Subscribe to wiki
Share wiki
Bookmark
XDC Network
The Agent Tokenization Platform (ATP):Build autonomous agents with the Agent Development Kit (ADK)
0%
XDC Network
XDC Network is an open-source blockchain protocol designed for enterprise use. It offers an EVM-compatible chain that enables enforceable smart contracts, making it well-suited to transform and decentralize the trade finance industry by tokenizing real-world assets and financial instruments. [1]
Overview
XDC Network was founded in 2017, with its community driven backbone, XDC Foundation, being established in mid 2021. The Foundation was created through a grant from XinFin, an enterprise ready hybrid blockchain, with the goal of increasing blockchain-based enterprise adoption. [2][3]
With its EVM compatibility, XDC Network provides the necessary speed, security, and trust to support a range of decentralized finance (DeFi) applications. This opens up possibilities for global, decentralized financial markets that operate 24/7, without any single central entity having excessive control or access. [1]
To achieve consensus, XDC Network employs a delegated proof-of-stake mechanism called XinFin Delegated Proof of Stake (XDPoS). This unique consensus mechanism ensures that the network operates with minimal energy consumption and remains highly resistant to spam attacks. [1][3]
Enterprise
The XDC Network welcomes enterprise participants with their experience, talent, and resources, offering a trusted environment for collaboration and development. By joining the network, enterprises gain access to the services and capabilities of the platform that supports a wide range of applications. [4]
Capabilities
Asset Tokenization
The XDC Network enables the transformation of real-world assets into digital assets through smart contracts. This facilitates access to existing and untapped capital markets, provides an eternal digital footprint for the asset, and enables borderless and barrier-free exchanges. Regulatory supported tokenization ensures compliance and regulatory standards are met. [4]
Digital Asset Composer
The XDC Network offers a user-friendly Digital Asset Composer that allows users to create digital assets without the need for coding knowledge. Users can develop smart contracts, entire DeFi protocols, fractionalized real-world assets (RWAs), and customizable utility non-fungible tokens (NFTs). [4]
ISO 20022
ISO 20022 is a global financial messaging standard, aiming to provide consistent, rich, and organized data. Financial institutions and corporations worldwide can leverage the XDC Network's ISO 20022 API Solution to send and receive financial data for cross-border and domestic payments. The simple API simplifies the migration to the new financial messaging standard, with the option to add instant settlement for digital assets within the financial messaging payload. [4]
Cross-chain Bridge
The XDC Network hosts multiple bridges that enable smart contracts to work seamlessly with other Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM)-compatible blockchains. This fosters multi-chain interoperability, aligning with XinFin's philosophy since its inception. [4]
Regulated Stablecoins
Financial institutions globally can participate in the XDC Network's regulated stablecoin ecosystem. This movement offers transparent and properly-reserved stablecoins, providing stability and reliability within the network. [4]
Custodial Solutions
To mitigate risks associated with trading digital assets on exchanges, the XDC Network offers custodial solutions that include collateral management and institutional custody. These solutions ensure the security and safekeeping of digital assets. [4]
Corporate to Bank Payments and Trade Finance Flows
The XDC Network serves as a channel for facilitating seamless movements of funds and trade finance flows on a digital ledger. It offers efficiency, transparency, and traceability in corporate-to-bank payment transactions. [4]
Compliance Solutions
