Subscribe to wiki
Share wiki
Bookmark
Scroll
We've just announced IQ AI.
Scroll
Scroll is a scaling solution for Ethereum that aims to address scalability issues. It is a Layer-2 solution built on the zkEVM (Zero-Knowledge Ethereum Virtual Machine), focusing on improving security and performance.[1]
Overview
Founded in 2021 by Haichen Shen, Sandy Peng, and Ye, Scroll is a Layer-2 scaling solution for Ethereum that addresses scalability challenges. It utilizes zkEVM (Zero-Knowledge Ethereum Virtual Machine) technology to process transactions off-chain and then bundle them for verification on the Ethereum mainnet.
Launched in October 2023, the Mainnet aims to improve Ethereum's scalability by reducing transaction costs and increasing processing speed through zero-knowledge proofs. The system seeks to enhance Ethereum's capacity while maintaining its security and decentralization.[1][2][3][4][5][6]

Ecosystem
Scroll Sepolia Testnet
The Scroll Sepolia testnet operates on top of Ethereum’s Sepolia Testnet, with Sepolia serving as the base network and Scroll Sepolia as a zero-knowledge rollup layer. It features demo applications including a bridge, block explorer, and rollup explorer.
Scroll Sepolia is used for testing and evaluating changes before they are deployed to Scroll Mainnet. It aims to provide a testing environment similar to the mainnet, allowing for the assessment of upgrades and performance in a live setting.[7][8]
Products
Scroll Origins
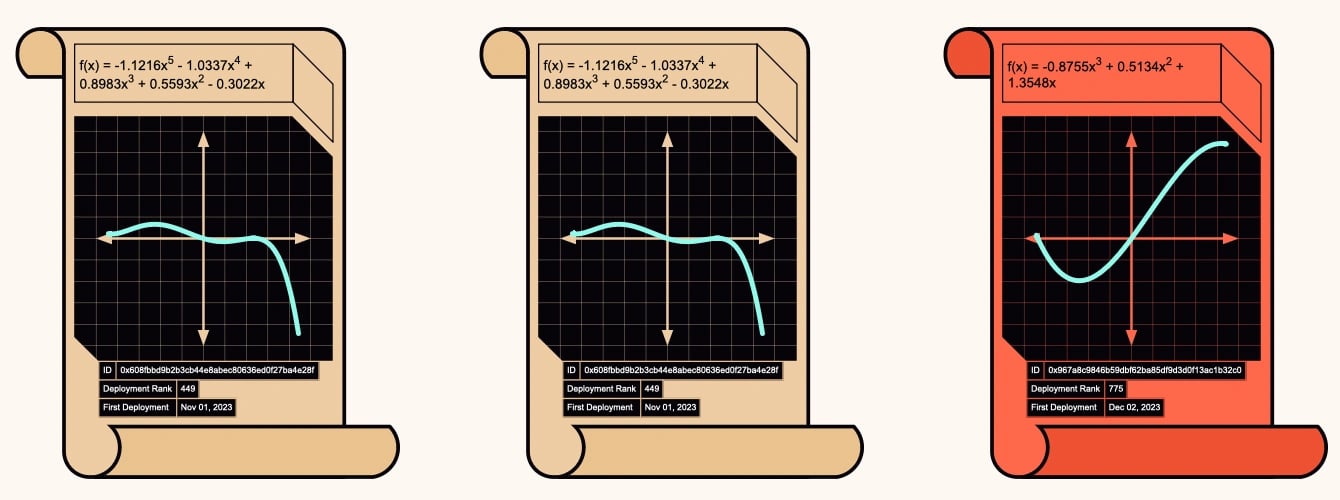
Scroll Origins is an NFT program intended to recognize developers who deployed contracts on Scroll Mainnet within 60 days of the Genesis Block, ending December 9, 2023. Each NFT features a distinct polynomial design related to zkEVM technology, reflecting deployment details such as date and address.
