Subscribe to wiki
Share wiki
Bookmark
DGrid
The Agent Tokenization Platform (ATP):Build autonomous agents with the Agent Development Kit (ADK)
0%
DGrid
DGrid is a decentralized artificial intelligence (AI) inference network being developed for the Web3 ecosystem. The project aims to provide an open, modular, and verifiable infrastructure for intelligent computation, with a stated mission to make AI services trustless, accessible, and community-driven. [1] [2]
Overview
DGrid is a decentralized AI infrastructure project that aims to connect AI model supply with application demand while addressing issues related to fragmentation, centralized control, and limited auditability in existing AI systems. It is designed to support both Web3 and traditional AI use cases by providing a unified framework for accessing large language models and AI agents with verifiable execution. The platform is structured around a multi-layer architecture that combines decentralized routing and verification, an open market for models and agents, and token-based governance through an AI-focused DAO. Core components include community-operated inference nodes, a standardized RPC access layer, a proof-of-quality mechanism for result verification, and on-chain billing and data availability to support transparent settlement and accountability. [1] [9] [10]
Key Features
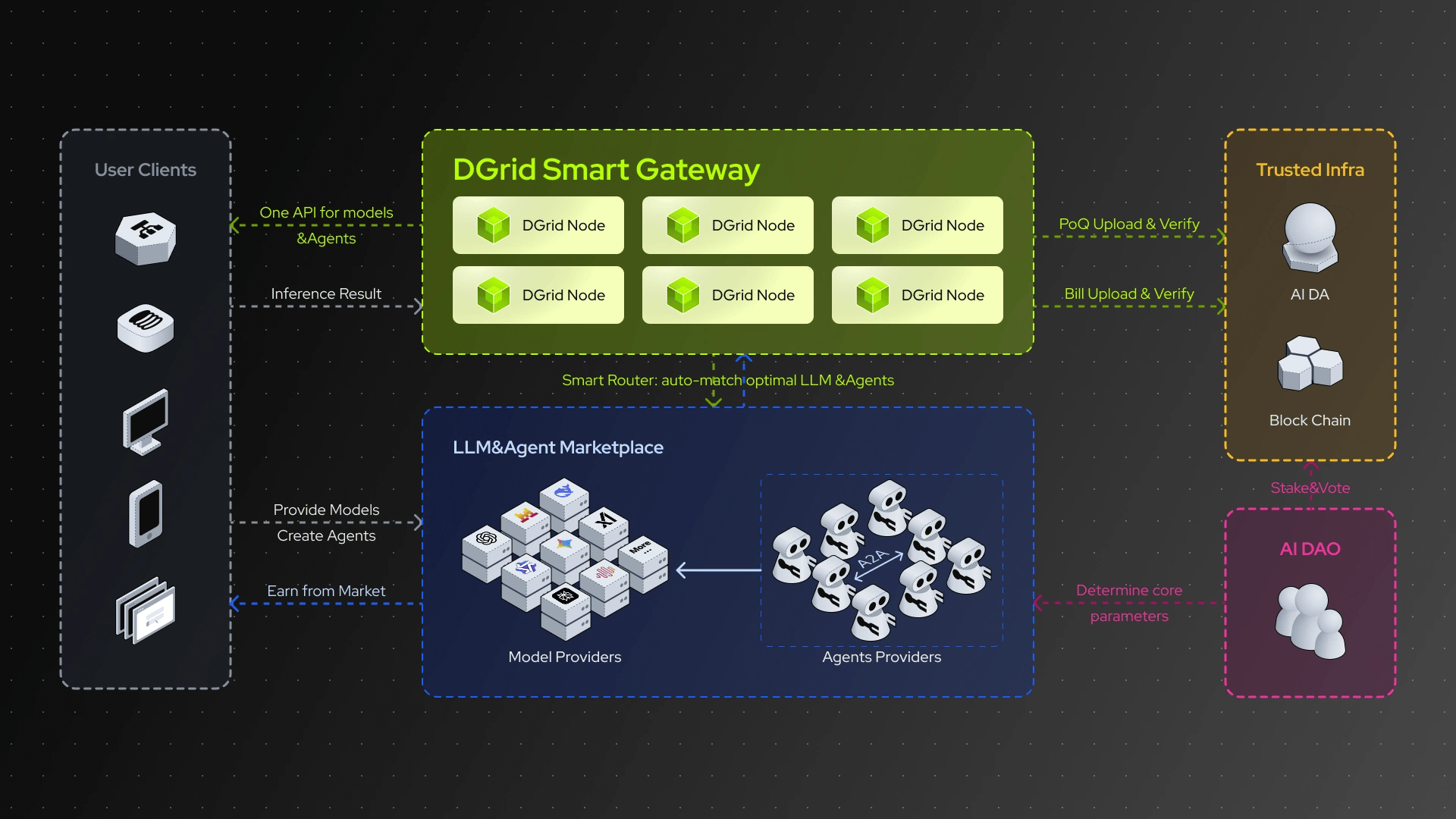
- Decentralized Routing and Verification: DGrid provides a unified API that allows developers to access multiple models and agents through a single interface, with tasks routed automatically based on factors such as performance, cost, and historical reliability. Output validity is assessed using a proof-of-quality mechanism to support traceability and resistance to censorship.
