Subscribe to wiki
Share wiki
Bookmark
Treehouse Finance
The Agent Tokenization Platform (ATP):Build autonomous agents with the Agent Development Kit (ADK)
0%
Treehouse Finance
Treehouse Finance is a decentralized fixed income protocol that introduces Treehouse Assets (tAssets) and Decentralized Offered Rates (DOR) to establish on-chain interest rate benchmarks for digital assets. It utilizes staking, arbitrage mechanisms, and a consensus framework to unify fragmented rates and support the development of rate-based financial products. [1]
Overview
Treehouse Finance is a decentralized protocol focused on fixed-income products in digital assets. It introduces two core components: Treehouse Assets (tAssets), such as tETH, and Decentralized Offered Rates (DOR), a system for establishing benchmark interest rates. Users deposit ETH or liquid staking tokens to mint tETH, which helps unify fragmented on-chain ETH yields and supports the DOR rate-setting process. Governance initially remains with the development team, with plans to transition to token-based governance over time. Treehouse emphasizes smart contract-based processes to reduce inefficiencies and maintain adaptability in a changing blockchain environment. [2] [3]
Architecture
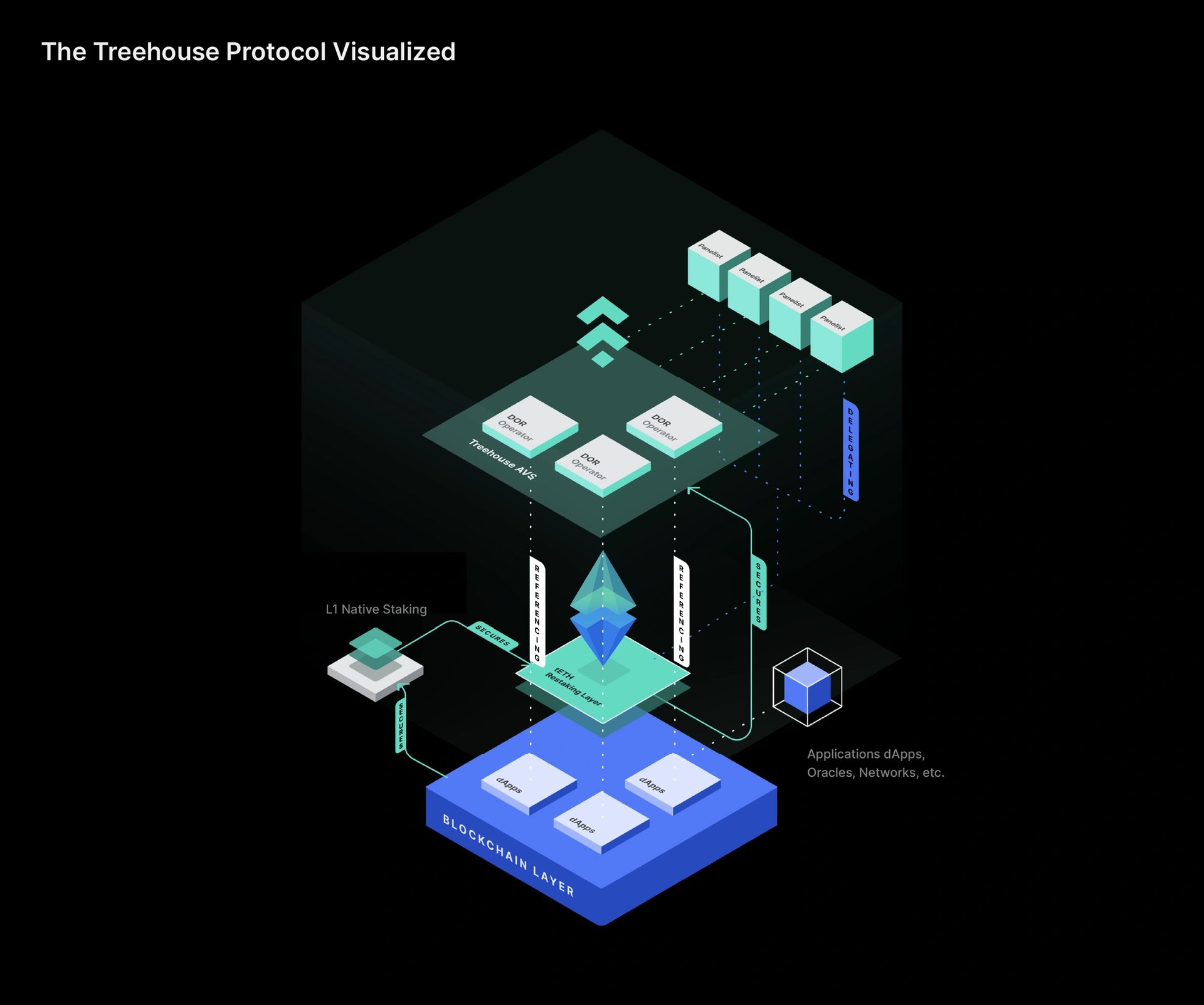
Treehouse operates through a decentralized architecture centered around tAssets and the Decentralized Offered Rate (DOR) system. tAssets, such as tETH, are liquid staking tokens designed to generate real yield above the base risk-free rate through interest rate arbitrage. DOR is a consensus mechanism for establishing reference interest rates, relying on input from various participants.