The XDC Network provides blockchain applications with compliance solutions, including monitoring and tracing capabilities for illicit cryptocurrency activities. Additionally, it offers risk scoring, flagging, and verification services for digital asset addresses, ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements. [4]
Trade Finance
XDC Network is attempting to disrupt the trade finance industry by providing a trustless blockchain platform for scalable, efficient, affordable, and accessible settlement of tokenized assets. [5]
Trade finance involves financing the movement of goods and services globally. XDC Network offers a decentralized trade ecosystem with scalable settlement rails for various tokenized assets. It enables digitized bills of lading, supply chain automation, risk management solutions, new capital markets, and improved access for SMEs. Their aim is to overcome obstacles such as borders, settlement inefficiencies, and regulatory variations, create non-competitive landscapes and limit funding accessibility for SMEs. [5]
Affiliations
XDC Network has partnered with prominent trade organizations, including the International Trade and Forfaiting Association (ITFA) and the Trade Finance Distribution Initiative (TFDi). These collaborations aim to enhance liquidity and digitize trade documents, contributing to a more accessible and efficient trade finance landscape. [5]
Developers
The XDC Network is a blockchain designed to be enterprise-ready while remaining accessible to developers and creators. It offers a wide range of capabilities and use cases for building innovative projects. [6]
Capabilities
Consensus Mechanism
The XDC Network utilizes the Delegated Proof of Stake (XDPoS) consensus mechanism. XDPoS is highly efficient, decentralized, and flexible, leveraging stakeholders' power to achieve consensus. With self-KYC requirements for nominators, XDPoS is well-suited for enterprise applications and offers adaptability. [6]
EVM Compatibility
The XDC Network is an EVM-compatible, Layer 1 protocol that enables seamless minting and deployment of Layer 2 tokens through Origin. It utilizes the reliable and efficient XDPoS consensus protocol. [6]
Bridges and Interoperability
As an EVM-compatible blockchain, the XDC Network provides a solid foundation for building projects. It supports interoperability with other chains, allowing projects to connect and interact with multiple chains simultaneously. [6]
Perks
Developers on the XDC Network enjoy benefits, including negligible gas fees, fast transaction times, EVM compatibility, and interoperable smart contracts. The XDC Community provides various platforms for developers to build, share, and collaborate with other community members. [6]
With a rich library of resources and tools similar to other EVM networks, developers can easily develop and migrate applications to the XDC Network. Real-time community support is available to assist with migration or development on the XDC Network. [6]
XinFin Delegated Proof of Stake (XDPoS)
The XDC Network ensures its security through a delegated proof-of-stake mechanism known as XinFin Delegated Proof of Stake (XDPoS). This consensus mechanism offers several key features that contribute to the network's robustness and resilience. [7]
XDPoS enables the XDC Network to achieve consensus while consuming virtually zero energy. This energy-efficient approach aligns with sustainable practices and reduces the environmental impact of blockchain operations. Additionally, XDPoS is designed to be highly resistant to spamming attacks, enhancing the network's security and stability. [7]
In the unlikely event that the ratio of adversarial masternodes exceeds one-third during an epoch, these adversarial masternodes would need to sign and certify specific messages to compromise the network's safety. The XDC Network incorporates on-chain forensics monitoring, allowing the detection and analysis of such embedded messages. This holistic integration of accountability and forensics adds an additional layer of security and monitoring to the blockchain. [7]
Voting
Staking