- LLM and Agent Marketplace: The network supports an open marketplace where model providers and AI developers can list models or agents, set pricing, and receive compensation directly from users. High-performing models and agents can be tokenized to reflect longer-term usage and demand.
- Decentralized Inference Nodes: Community-operated nodes execute inference tasks, host different classes of models based on hardware capacity, and report performance metrics such as latency and compute usage. Distributing workloads across independent nodes reduces reliance on centralized infrastructure and supports geographic redundancy.
- DGridRPC Access Layer: A standardized JSON-RPC protocol enables consistent access to models and agents across the network, with request verification handled through cryptographic signatures to ensure authorization and prepaid execution.
- Proof of Quality (PoQ): A verification framework evaluates inference outputs using criteria such as accuracy alignment, consistency across nodes, and compliance with output requirements. Quality scores and execution records are made verifiable on-chain to allow users to confirm result integrity.
- Billing and Data Availability: On-chain billing contracts automate fee calculation and settlement based on compute usage and latency, while a decentralized data availability layer stores inference and billing records for auditability.
- Security and Accountability: The network enforces fixed execution environments for models, resource usage limits, on-chain logging of critical activities, and automated penalties for misbehavior. Governance decisions related to security parameters and upgrades are managed through token-based voting. [8] [11] [12]
Use Cases
- Integrating trustless AI and LLM functionalities into decentralized applications
- Powering in-app coding assistants or development tools
- Developing automated customer service bots for decentralized services
- Creating AI-driven tools for specialized fields, such as medical analysis [2]
- Enabling creative applications like AI-powered novel continuation or content generation [1]
- Providing a platform for AI developers and researchers to monetize their models in an open marketplace
- Allowing individuals to earn rewards by contributing spare computing resources to the AI inference network [2]
Road Map
- 2025 Q1–Q2 (Infrastructure Construction): Development of core network modules, including DGridNode, GridRPC, and quality verification mechanisms; design of the proof-of-quality consensus approach, network architecture, economic framework, and node presale module.
- 2025 Q3–Q4 (Testnet): Release of the official website and whitepaper, completion of seed financing, deployment of DGridNode Validator Node V1, and initiation of node presales.
- 2026 Q1–Q2 (Mainnet Launch and Expansion): Launch of the mainnet, release of GridRPC with integration of enterprise-grade models, activation of node mining and incentive pools, multi-chain payment support, and onboarding of ecosystem projects.
- 2026 Q3–Q4 (Governance and Ecosystem Expansion): Introduction of node staking, activation of on-chain governance and voting through an initial AI DAO framework, and launch of the model and agent marketplace alongside the DGrid browser.
Tokenomics
$DGAI is the native utility token of the DGrid.AI ecosystem, used to support value exchange, incentives, and governance within its decentralized AI inference network. Issued as a BRC-20 token, it is compatible with BNB Chain and other EVM-compatible blockchains, enabling interoperability with wallets, exchanges, and smart contracts. The total supply is fixed at 1 billion tokens with no post-launch inflation, and the token incorporates EIP-2612 (permit) functionality to allow gasless approvals for inference payments and staking-related operations. [5] [12]
Allocation
- Nodes: 50%
- Community: 20%
- Team Incentives: 10%
- Investors: 10%
- Airdrops: 5%
- Initial Liquidity: 5% [6] [12]
Token Utilities
- Powering the AI DAO for community governance over the protocol.
- Being used for settlement and reward distribution within the node incentive economy.
- Facilitating revenue and value capture within the planned LLM & Agent Marketplace. [2]
- Enabling a "dual-token rewards" system for holders of the DGrid Genesis Pass. [1]
Governance
DGrid’s network governance is conducted through the DGAI staked, linking governance influence to active participation in the network. [7]
Backers and Investors
See something wrong?
The Agent Tokenization Platform (ATP):Build autonomous agents with the Agent Development Kit (ADK)