Operators initiate and maintain DOR feeds, with Treehouse acting as the first Operator to launch the Treehouse Ethereum Staking Rate (TESR) Curve. Panelists, selected entities with proprietary models and Treehouse’s software, supply rate data or forecasts. Only pre-approved Panelists are currently permitted to ensure protocol integrity. Referencers are entities that incorporate DOR feeds into their financial products, utilizing the rates for pricing or settlement purposes. Delegators assign their tAssets to Panelists for DOR-related duties, retaining asset ownership while granting operational authority to the selected Panelists. [12]
DOR
Decentralized Offered Rates (DOR) are benchmark interest rates generated through the Treehouse Protocol, designed to produce objective, verifiable reference rates for financial products in digital asset markets. Unlike traditional benchmarks influenced by subjective inputs or centralized control, DOR relies on transparent, on-chain consensus grounded in measurable data such as trading activity or index formulas.
The protocol addresses shortcomings in legacy systems, such as LIBOR, which suffered from manipulation, and SOFR, which introduces centralization risks due to its reliance on a single publishing entity. Treehouse improves on these models through three key principles: accuracy, decentralization, and agnosticism.
Accuracy is maintained using game theory, where Panelists stake capital and are rewarded or penalized based on the reliability of their input. Decentralization is supported by open participation and transparent rate calculations, allowing anyone with relevant expertise to contribute or delegate. The framework is agnostic, meaning it can be used to generate reference rates across a broad range of assets, from cryptocurrency yields to real-world financial indicators, such as mortgage rates. [4]
Ethereum Staking Rate
The Ethereum Staking Rate (ESR) represents the native “risk-free” yield within the Ethereum ecosystem, derived from its staking dynamics. Through the Treehouse Protocol, ESR is calculated using a transparent, tamper-resistant framework, allowing for the construction of an ESR curve. This curve provides a structured view of staking yields, serving as a foundation for developing financial instruments such as staking rate futures and swaps, which can be used for risk management and return optimization within the Ethereum ecosystem. [5]