The NFTs are categorized based on deployment timing: Quintic for the first 30 days, Quartic for days 30 to 45, and Cubic for days 45 to 60. These non-transferable NFTs were available for claiming on the Scroll website starting December 14, 2023.[11][12]
Scroll Canvas
Scroll Canvas aims to provide a platform for displaying on-chain credentials and achievements within the Scroll ecosystem using verified Badges. These non-transferable badges serve as proof of user participation and milestones and are linked to individual wallets.
The integration with the Ethereum Attestation Service ensures that each Badge is authentic and verifiable. Users can use Scroll Canvas to document their achievements, organize Badge collections, and access new opportunities. Builders can issue Badges to facilitate user engagement and recognition.
As an open-source platform, Scroll Canvas invites community contributions and development. Users can mint their Canvas with a small fee, with opportunities for discounts available through invite codes.[13]
Architecture
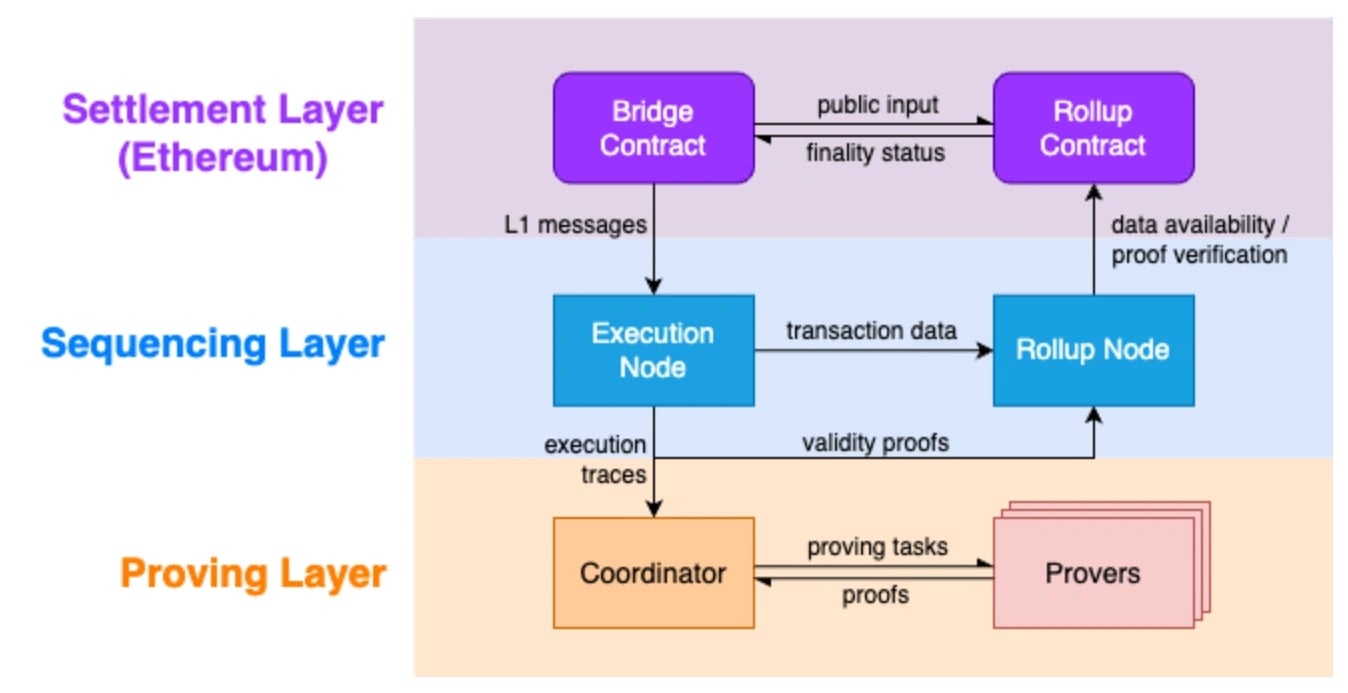
Scroll’s architecture is organized into three layers:
The Settlement Layer utilizes Ethereum to provide data availability, ordering, and validity proof verification. It supports communication and asset transfers between Ethereum and Scroll by deploying necessary contracts on Ethereum.
