Read
Edit
History
Notify
Share
TimeSwap
TimeSwap is a protocol for lending and borrowing without oracle reliance, creating money markets for various ERC-20 tokens. It's the first fully permissionless, oracle-less, non-liquidatable platform, introducing a fixed maturity lending and borrowing system.[1][2][3]
Overview
TimeSwap, established in 2020 by Ricsson Ngo, Ameeth Devadas, and Harshita Singh, aims to pioneer a fully permissionless, oracle-less lending and borrowing protocol. Operating across various platforms like Arbitrum, Mantle, Polygon PoS, Polygon zkEVM, and Base, TimeSwap facilitates the creation of money markets for any ERC-20 tokens without reliance on oracles, aiming to mitigate risks associated with oracle manipulation in DeFi.
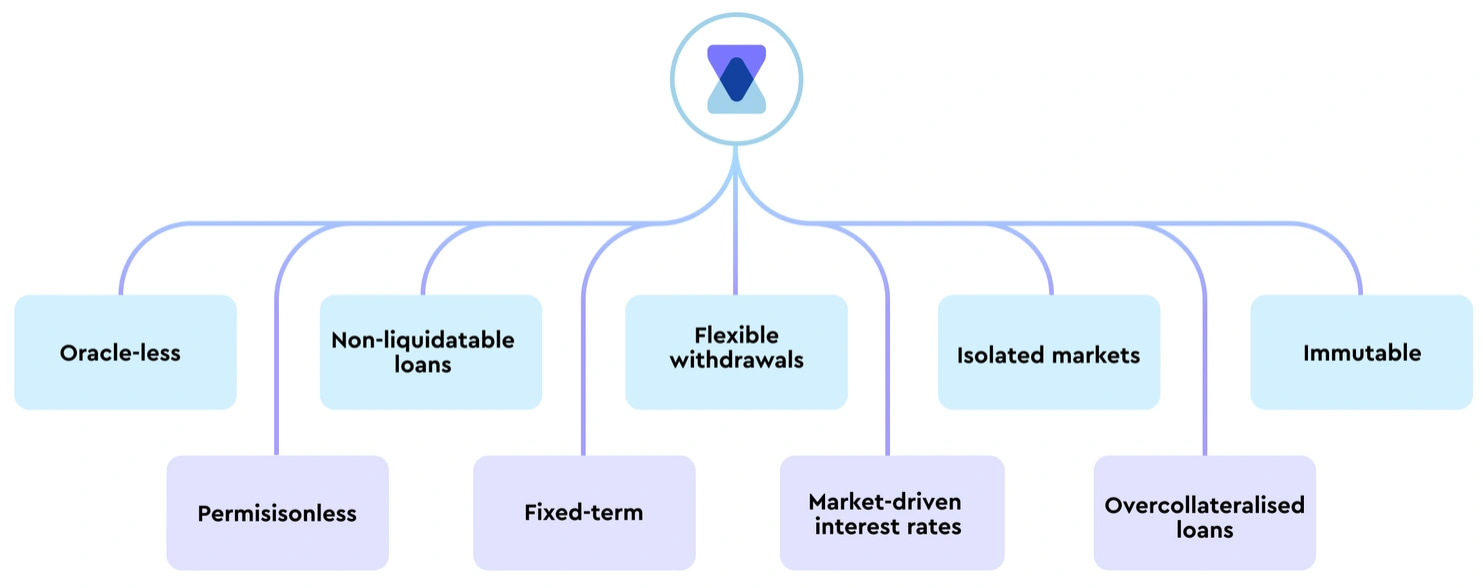
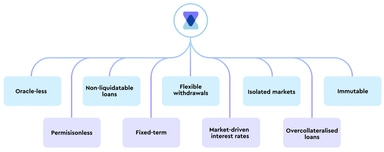
The protocol offers several key features, including oracleless operation and permissionless access for creating markets and participating in lending, borrowing, and liquidity provision. It seeks to ensure security through non-liquidatable loans and fixed-term transactions, providing users with certainty and predictability. Users also aim to benefit from flexible withdrawals, market-driven interest rates, isolated markets, and overcollateralised loans, enhancing security and stability.
TimeSwap aims to represent a significant shift in the DeFi landscape, offering a fully decentralized protocol operating without oracles or governance, aiming to unlock liquidity and capital efficiency while maintaining security and decentralization.
