Subscribe to wiki
Share wiki
Bookmark
Liquid Staking
The Agent Tokenization Platform (ATP):Build autonomous agents with the Agent Development Kit (ADK)
0%
Liquid Staking
Liquid Staking is a staking solution in blockchain and cryptocurrency that allows users to stake their tokens while keeping them liquid and tradable. It bridges the gap between staking, which involves locking up tokens for network validation and earning rewards, and maintaining liquidity, which enables users to freely trade their assets. [1][2]
Overview
Liquid staking is a type of staking that allows users to earn staking rewards without locking up their tokens. It involves storing funds in DeFi escrow accounts. Users can still access their funds during the staking period, which makes the protocol liquid. [2][3][7]
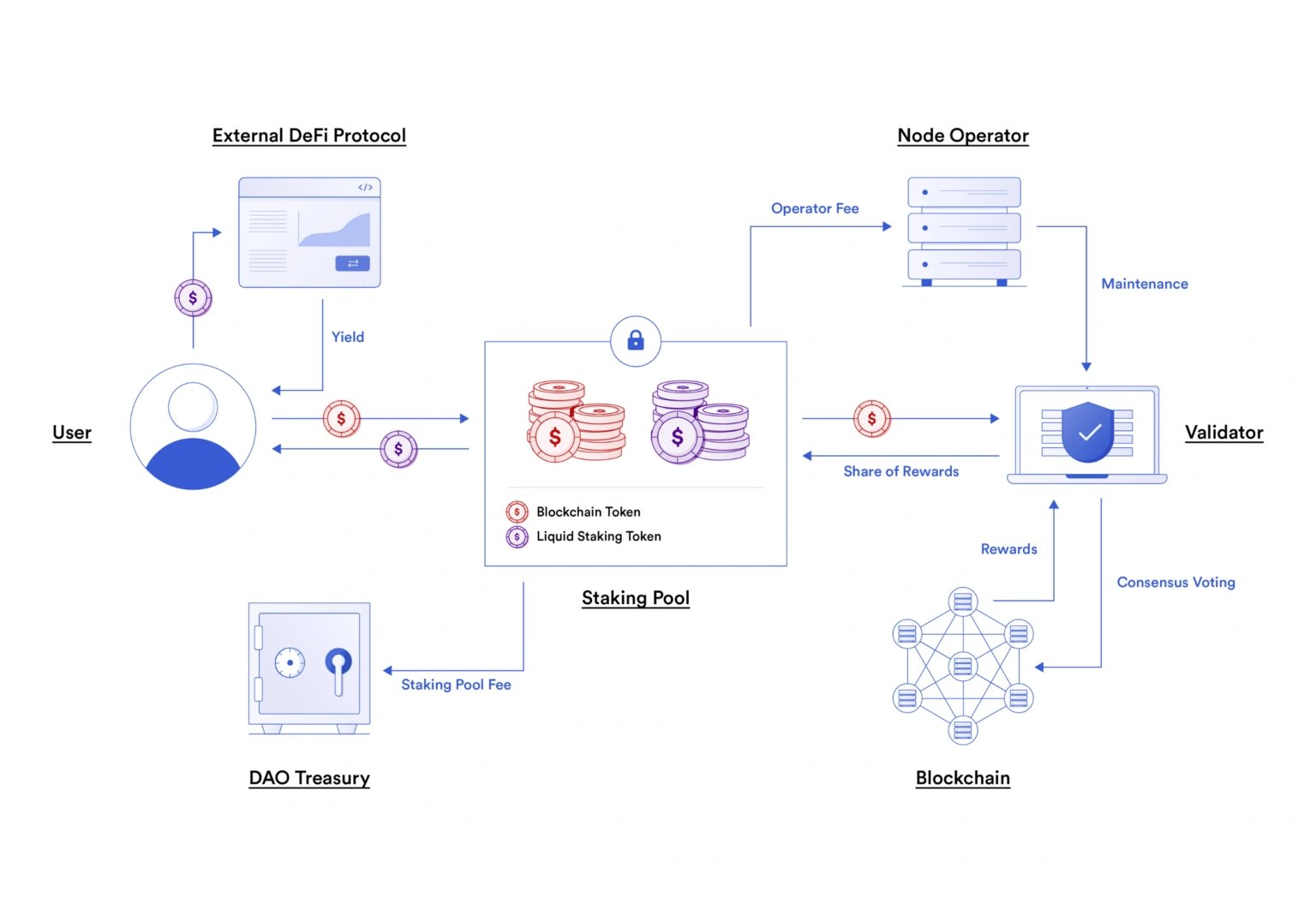
Staking is a crucial mechanism in PoS-based blockchain networks, where users lock up a certain amount of cryptocurrency as collateral to participate in the network's consensus mechanism. In return, they receive rewards in the form of additional cryptocurrency tokens. However, traditional staking mechanisms often involve a significant trade-off: once a user's tokens are staked, they are typically locked up for a fixed period, often ranging from weeks to months, making them illiquid and inaccessible during that time. Liquid staking seeks to address this liquidity issue by introducing a layer of abstraction and financial instruments that represent the user's staked assets. These instruments, often referred to as "staking derivatives" or "liquid tokens," can be traded and utilized while the underlying tokens remain staked in the network's consensus mechanism. [4][5][6]
Liquid staking mechanisms vary across blockchain networks and DeFi platforms, but it works through the representation of staked tokens that can be used in liquidity pools, decentralized exchanges (DEXs), or other DeFi. This is done by issuing liquid staking tokens (LSTs) to users who stake their tokens. LSTs are tokens that represent the staked tokens, and they can be traded, transferred, and used in other DeFi applications. It works by pooling users staked tokens and delegating them to validators on the underlying blockchain. The validators are responsible for securing the network and processing transactions. In return, they earn staking rewards. The liquid staking platform then distributes these rewards to the LST holders. Liquid staking enables users to access liquidity while also staking their tokens.[6][7][8][2]
Liquid Staking Platforms
Lido Finance
Lido Finance is a DeFi platform that offers liquid staking for Ethereum. Users can stake their ETH with Lido and receive staked Ether (stETH) tokens in return. These stETH tokens represent their staked ETH, continue to earn staking rewards, and are tradable in DeFi applications or exchanges. Users can easily convert stETH back to ETH, ensuring liquidity. Lido supports Ethereum, Polygon, and Solana and provides 4.4% - 6.7% APY for its users. By staking ETH, MATIC, and SOL tokens, users get stETH, stMATIC, and stSOL tokens. Lido charges 10% fees and the staking period is 1 year, however, there is no minimum staking amount limit, and it has a daily payout feature. [9]
Lido Finance also deployed Lido V2, which introduces new features like dynamic fees and improved validator selection. Lido V2 brings two vital components to the Lido protocol: withdrawals and the staking router. Lido Finance also announced plans to expand its liquid staking offering to other blockchains like Solana and Cosmos.[12]
