Kakarot
Kakarot is an L2 zkEVM developed in Cairo. It focuses on scaling Ethereum and introducing community-driven features like native account abstraction. Elias Tazartes and Clement Walter are the co-founders, co-CEOs, and co-CTOs of Kakarot. [1]
Overview
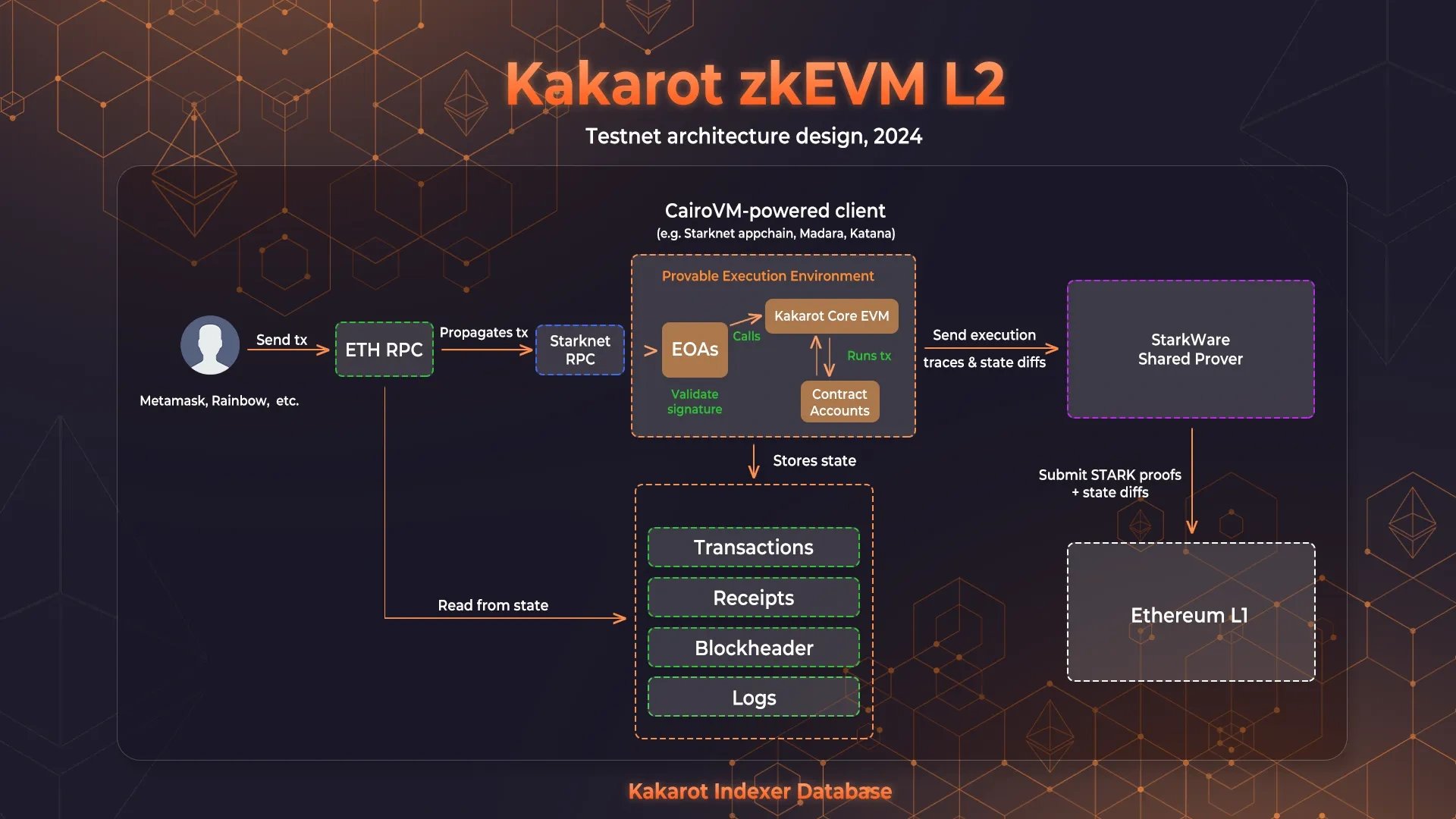
Created in October 2022, Kakarot is a zkEVM implemented in Cairo, the provable language utilized by Starknet and StarknetOS chains (also known as CairoVM chains or Starknet appchains). Serving as an Ethereum-compatible Layer 2 solution or zkRollup, Kakarot prioritizes compatibility and aims to innovate within the L2 space. It introduces native account abstraction to the EVM, leveraging Cairo's capability to generate execution traces and Stark Proofs. This allows Kakarot to process numerous transactions, consolidate them into a single proof, and verify them on Ethereum, effectively operating as an L2 zkEVM. [1][2]
In Kakarot zkEVM, the core EVM implementation operates on a StarknetOS chain powered by CairoVM, where EVM smart contracts are deployed as unique Starknet smart contracts. Users interact with Kakarot through an Ethereum-compatible RPC layer, shielding the underlying CairoVM chain from direct user interaction. This design ensures all Cairo execution traces are provable, allowing Kakarot to batch blocks and submit proofs to Ethereum Layer 1 using the Starkware Shared Prover (SHARP). Future implementations like Lambdaclass' Stark Platinum Prover promise enhanced security through multi-proof capabilities. [1][2]
Under the hood, each EVM smart contract and user-owned account (EOA) in Kakarot is represented as a Starknet smart contract, with specific mappings and functionalities transparent to users. Transactions are wrapped in Starknet transactions, maintaining integrity through provable processing via Cairo's signature verification. While Kakarot adopts Pedersen hash for state roots and MPT computations for efficiency and zk-friendliness, these details do not affect EVM compatibility at the functional level. [1][2]
CairoVM
The CairoVM is a virtual machine designed for provable execution. It serves as the core of Starknet, a Layer 2 validity rollup on Ethereum. By representing execution through polynomials, the CairoVM enables every transaction on Starknet to be validated using STARKs. This requires developers to use Cairo, the associated programming language, to build decentralized applications (dApps). [1][2]
Technology
Precompiles
Precompiles in Kakarot are predefined smart contracts with specific addresses that offer specialized functionalities. Unlike regular EVM bytecode, these contracts are executed directly by the Kakarot client using Cairo, aiming to handle computationally intensive tasks efficiently. They enable complex functions and facilitate interactions between Layer 1 (L1) and Layer 2 (L2) of Ethereum. Kakarot supports existing Ethereum precompiles and introduces additional precompiles tailored for L2 operations, allowing smart contracts to invoke them akin to Solidity function calls. [3]
Partnerships
Investors
Kakarot raised $1 million in pre-seed funding, and Starkware and Lambda Ventures led the investment round. Notable angels included Vitalik Buterin, Nicolas Bacca (Co-founder of Ledger), and Rand Hindi (CEO of Zama). [4]
Viper Network
On May 20th, 2024, Viper Network announced its first chain integration via a strategic partnership with Kakarot zkEVM. The collaboration aimed to offer trustless and high-performance access to Kakarot’s zkRollup technology through Viper’s decentralized infrastructure network. [5]