Furthermore, TimeSwap V2, launched on Polygon Mainnet in February 2023, aims to enhance capital efficiency while retaining core attributes like permissionlessness and oracle independence.[2][3][4][5][6][7][8]
History
2021
In 2020, TimeSwap was established with the aim of developing a fully decentralized money market protocol, spearheaded by Ricsson Ngo, Ameeth Devadas, and Harshita Singh. Throughout 2021, the team took significant steps towards realizing this vision, including closing a seed round, launching an Alpha Testnet, and initiating a Gamified Testnet.
The Alpha Testnet drew substantial community participation, with over 64,000 transactions recorded within the first three days. Subsequently, the Gamified Testnet offered participants a simulated market environment to devise strategies and optimize yield. Despite minimal promotional efforts, the community experienced growth, with Discord membership surpassing 30,000 and Twitter followers exceeding 22,000.[9]
2022
In 2022, TimeSwap continued its efforts to develop a decentralized money market protocol. The team achieved milestones such as launching the V1 AMM on mainnet and introducing NFTs. The V1 mainnet witnessed substantial activity, with over 45,000 transactions and $2.5 million in lending and borrowing, underscoring the demand for a market-driven and oracle-less system.
The Supernova upgrade facilitated permissionless liquidity addition, with Time Travelers contributing over $2.7 million. Partnerships with Biconomy and QiDAO aimed to improve user experience and asset options. Community engagement remained robust, with initiatives like meme battles and educational threads.[10]
2023
