订阅 wiki
Share wiki
Bookmark
IOTA
0%
IOTA
IOTA 是一个公共分布式账本,它使用称为 Tangle 的 有向无环图 (DAG) 结构来存储交易。它专为物联网 (IoT) 设计,是一种 加密货币,可促进机器和设备之间安全且无费用的微交易。 [2]
概述
IOTA 是一个基于 区块链 的公共基础设施,成立于 2015 年,旨在支持开发者、企业和政府之间安全、可扩展和可验证的交互。它采用双层架构,第一层 支持基于 Move 的 智能合约,专注于资产安全和并行交易处理。第二层 提供与 以太坊 的 EVM 和 Solidity 的兼容性,以利用现有的 智能合约 工具。IOTA 使用 委托权益证明 (DPoS) 共识机制 来高效验证交易,同时最大限度地减少能源消耗。其代币 IOTA 可以被分成更小的单位,称为 NANOs,网络交易需要以 IOTA 支付 gas 费用。该平台旨在通过其灵活的虚拟机架构和多链支持,实现现实世界的应用和可互操作的数字经济。 [3]
技术
Tangle
Tangle 是 IOTA 的基础技术,其特点是 有向无环图 (DAG) 结构。与传统的 区块链 不同,在区块链中,交易被分组到 区块 中并按线性顺序排列,而 IOTA 的交易则以网络状结构相互连接。该网络采用 工作量证明 (PoW) 机制进行操作。
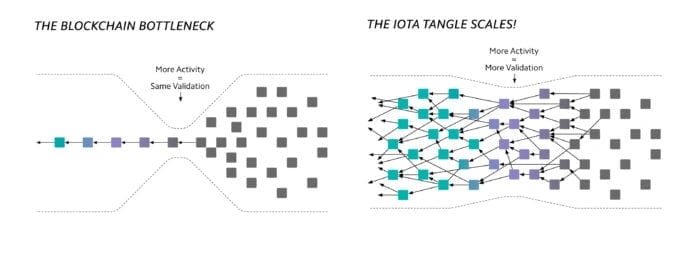
Tangle 中的每个用户在发送其交易之前,都会验证之前的两个交易,只需进行最少的计算工作,而不是依赖于中心化的 挖矿 农场来验证交易 区块。这意味着交易的唯一“成本”是验证这两个过去交易所需的一小部分电力,从而无需矿工设置交易费用。
Tangle 的设计缺乏 区块,允许立即进行交易验证。交易并行处理,从而实现近乎即时的确认。在这个系统中,每个新交易都会确认前两个交易,从而确保分散且可扩展的网络。 [4] [5]
网络弹性
IOTA的Tangle网络旨在抵抗量子计算威胁和51%攻击。与传统的区块链不同,要成功地对IOTA发起双重支付攻击,不仅需要大量的计算能力,还需要完全了解网络,并与许多节点合作来传播恶意活动。由于节点之间的连接是私有的,网络拓扑结构是模糊的,这使得攻击者难以协调此类行动。即使攻击开始,网络也能迅速检测到异常情况并在损害发生前做出反应。[3]
抗量子性
IOTA 使用 Winternitz 基于哈希的签名,而不是椭圆曲线密码学,这使得 IOTA 能够抵抗量子计算。IOTA 采用基于哈希的函数,因为它们在面对量子威胁时提供了更高的安全性。 [8]
Move
IOTA Move 是一种 智能合约 语言,旨在通过使用基于对象的模型而非全局共享状态来解决性能、可扩展性、成本和安全问题。这允许并行交易执行,从而减少拥塞和费用。Move 语言在设计时考虑了安全性,并受到 Rust 的影响,具有严格的类型和编译器检查,可以在部署前捕获常见的编程错误,从而防止重入和未经授权的资产访问等漏洞。在 IOTA Move 中,原生和自定义代币被统一视为帐户拥有的对象,从而消除了复杂的审批流程并增强了用户控制。虽然其开发者工具不如 Solidity 成熟,但 Move 的安全性和错误检测功能可以实现更安全和创新的合约开发。IOTA 提供 Move 和 EVM 智能合约 选项,让开发者可以在 Move 的安全性和可扩展性或 EVM 的熟悉性和易于迁移之间进行选择。 [14]
IOTA 身份
IOTA 身份框架为个人、组织和设备提供去中心化和可验证的数字身份,作为 IOTA 生态系统中的信任层。它支持 IOTA 特定的和与 DLT 无关的标准,与去中心化身份的全球协议保持一致。对于个人而言,它支持自主身份,使用户能够控制其数据并允许选择性披露,而无需中心化中介。
组织可以使用该框架来满足 GDPR 等监管要求,方法是将数据所有权委托给用户,并集成可验证的凭证,用于 KYC 和 AML 等流程。对于设备,物联网身份为每个设备分配一个唯一的、可验证的身份,能够证明其功能并在 IOTA 账本上记录操作,从而支持自动化和安全交互。该框架为跨各个部门管理数字身份提供了灵活且可互操作的基础设施。 [15]