tAssets
Treehouse Assets (tAssets) are liquid staking tokens designed to address fragmented interest rates across blockchain networks by enabling unified and yield-optimized participation. These tokens generate yield through interest rate arbitrage above the base staking rewards, while remaining usable in decentralized finance (DeFi) applications. Risk associated with tAsset strategies is actively managed to maintain yield performance with reduced exposure. The initial version, tETH, targets Ethereum’s rate fragmentation and also contributes to the cryptoeconomic security of the Treehouse Actively Validated Service (AVS) through token holdings. [6] [7]
tETH
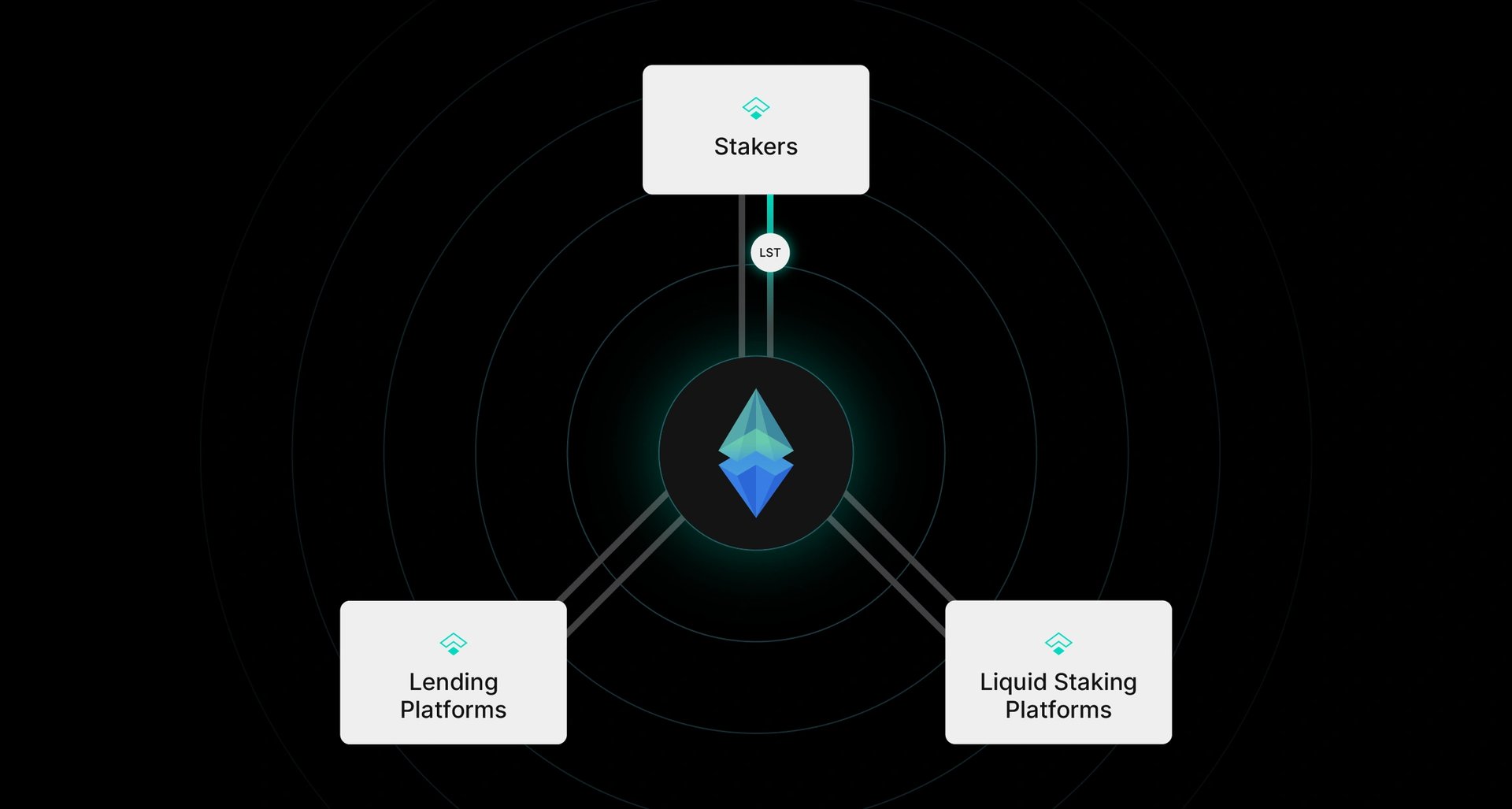
tETH is a liquid staking token that aims to unify fragmented on-chain ETH interest rates by enabling interest rate arbitrage above Ethereum’s native Proof-of-Stake (PoS) rewards. While earning real yield, tETH holders can continue using the asset within DeFi ecosystems. tETH also plays a foundational role in supporting Treehouse’s Decentralized Offered Rates (DOR) by contributing to its cryptoeconomic security.
tETH operates by reallocating ETH or liquid staking tokens into lending and staking platforms where arbitrage opportunities exist. As market participants borrow more ETH and interest rates rise, tETH helps balance borrowing and lending activity, aligning them with the Ethereum staking rate. This convergence enhances on-chain rate efficiency and lays the groundwork for fixed-income derivatives, including interest rate swaps and options.
The token also expands access to arbitrage strategies that were traditionally limited to institutional actors, enabling broader participation in fixed-income activities. By doing so, tETH supports the development of stable, predictable financial markets in the cryptocurrency space and serves as a core mechanism in the Treehouse Protocol's broader rate-setting framework. [8] [9]
Partnerships
See something wrong?
The Agent Tokenization Platform (ATP):Build autonomous agents with the Agent Development Kit (ADK)