In 2023, TimeSwap progressed in its endeavor to establish a decentralized money market protocol. The launch of TimeSwap V2 aimed to enhance user experience and capital efficiency. Despite challenges in the crypto market, TimeSwap demonstrated resilience with strong community support.
Expansion to seven chains aimed to cater to a broader market, achieving over $50 million in lend/borrow volume. Strategic partnerships with various projects aimed to diversify TimeSwap's user base. Qualifying for Arbitrum's STIP and introducing the $TIME token premine were steps to foster community engagement. These developments underline TimeSwap's commitment to revolutionize DeFi lending while prioritizing security and independence.[11]
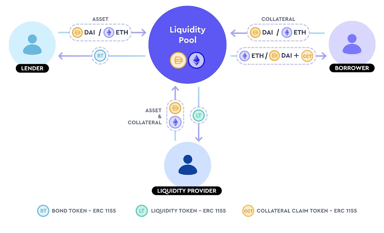
Market Participants
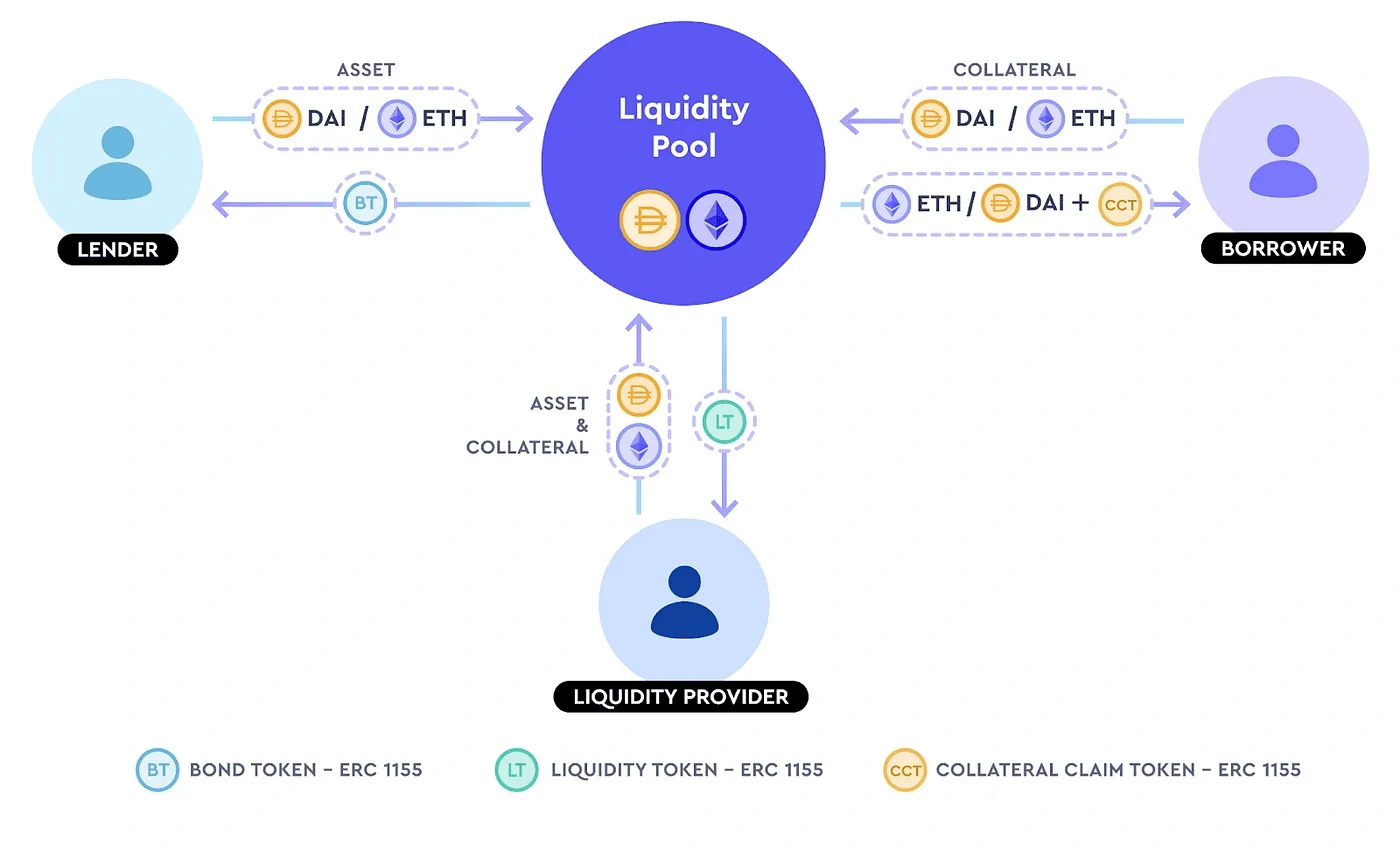
TimeSwap accommodates three main market participants: lenders, borrowers, and liquidity providers (LPs). In a simplified model, lenders contribute funds to TimeSwap pools for borrowers to borrow, earning fixed interest. Borrowers access these pools, securing loans with collateral, and repay with interest. LPs supply liquidity to the pools, earning transaction fees from lenders and borrowers.[12]
Lenders
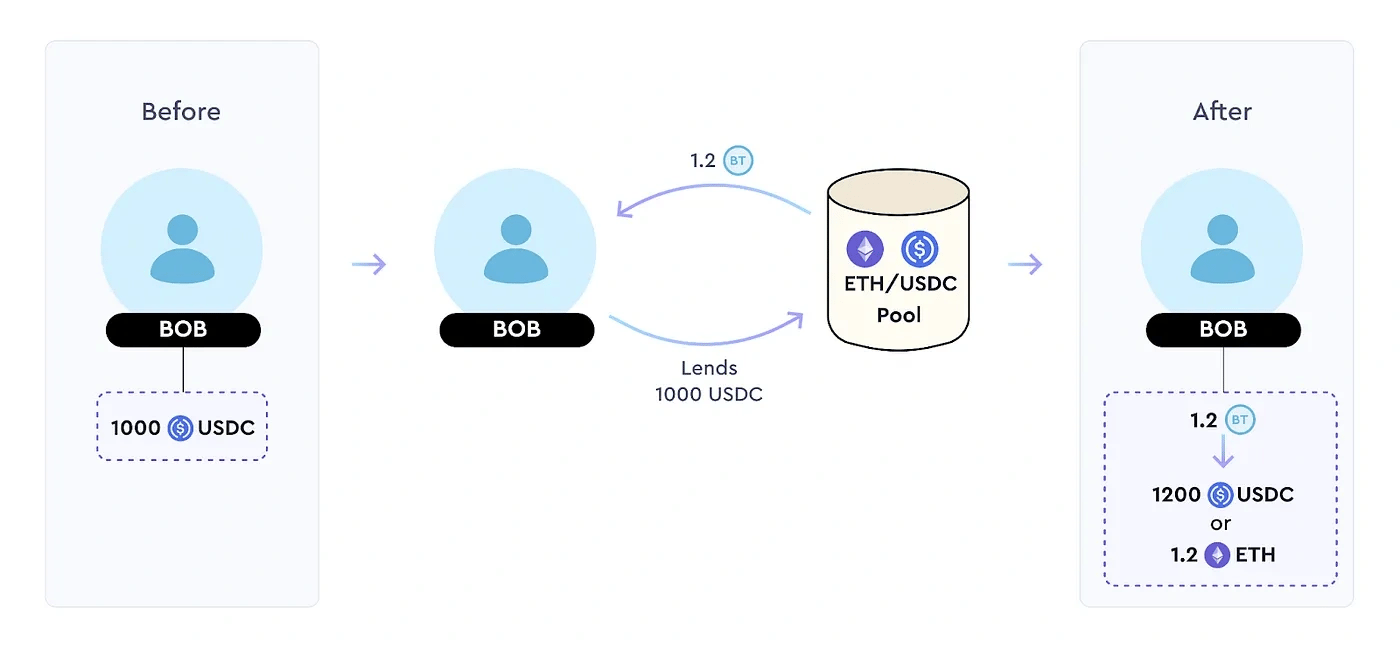
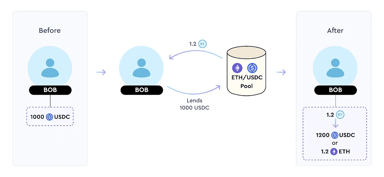
Lenders play a crucial role in TimeSwap by funding pools for borrowers, earning fixed interest. A diagram outlines their interaction with pools, such as the USDC/ETH pool, where borrowers can access USDC by locking ETH collateral.