In the XDC Network, users can stake their tokens by sending them to a staking contract. To be eligible for voting, users need to stake an amount greater than the minimum required. After staking, users must wait for a specific duration before they can participate in the voting process for selecting validators. [10]
Delegating
Once users have staked their tokens and waited for the required duration, they can delegate their voting power to a validator of their choice. This delegation becomes active after a specific period of time. Users can only cast new votes at certain intervals. Each user can only delegate their tokens to a single validator. If users wish to delegate to multiple validators, they must create separate accounts and register as nominators individually. [10]
Withdrawing
Users who have delegated their tokens can withdraw them by revoking their vote. After waiting for a certain period of time, the staked tokens become unlocked and are returned to the user's wallet. [10]
Registering Validators
To become a validator, participants need to send a specific amount of tokens to the registration function. This amount helps control the number of validators in the network. The tokens sent for registration are burned. Validators are also required to upload a KYC certificate signed by a recognized authority to ensure compliance with regulatory standards. [11]
Choosing Validators
Validators are selected for their roles in the network. The distribution of stakes is balanced to ensure fairness among validators. The top validators based on stake are included in the Active Validator Set, responsible for producing blocks in the network. [12]
Rewards and Slashing
Validators receive rewards based on their stake in the network, and nominators also receive rewards as an incentive for participating in staking. Rewards can be distributed directly to nominators or calculated by validators and paid to nominators at a later time. The network has measures in place to detect and punish validators for bad behavior. Validators may be penalized, which could result in a reduction or confiscation of their stake, if they engage in actions such as consistently delayed block propagation, prolonged offline periods, or provide fraudulent KYC certifications. [13][14][15]
Masternodes
The XDC Network relies on Masternodes operated by third parties, with different subcategories: Validator, Standby, and Archival. Validator and Standby Masternodes require operators to stake 10 million XDC and comply with KYC procedures. Validators propose and validate new blocks using the XDPoS consensus mechanism. Changes to the network protocol undergo a decentralized process, including proposal through the XIP process and adoption by two-thirds of Validator operators. Standby Masternodes serve as backups when the number of Validators drops below 108. Archival Masternodes store blockchain data but lack validation functionality. Operators' decisions mainly involve software updates. [16]
Becoming a Masternode Operator
To become a masternode operator, a minimum deposit of 10,000,000 XDC is required. Currently, masternode ownership and operation are mostly limited to early investors due to the substantial investment required. This has a stabilizing effect on the XDC price in retail markets. As of September 14, 2021, a total of 1,863,025,000 XDC tokens have been staked in masternodes.
XDC 2.0
XDPoS 2.0
XDC 2.0 is a proposed upgrade to the XDPoS consensus mechanism, introducing advanced features to further strengthen the network's security and performance. By incorporating an advanced BFT consensus protocol, XDC 2.0 aims to eliminate forking in the finalized blockchain, ensuring the immutability of transactions. [7]
Hierarchical Delegated Proof of Stake (HDPoS)
With the introduction of HDPoS, the XDC Network implements a multi-tiered structure of validators. This design enhances scalability and increases transaction throughput by allowing for parallel processing of transactions across multiple validator tiers. It enables the network to handle a higher volume of transactions while maintaining fast confirmation times and efficient block production. [8]