The Sequencing Layer includes an Execution Node that processes transactions and generates L2 blocks. It also contains a Rollup Node that batches transactions, posts data to Ethereum, and submits validity proofs for finality.
The Proving Layer is composed of provers that generate zkEVM validity proofs to verify L2 transactions, with a coordinator managing the distribution of proving tasks and relaying proofs to the Rollup Node for finalization on Ethereum.
This layered structure aims to ensure efficient transaction processing and security within the Scroll network, utilizing Ethereum’s infrastructure for data and finality.[9]
Scroll Node
The Scroll node facilitates interaction with the network through three components:
The Sequencer processes L2 transactions and generates new blocks, utilizing the Go-Ethereum (Geth) implementation for compatibility and security.
The Coordinator handles execution traces from the Sequencer and assigns proof generation tasks to Rollers.
The Relayer monitors the status of L2 blocks and manages message relays for deposits and withdrawals between Ethereum and Scroll. This setup aims to support effective network operations and communication.[10]
Roller Network
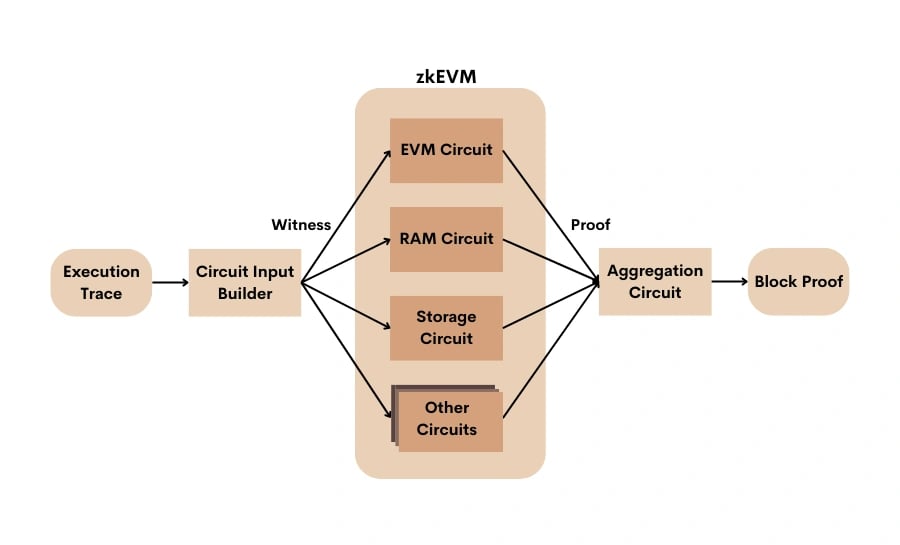
The Roller Network consists of Rollers that generate validity proofs for the zkRollup. These Rollers use hardware accelerators, such as GPUs, FPGAs, and ASICs, to reduce proving time and costs.
The process involves converting execution traces from the Coordinator into circuit witnesses, creating proofs for each zkEVM circuit, and aggregating these proofs into a single block proof. This setup aims to enhance the efficiency and accuracy of proof generation.[10]
Rolllup and Bridge Contracts
Scroll interacts with Ethereum through Rollup and Bridge smart contracts. The Rollup contract manages L2 state roots and blocks, storing data on Ethereum to support data availability and security for Scroll blocks. It aims to finalize L2 blocks on Scroll once block proofs are verified.
The Bridge contracts enable the transfer of messages and assets between L1 and L2. Users initiate these transfers through the Bridge contract, with the Relayer indexing and processing transactions for inclusion in L2 blocks and vice versa. This setup aims to facilitate communication and asset movement between the two layers.[10]
Funding
Scroll secured $50 million in its Series B funding round on March 6, 2023, bringing its total funding to $80 million across two rounds. The lead investors in this round included Polychain, Sequoia Capital China, and others. Scroll has 20 institutional investors and was valued at $1.8 billion as of March 7, 2023.[6][5]
See something wrong?
