR。
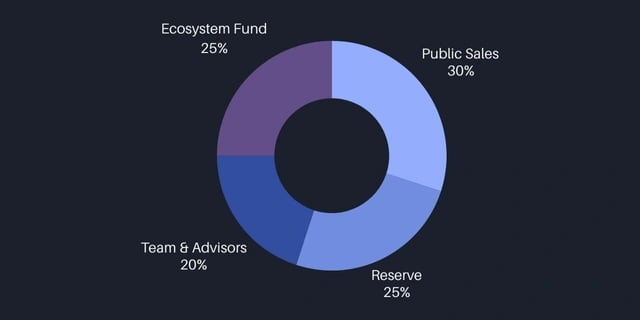
- 初始分配:公开销售 (30%)、团队和顾问 (20%)、生态系统基金 (25%) 和储备金 (25%)。
CHR 可在 加密货币 交易所进行交易,包括 Gate.io、KuCoin 和 Uniswap。
应用
Chromia 在多个领域托管 dApp:
- 游戏:管理游戏内资产的平台,例如 My Neighbor Alice。
- 去中心化金融:包括代币交易所和借贷协议在内的服务。
- 企业系统:用于供应链跟踪和数字身份验证的解决方案。
与 Antler Interactive 和 Green Assets Wallet 等实体的合作证明了其在多个行业的应用。[2] [3] [5] [7] [6] [10]
未来发展
在 主网 启动后,Chromia 的开发重点包括:
- 集群的去中心化:将集群运营从 ChromaWay 过渡到独立的 节点 运营商。
- 互操作性升级:扩展对跨链资产转移以及与 Polkadot 和 Cosmos 等网络的通信的支持。
- 生态系统激励:赠款和流动性计划,以吸引 dApp 开发人员,尤其是在游戏和 DeFi 领域。
挑战包括来自已建立的 layer 1 区块链的竞争,以及需要在开发人员中提高其关系数据库模型的采用率。[4] [7] [11] [12] [13] [14] [15] [16]
发现错误了吗?