Rocket Pool
Rocket Pool is a decentralized Ethereum staking platform that allows users to stake their ETH and receive tradable rETH tokens in return while contributing to Ethereum network security. It offers liquidity and rewards, and it's non-custodial with decentralized governance. Rocket Pool is also one of the largest liquid staking platforms and it is suitable for community-driven staking. The protocol itself is owned and run by a community and it has a strong online presence on Reddit. It holds over $1.8 billion total value locked (TVL) as of August 2023. Its unique feature is that one can stake as much as 0.01 ETH and start earning rewards. [9]
Rocket Pool launched its decentralized node infrastructure (rETH dApp) enabling anyone to run a Rocket Pool node. [13]
Frax Ether
The Frax Ether system consists of three core components: frxETH, sfrxETH, and the Frax ETH minter. [10][17]
- Frax Ether (frxETH) is a liquid ETH staking derivative and stablecoin system designed to uniquely leverage the Frax Finance ecosystem to maximize staking yield and smoothen the Ethereum staking process for a simplified, secure, and DeFi-native way to earn interest on ETH.
- sfrxETH is the staked version of frxETH that accrues staking yield. All profit generated from Frax ETH validators including staking rewards, transaction fees, and MEV (maximal extractable value), are distributed to sfrxETH holders. Users can exchange their frxETH for sfrxETH at any time by depositing it into the sfrxETH vault.
- The FraxETH minter contract mints frxETH when it receives ETH deposits. Whenever a deposit pushes the minter balance over 32 ETH, the contract automatically spins up a new validator.
sfrxETH (Staked Frax Ether) is eligible for the Ethereum staking yield that comes from validators. It is an interest-bearing token where the exchange rate of frxETH per sfrxETH always increases, so it does not keep a 1:1 peg with frxETH but its price is indexed. [11]
These tokens can then be utilized as collateral to mint various stablecoins, such as USDC, USDT, and more.[9] Users can deposit their Ethereum (ETH) into the Frax ecosystem to participate in Ethereum staking. In return for their staked ETH, they receive Frax Staked Ethereum tokens. These tokens represent their staked ETH holdings and are often used within the Frax ecosystem. The sfrxETH tokens may be tradable or used in various DeFi applications while still earning staking rewards from the underlying ETH deposits.
With the recent launch of the Frax Share (FXS) token vesting schedule, the broader Frax ecosystem might see more focus on core components like Frax Pro (algorithmic stablecoin) and less emphasis on side projects like frxETH.[14][15]
Coinbase Prime
Coinbase Prime liquid staking allows investors to stake their Ethereum (ETH) assets while maintaining liquidity. This is done by partnering with Liquid Collective, a decentralized staking protocol. When users stake ETH on Coinbase Prime, the ETH is deposited into Liquid Collective's smart contract. Liquid Collective then stakes the ETH on the Ethereum network. In return, users receive LsETH tokens, that can be traded, transferred, and used in DeFi applications. The minimum staking amount limit on Coinbase Prime is 0.1 ETH, and users can cash their rewards daily or quarterly.[9]
StaFi Protocol
StaFi Protocol offers liquid staking solutions for multiple blockchains, including Ethereum, Polkadot, and more. Users can stake their tokens and receive rTokens in return, which are tradable and liquid.