In TimeSwap, loans are fixed-term and non-liquidatable. At maturity, lenders receive either the supplied asset (e.g., USDC) or collateral asset (e.g., ETH), depending on borrower actions. They always receive locked-in interest upfront. Compared to conventional DeFi lending, TimeSwap lenders have a different risk profile, actively managing ratios.
Though loans are fixed-term, lenders can exit early with potential slippage. They provide the supplied asset and receive an ERC-1155 Bond Token (BT).[13]
Borrowers
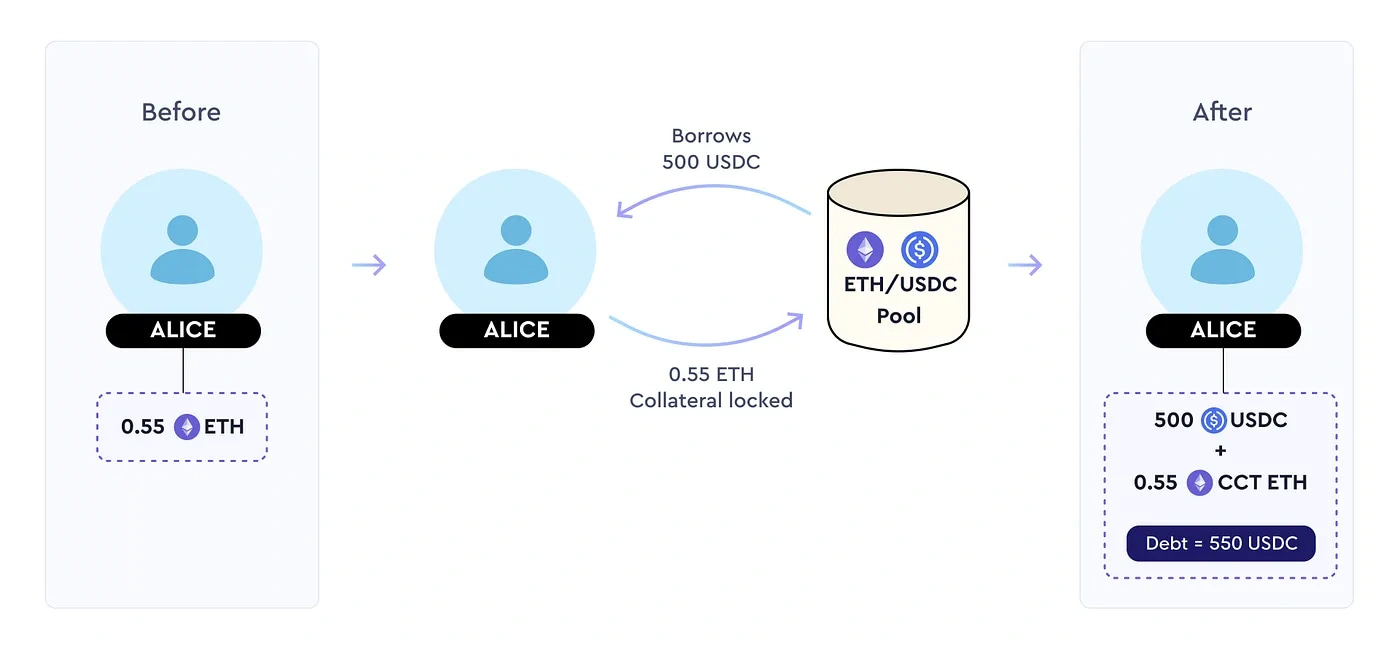
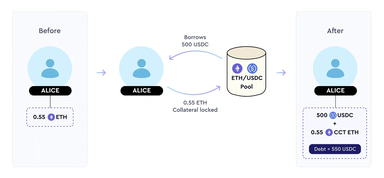
Borrowers in TimeSwap borrow from pools seeded by lenders and liquidity providers. In this system, loans are fixed-term and non-liquidatable. At maturity, borrowers can either repay their debts or forfeit collateral, depending on values. Interest is paid to lenders and liquidity providers accordingly, with the transition price (TP) indicating the optimal action point.
Compared to traditional DeFi protocols, borrowers in TimeSwap face a different risk profile due to the absence of liquidations. They can decide whether to repay or not at maturity, with the option for early debt closure albeit with potential slippage.
Borrowers lock in collateral (e.g., ETH) to receive the borrowed asset (e.g., USDC) and an ERC-1155 Collateral Claim Token (CCT).[14]
Liquidity Providers
Liquidity providers (LPs) contribute liquidity to TimeSwap pools, acting as counterparts to lenders and borrowers. They function similarly to LPs in Uniswap, facilitating transactions for fees.
In TimeSwap, where fixed returns are provided, LPs play a key role in matching total interest payments. LPs receive assets based on borrowers' decisions at maturity, with exposure to divergence loss based on interest spreads.