Cross-chain Interoperability
XDC 2.0 focuses on cross-chain interoperability, enabling seamless communication and value transfer between the XDC Network and other blockchain networks. This feature facilitates the exchange of assets, data, and services across different blockchain platforms, promoting interoperability and expanding the utility of XDC tokens. It opens up opportunities for cross-chain collaborations, enabling users to leverage the strengths of multiple blockchain networks. [8]
Enhanced Security Measures
XDC 2.0 introduces a BFT committee, a set of masternodes selected using a deterministic and verifiable algorithm at the beginning of each epoch. This committee utilizes an advanced BFT protocol called Chained Hotstuff to achieve consensus. Importantly, the BFT committee possesses the capability to identify and handle malicious actors by leveraging cryptographically provable forensic evidence. It also introduces improved slashing conditions that swiftly detect and penalize malicious behavior within the network, discouraging validators from engaging in activities that could compromise the security or stability of the XDC Network. [8][9]
Governance Mechanism
XDC 2.0 aims to streamline the governance process by implementing efficient voting mechanisms and decision-making protocols. This enables token holders to actively participate in network governance, contributing to important decisions and protocol upgrades. The enhanced governance mechanism promotes a more decentralized and inclusive approach to decision-making, ensuring that the interests of the XDC community are represented and enabling the network to adapt and evolve over time in a transparent and efficient manner. [8]
XDC Token
The XDC token is the primary utility token used in XinFin's Hybrid Blockchain ecosystem. It serves as a means of settlement for decentralized applications (DApps) running on the XinFin Hybrid Blockchain. [17]
Tokenomics
XDC Supply
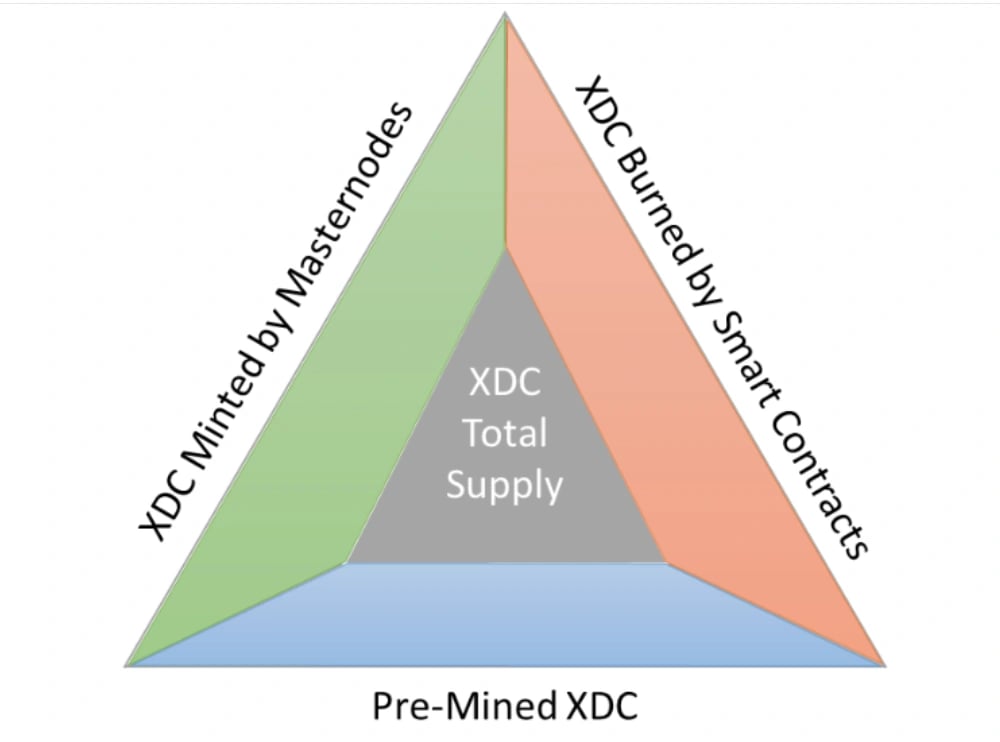
The total supply of XDC is influenced by three factors: pre-mining, minting, and burning. Initially, 37.5 billion XDC tokens were pre-mined during the creation of the mainnet. Masternodes, which validate transactions, mint approximately 86.7 million XDC tokens per year, contributing to inflationary pressure. However, a portion of transaction fees burned through smart contract execution counteracts this inflation, making the network deflationary over time. [18]
Initial Supply
At the inception of the XDC Network's mainnet, a snapshot taken on May 30, 2019, revealed that xdc54d4369719bf06b194c32f8be57e2605dd5b59e5 held the entire pre-mined supply of approximately 37.5 billion XDC tokens. It's important to note that this is not the maximum supply but rather the amount present in the genesis wallet. [19]
Mint
Each block, closing approximately every 2 seconds, mints 5.5 XDC tokens as rewards for Masternode operators. The XDC Network employs a Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) consensus algorithm with 108 Masternodes responsible for block creation. [21]
Burn
Smart contracts executed on the XDC Network burn 20% of the transaction fees, leading to a deflationary effect on the overall supply. As network utility grows through the deployment and execution of smart contracts, the rate of XDC burning is expected to increase. [20]
XDC Allocation
The XDC Network allocated tokens through different categories: [22]
- Founders/Team (40%): 15,000,000,000 XDC tokens were allocated to the founders, advisors, core team members, and the community at the launch of the mainnet.
- Ecosystem Development (27%): 10,000,000,000 XDC tokens were dedicated to the development of the ecosystem, including bounty programs.
- Treasury (6%): 2,500,000,000 XDC tokens were allocated to the XDC Foundation's treasury for network maintenance and support.
- Pre-Placement (27%): 10,000,000,000 XDC tokens were reserved for exchanges and early investors.