产品
IOTA EVM
IOTA EVM 是首个完全 EVM-兼容的 智能合约 链,集成到 IOTA 主网 中,结合了 IOTA 的可扩展和安全基础设施与 以太坊虚拟机 (EVM) 兼容性。它实现了快速、可扩展和可组合的 智能合约,具有原生随机性、并行处理和使用 Solidity 的无缝互操作性等功能。该平台支持高级功能,如用于跨链交互的魔法智能合约和无桥代币转移,允许在 智能合约 代币和原生 IOTA 代币之间轻松转换。
IOTA EVM 与 LayerZero 集成,用于跨链连接,旨在创建一个统一的 Web3 生态系统,支持常见的 EVM 工具,如 MetaMask 和 HardHat,同时保持高网络正常运行时间和强大的安全性,并由 Zokyo 审计。它是可扩展、高效和安全的 智能合约 执行的基础,具有模块化和内置的 预言机 随机性,促进 现实世界资产 的代币化和无缝的多链交互。 [16] [17]
Rebased Mainnet
IOTA Rebased 是升级后的 IOTA 主网,它为 IOTA 网络上的去中心化应用程序引入了一个经过彻底改造和优化的基础。此更新包括新的工具和资源,例如改进的钱包和仪表板,用于资产管理、Rust 和 TypeScript 中的开发者 SDK、节点 API、命令行界面以及对 Move 编程语言的支持。其他功能包括用于简化代币使用的 IOTA Gas Station、自主身份解决方案以及用于实时交易跟踪的区块链浏览器。此次升级还引入了 IOTA EVM 桥和 EVM 浏览器,以实现 IOTA 的 Layer 1 与其他网络之间的互操作性,标志着该项目在可扩展性和跨链功能开发方面的一个重要里程碑。 [18]
TWIN
TWIN是一个基于IOTA技术的去中心化数字基础设施,旨在实现全球供应链中实时、可验证的数据共享。它支持可扩展、可互操作的贸易生态系统,具有自主身份、数字产品护照等功能,并符合Gaia-X等国际标准。TWIN旨在提高透明度、信任度和效率,采用开放式模块化基础设施、分布式账本技术和智能合约,以促进贸易网络中的安全数据交换和合规性。它为东非的TLIP等项目提供支持,并支持更广泛的倡议,包括边境贸易和新鲜农产品供应链,旨在创建一个全球互联的、可互操作的贸易生态系统网络。[19]
IOTA 代币
IOTA 网络的本地资产称为 IOTA。在 IOTA Rebased 启动时,46 亿个 IOTA 代币从之前的 Stardust 网络迁移过来,并且每个 epoch 铸造 767,000 个新代币,从而产生一个灵活的总供应量,该供应量根据通货膨胀和费用燃烧而变化。
IOTA 代币有四个主要功能:质押以参与委托权益证明,支付网络运营的交易费用,充当价值转移和智能合约使用的流动资产,并通过链上投票对协议事项进行治理。[6] [7]
MIOTA
MIOTA (兆IOTA) 是 IOTA 的 加密货币 的一个单位。1 MIOTA 等于 1,000,000 IOTA。它通常用于以更易于管理的方式表示大量的 IOTA。 [10]
代币分配
IOTA的代币供应在启动时已固定,总供应量和最大供应量为278万MIOTA,在单个创世交易中创建。该网络不依赖于挖矿,因此不会生成新的代币或分配挖矿奖励。该项目的创始人和开发者没有为自己预先分配代币;相反,他们像其他用户一样参与了众筹。
销售结束后,社区捐赠了一些代币,以建立和资助IOTA基金会,该基金会现在负责监督该项目的发展。代币后来在交易所上提供,以供更广泛的公众访问。 [10]
IOTA基金会 (IF)
2017年,早期的IOTA代币投资者捐赠了总代币供应量的5%,以支持持续开发并建立IOTA基金会。2018年,IOTA基金会在柏林正式注册为Stiftung(或基金会)。其主要任务是促进IOTA技术的研究、开发、教育和标准化。IOTA基金会是国际可信区块链应用协会(INATBA)的董事会成员。此外,它还是可信物联网联盟和移动开放区块链倡议(MOBI)的创始成员。这些协会旨在鼓励区块链和分布式账本技术在监管框架、物联网生态系统和移动领域的整合。 [3]