Despite the fixed-term nature of positions, LPs can withdraw early, albeit with potential slippage. In return for their involvement, LPs earn fees for each transaction and receive ERC-1155 Liquidity Tokens (LT).
The initial LP of a pool, known as the pool creator, sets the pool's initial parameters, similar to Uniswap.[15]
Technology
The AMM
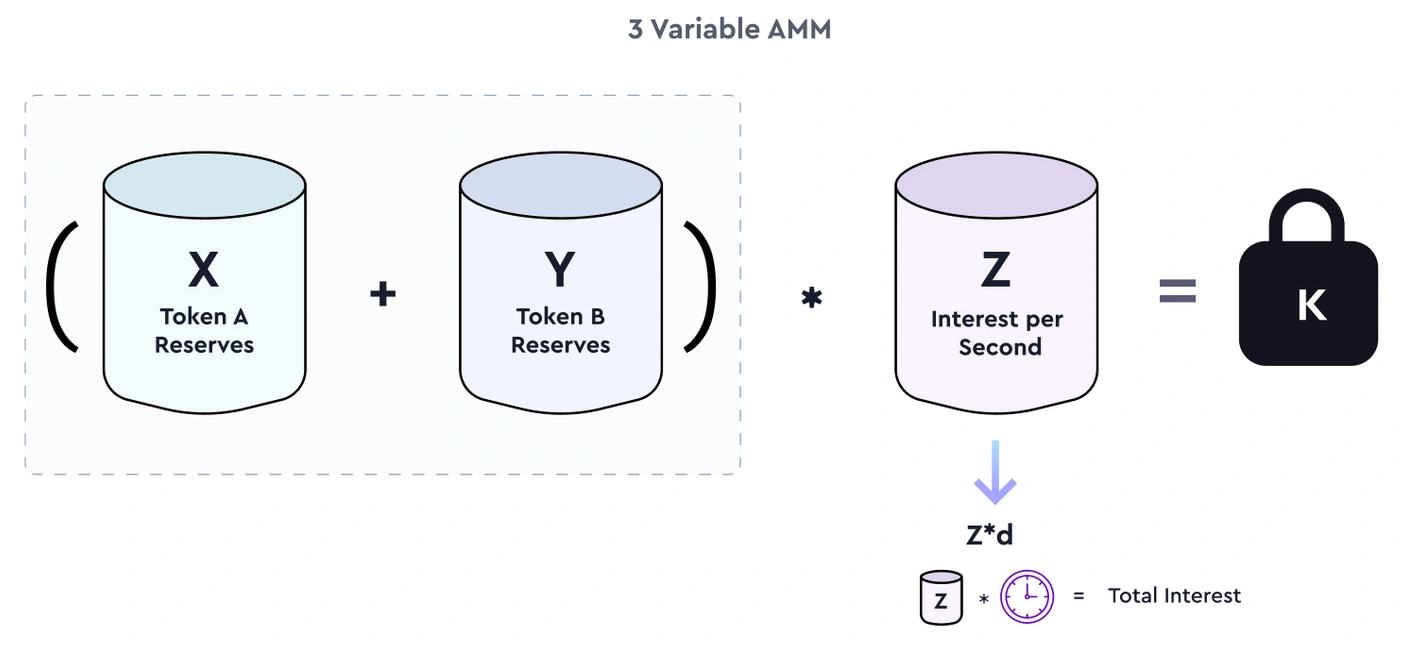
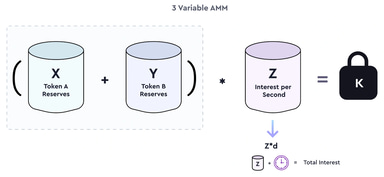
Timeswap utilizes a DW-CSPMM, enabling permissionless lending/borrowing pools for ERC-20 tokens. Participants interact with this AMM to discover interest rates.
The formula includes variables X, Y, Z, and K, with d influencing the AMM's behavior. The TP determines borrowing ratios, impacting market dynamics.
Timeswap's AMM is duration-weighted, ensuring interest payments only apply during an interaction. It comprises two main components: the Constant Sum Component ((X+Y)) and the Constant Product Component ((X+Y)*Z), facilitating overcollateralization and interest rate discovery.
Flexibility allows users to adjust risk-return profiles, influencing APR for lending or borrowing. Time decay is addressed to prevent impermanent loss.
Y and Z pools, representing interest rates and collateral factors, remain stable over time, mitigating losses for liquidity providers.[16][17]
Tokenomics
TimeSwap Token ($TIME)
The TIME token serves as an incentive mechanism for Timeswap protocol participants, including Lenders, Borrowers, and Liquidity Providers. It has a total supply of 1,750,000,000.
Users receive non-transferable TIME tokens during the premine phase, redeemable for TIME tokens during the Token Generation Event (TGE). There is a 1:1 claim ratio with no vesting schedule during the TGE, scheduled tentatively for Q1 2024.[18][19]