Token Standards
The XDC Network embraces various token standards to ensure seamless integration of smart contracts and dApps while promoting interoperability among projects built on the network. [7]
XRC20
XRC20 is the established technical standard for fungible tokens within the XDC Network ecosystem. It serves as the foundation for token implementation in a majority of smart contracts. XRC20 tokens have the versatility to digitally represent a wide range of assets and enjoy broad acceptance by wallets and exchanges. [7]
XRC721
XRC721 is the standard used to develop NFTs on the XDC Network. It outlines the essential requirements for smart contracts to enable ownership, management, and trading of NFTs. [7]
XRC1155
XRC1155 is a multi-standard token that combines the functionalities of both XRC20 and XRC721 standards. This innovative token standard enables the generation of multiple tokens within a single contract. With XRC1155, a single smart contract can represent and govern an infinite number of tokens, offering enhanced flexibility and efficiency. [7]
XDC Network Improvement Proposal (XIP)
XDC Network Improvement Proposals (XIPs) serve as a means for the XDC Community to propose and discuss new features, gather technical insights, and document design decisions within the network. Inspired by Ethereum Improvement Proposals (EIPs), which draw from Bitcoin Improvement Proposals (BIPs) and Python Enhancement Proposals (PEPs), XIPs foster the open-source ecosystem on the network and encourage developers and builders to contribute to network and industry standardization. [7][23]
XIPs encompass a range of topics, including core protocol specifications, client APIs, and contract standards, while network upgrades are addressed separately. [7]
XIP editors ensure that proposals adhere to formatting and style guidelines. Before drafting a formal XIP, it is recommended to propose the idea on the developer forum and subject it to community scrutiny. Once vetted, the XIP can be authored on GitHub, allowing interested parties, editors, developers, and the XDC community to review and provide input. [23]
The XIP framework comprises different types, including Standards Track XIPs, Meta XIPs, and Informational XIPs. These proposal types serve distinct purposes in shaping the XDC platform, promoting collaboration, and facilitating the development of industry-wide standards. [23]
Partnerships
Protocol Lab
Protocol Lab partners specialize in network protocols and contribute to various aspects of blockchain networks. They focus on network consensus, network upgrades, and network tools to enhance the functionality and efficiency of the protocols. Additionally, they conduct research and development activities to improve network protocols and ensure their security and stability. Security and stress testing are also carried out to assess and address potential vulnerabilities and performance issues within the protocols. Partners in this branch are: [24]
- 4ireLabs
- SotaTek
- Hash Labs
- SoluLab
- Carry.so
Infrastructure Integration Level Developers
These partners focus on integrating blockchain infrastructure into various systems. They develop wallet connectors, exchange connectors, and custodian connectors to facilitate seamless interactions between blockchain networks and external platforms. Additionally, they conduct security and stress testing to ensure the reliability and resilience of the integrated infrastructure. Partners in this branch are: [24]
- Gitcoin.co
- IoTrust
- MyWish
- Tatum
- Wanchain
- Unmarshal
Application Level Developers
Application Level Developers are developers who build applications on blockchain platforms using smart contracts. They utilize middleware for enhanced functionality and simplify development. Oracles and Price Feeds provide external data to smart contracts. Cross-chain bridges enable interoperability between different blockchains. Security and stress testing ensure robustness and identify vulnerabilities. Partners in this branch are: [24]
- Cordite Foundation
- Lab5577
- Yodaplus
- Trace Financial (ISO20022 - Financial Messaging Integration)
- LeewayHertz
- DASL
- Chainlink (Oracles and Price Feeds)
- Razor Network (Oracles and Price Feeds)
- JellySwap (Cross-chain DEX)
- Meherett
- Dimo Finance
- Blocksscan
- Rock'n'Block
- Umbrella Network (Oracles and Price Feeds)
- Plugin (Oracles and Price Feeds)
Institutional & Custodian Partners
- SBI Holdings
See something wrong?
The Agent Tokenization Platform (ATP):Build autonomous agents with the Agent Development Kit (ADK)