Shimmer 网络
Shimmer 网络于 2022 年 9 月 28 日启动,旨在测试和验证 IOTA 协议中的创新。该网络复制了 IOTA 协议,并专门使用其原生代币 SMR 运行。对 IOTA 协议的任何增强功能都会先在 Shimmer 网络上进行试验,然后再集成到 IOTA 主网中。
IOTA Stardust 代币化协议升级与 Shimmer 网络的启动同时推出。此升级在 Shimmer 网络上进行了社区验证和测试。
Shimmer 网络和 IOTA 协议上的 Stardust 升级框架的兼容性使其可以扩展并用作多链架构。开发人员可以利用这些功能来构建保持可组合性的去中心化智能合约。鉴于 Shimmer 在 Tangle 分布式账本技术 (DLT) 上运行,交易在其网络上使用其原生代币运行,并且 NFT 也是无费用且可扩展的。 [11]
争议
合作关系批评
2017年11月,有报道称IOTA与包括微软在内的多家大型公司建立了合作关系。然而,后来 выяснилось,这并非传统意义上的直接“合作”。实际上,微软和其他几家公司参与了IOTA开发的数据市场试点项目。在误解和澄清之后,IOTA受到了加密货币社区和媒体的一些批评。 [5]
Curl争议
IOTA使用SHA-3工作量证明(PoW)加密算法来安全地存储其交易,在概念上类似于比特币的SHA-256 PoW,尽管机制有所不同。然而,与许多传统的加密货币不同,IOTA网络中的节点不会因其努力而获得MIOTA代币作为奖励。这种方法引发了关于用户在没有此类激励措施的情况下运营节点的动机的担忧。
IOTA最初实现了一个名为Curl的哈希函数。然而,在2017年MIT和波士顿大学的研究人员指出其存在漏洞后,IOTA过渡到使用其他更广泛接受的哈希函数。漏洞发现后的辩论强调了在广泛采用加密算法之前彻底审查和同行评审的重要性。 [2]
Trinity Wallet Hack
2020年2月,IOTA基金会宣布其官方桌面钱包Trinity遭受安全漏洞攻击。该漏洞源于用于生成二维码的第三方库中的一个漏洞,导致未经授权的访问和部分用户的钱包被盗。
IOTA团队迅速建议用户更改密码并加强账户安全。此外,他们还推出了Trinity钱包的修补版本,以解决该漏洞。 [20]
电子克朗
2017年9月,瑞典中央银行(Riksbank)宣布通过电子克朗项目调查使用数字货币。该倡议源于对该国纸币和硬币使用量减少的担忧,尤其是在数字货币和支付方式在技术上不断发展的情况下。该项目旨在确定是否应以电子方式发行克朗,称为“电子克朗”。在提交给瑞典中央银行的33份提案中,只有19个组织被选中进行对话。IOTA基金会是这些选定的组织之一。 [6] [7]
投资
博世
2017年12月,博世集团的风险投资公司Robert Bosch Venture Capital GmbH (RBVC) 通过购买IOTA代币对IOTA进行了重大投资。此次合作旨在提升该技术的应用,并推动IOTA生态系统的发展。 [12]
ITIC
2018年1月,IOTA宣布与国际交通创新中心(ITIC)合作,旨在为自动驾驶汽车构建全球智能交通测试平台联盟。该合作计划建立一个基于开源协议和IOTA分布式账本技术的全球智能交通测试平台生态系统。 [13] [14]
Tangle EE
IOTA基金会于2020年2月11日与Eclipse基金会合作启动了Tangle EE(企业版)工作组。此次合作旨在通过为组织构建应用程序和探索行业范围的解决方案提供平台,从而支持企业采用IOTA的分布式账本技术。
Tangle EE专注于企业需求,特别是围绕应用层和协议层面的讨论。它目前负责监督两个主要的Eclipse项目:Tangle Identity,它实现了去中心化标识符和可验证凭证;以及Tangle Marketplaces,它使用IOTA的基础设施构建以数据为中心和基于交换的数字市场。 [8]
发现错误了吗?