Harmony
Harmony, a blockchain platform, has introduced a liquid staking mechanism called "Staking as a Service" (SaaS). Users can stake their ONE tokens and receive sONE tokens in return, which are liquid and can be traded or used in DeFi.
Liquid Staking Tokens
Liquid Staking Tokens (LSTs) or Liquid Staking Derivatives (LSDs) are blockchain receipts that prove ownership of a staked digital asset and are pegged to the value of the initial asset staked. LSTs are suitable for varying purposes within the DeFi ecosystem. They can be traded, swapped, and used as collateral for borrowing other crypto tokens. stETH (Lido) is the liquid staking token representing Ether and is one of the most popular LSTs.[7]
LST architecture models
Here are the 3 main LST architecture models.[16]
- Rebase tokens: tokens that automatically adjust their balance in response to deposits and rewards. This process, known as rebasing, typically happens daily. During rebasing, there is no visible transactional activity for the token holders.
Examples of such tokens include Lido's stETH and Binance's BETH, both of which are classified as rebase tokens. This type of LST is designed to be user-friendly, as the balance of your LST increases in line with your staking activities. - Rewards-bearing tokens: tokens that increase in value over time, with the value and rewards determined by the changing exchange rate between the token and the staked asset. The quantity of LST stays the same, but its rate varies. This single-token model is convenient but less straightforward than rebase tokens. Holders benefit from rising rewards, examples of which include rETH, cbETH, swETH, osETH, and ETHx.
- Wrapped tokens: certain LSTs are available in wrapped versions. After wrapping, these tokens no longer experience automatic balance adjustments and become reward-bearing tokens. Unlike rebasing, which occurs without any transactions, changes in the balance of wrapped tokens are achieved through actions like minting, burning, or transferring. The rewards are integrated into the exchange rate. Wrapped LSTs, such as stETH and BETH, often see higher popularity and volume in DeFi and trading sectors because they aren't subject to rebasing.
How Liquid Staking Works
The process of liquid staking typically involves several key components:
- Staking Pool: Users delegate their tokens to a staking pool, which is responsible for participating in the blockchain's consensus mechanism on behalf of its members. The staking pool manages the staked assets and distributes staking rewards proportionally to the pool's participants.[8]
- Staked Asset Tokens: When a user delegates their tokens to a staking pool, they receive a corresponding number of staked asset tokens (e.g., liquid staking tokens) that represent their stake in the pool. These tokens are fungible and can be freely traded or utilized in various DeFi (Decentralized Finance) applications.[1][7]
- Yield Generation: The staking pool generates rewards through its participation in the blockchain's consensus mechanism. These rewards are then distributed to participants in the form of additional staked asset tokens or native tokens, depending on the specific implementation.[8]
- Redemption: At any time, users can redeem their staked asset tokens for the original staked tokens, plus any accrued rewards. This process is typically facilitated by the staking pool, which may charge a fee for this service.[7]
Benefits
Liquid staking offers several advantages to participants and the broader blockchain ecosystem:
- Liquidity: Users can access their staked assets at any time, providing greater flexibility and liquidity compared to traditional staking, where tokens are locked up for a predetermined period.[5][1]
- Capital Efficiency: Liquid staking allows users to maximize the utility of their assets by simultaneously participating in staking and engaging in DeFi activities, such as lending or yield farming.[1][7]
- Market Efficiency: Liquid tokens can be traded on secondary markets, which can lead to price discovery and improved market efficiency for staked assets.[8][6]
- Increased Participation: By reducing the barriers to entry and exit, liquid staking can attract a broader range of participants to PoS networks, potentially increasing network security.[8]
Challenges and Risks
While liquid staking offers numerous benefits, it also presents challenges and risks:
- Smart Contract Risks: Liquid staking platforms rely on smart contracts, which can be vulnerable to exploits or bugs. Users must be cautious when interacting with these contracts.
- Centralization: Staking pools may become centralized if a few large pools dominate the network, potentially leading to centralization risks.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: The treatment of liquid staking tokens under various regulatory frameworks is still evolving, which could lead to legal and compliance challenges.
- Slashing Risks: Users who delegate their tokens to staking pools must be aware of potential slashing risks, where a portion of their staked assets may be forfeited in the event of malicious behavior by the pool.[5][2]
See something wrong?
The Agent Tokenization Platform (ATP):Build autonomous agents with the Agent Development Kit (ADK)