Native Tokens
Timeswap utilizes a simplified system of native tokens for precise accounting within the protocol. In Timeswap V2, there are three native tokens, which have been standardized as ERC-1155 NFTs for improved contract simplicity and user experience.[20]
Collateral Claim Tokens (CCT)
Timeswap employs Collateral Claim Tokens (CCT) as a means of tracking collateral for borrowers. Borrowers receive CCT as a receipt when they use collateral to obtain an asset, serving as proof of their locked collateral until the debt is repaid. However, CCT can only be utilized before the loan maturity date. Once the loan matures, CCT becomes obsolete and holds no value.[20]
Bond Token (BT)
Bond Tokens (BT) represent a lender's principal and yield. They can be redeemed before or after maturity, with a slight reduction in yield upon early exit. Holding both a Collateral Claim Token (CCT) and a BT indicates a neutral position.[20]
Liquidity Token (LT)
The Liquidity Token (LT) represents liquidity providers' share of the pool's liquidity. Exiting the pool requires burning LT, resulting in reduced yield for early exits. However, no yield reduction occurs if the withdrawal happens after maturity, encouraging providers to maintain liquidity in the pool with the option to exit at their discretion.[20]
TimeSwap
Commit Info
Edited By
Edited On
May 13, 2024
Feedback
Average Rating
How was your experience?
Give this wiki a quick rating to let us know!
Twitter Timeline
Loading
Media






REFERENCES
[1]
[2]
[3]
[4]
[5]
[6]
[7]
[8]
[9]
[10]
[11]
[12]
[13]
[14]
[15]
[16]
[17]
[18]
[19]
[20]