위키 구독하기
Share wiki
Bookmark
Internet Computer (ICP)
0%
Internet Computer (ICP)
인터넷 컴퓨터는 안전하고 분산된 프로토콜에서 웹 기반 서비스를 생성할 수 있도록 하는 블록체인 네트워크입니다. 인터넷 컴퓨터는 이전에는 DFN으로 알려졌던 인터넷 컴퓨터 프로토콜(ICP) 토큰으로 구동되며, 이를 통해 사용자는 웹을 재창조하고 앱을 더욱 확산된 형태로 구동하며, 블록체인에서 트랜잭션 수수료를 지불하고(트랜잭션 가스 역할), 참가자 또는 데이터 센터에 보상을 제공하고, 보유자가 네트워크의 미래에 대해 투표할 수 있는 거버넌스 결정을 내릴 수 있습니다. ICP 토큰은 인터넷 컴퓨터 네트워크에서 핵심적인 역할을 하는 유틸리티 토큰입니다. [8] [9] [3]
역사
2016년 초, 인터넷 컴퓨터는 DFINITY의 설립자이자 수석 과학자인 도미닉 윌리엄스가 구상한 아이디어로 시작되었습니다. DFINITY는 인터넷 컴퓨터 프로젝트를 개발하고 공식 출시 전 5년 동안 유지 관리한 비영리 디지털 재단입니다. [5] [6] 2018년까지 Dfinity에 대한 자금 조달 라운드가 진행되었으며, Andreessen Horowitz, Polychain Capital, Aspect Ventures [16] 등으로부터 약 1억 2,100만 달러를 모금했으며, 네트워크 토큰이 배포되기 전인 2017년에 초기 코인 공개(ICO)를 포함했습니다. 약 3,500만 달러 상당의 토큰은 2018년에 에어드랍 [13]을 통해 출시되었습니다.
2019년까지 토큰의 본격적인 개발이 시작되어 Copper가 출시되었고 ICP는 2021년 5월에 출시되었습니다. 이를 통해 블록체인 특이점에 도달할 수 있게 되었습니다. 즉, 제3자의 간섭 없이 안전한 프로토콜에서 모든 것을 갖춘 인질에서 스토리지 및 서비스로 웹을 실행할 수 있는 블록체인입니다. 이더리움과 유사하게 ICP는 네트워크에서 탈중앙화 애플리케이션(DApp)을 시작할 수 있지만, ICP 네트워크에서 캐니스터라고 하는 스마트 계약의 업그레이드된 버전을 사용합니다. [14]
설립자에 따르면 인터넷 컴퓨터 프로토콜(ICP) 토큰은 비트코인과 이더리움 이후 블록체인 기술의 세 번째 주요 혁신을 상징합니다. 이 혁신은 인터넷을 다음 큰 이벤트로 진화시키는 것으로 인식됩니다.
"인터넷 컴퓨터는 대규모 기술 독점을 종식시키고 과도하게 유통되는 클라우드 서비스 시스템을 보다 분산된 세계 네트워크로 대체하고 인터넷의 확장으로 발전하는 것을 목표로 합니다." - 도미닉 윌리엄스
개요
인터넷 컴퓨터(ICP)는 도미닉 윌리엄스가 설립한 Dfinity 재단에 의해 2021년에 출시되었습니다. 이 네트워크는 모든 개발자, 기업 및 비즈니스 소유자가 "개방형 인터넷"에서 소프트웨어를 구축하고 배포할 수 있도록 설계되었습니다. 제작자는 개인 인터넷 인프라를 대체하고 개선하여 보안 플랫폼과 기존 기술에 전적으로 의존할 필요가 없도록 계획하고 있습니다. 따라서 주요 아이디어는 웹 3 및 DeFi 애플리케이션을 포함하여 웹의 전체 기본 계층을 지원하고 실행할 수 있을 만큼 빠른 블록체인 기술로 구동되는 분산형 글로벌 네트워크를 갖는 것입니다. [12]
인터넷 컴퓨터는 네트워크 신경 시스템(NNS), 인터넷 아이덴티티, 임계값 릴레이 합의 등 다른 시스템으로 구성된 체인 키 기술이라는 기술을 기반으로 작동합니다. 수천 개의 노드가 네트워크를 보호하기 위해 실행되며, 그룹화되면 서브넷을 형성합니다. 이러한 서브넷은 지분 증명(PoS) 메커니즘을 가지고 있어 더 많은 토큰이 스테이킹될수록 더 많은 보상을 받습니다. [11]
Network Nervous System (NNS)
인터넷 컴퓨터는 세계에서 가장 큰 DAO 중 하나인 NNS에 의해 관리됩니다. 완전한 온체인, 무허가 시스템으로 운영되며, ICP 토큰 보유자들의 투표를 통해 인터넷 컴퓨터의 지속적인 업그레이드를 용이하게 합니다. [19]
스테이킹
NNS를 통해 사용자는 ICP 거버넌스 토큰을 스테이킹하여 투표 뉴런을 생성할 수 있습니다. 이는 커뮤니티가 알고리즘을 통해 집단적 의지를 표현하는 메커니즘으로 작용합니다. 뉴런은 계정 역할을 하며 인출 통지가 필요하며, 해산 지연 구성이 통지 기간을 결정합니다. 뉴런의 투표력과 투표 보상에 대한 상대적 청구는 스테이킹된 ICP 수량, 해산 지연 및 연령에 따라 결정됩니다. 뉴런은 다른 뉴런을 따라 수동 또는 자동으로 투표할 수 있어 액체 민주주의가 가능합니다. NNS의 제안은 ICP 토큰을 스테이킹하는 커뮤니티 구성원이 생성한 뉴런을 포함하는 투표 프로세스를 통해 결정됩니다. 토큰 보유자는 인출 전에 고정된 통지 기간이 있는 이러한 뉴런에 스테이킹된 ICP 토큰을 잠금으로써 보상을 얻습니다. 뉴런 소유자는 해산 지연을 최대 8년까지 구성할 수 있지만 투표 자격을 얻으려면 뉴런에 최소 6개월의 해산 지연이 있어야 합니다. [20][25]
뉴런 보유자는 인터넷 컴퓨터 네트워크의 장기적인 가치를 높이는 방식으로 제안에 찬성하거나 반대하거나 뉴런 팔로우를 구성하여 자동으로 투표하도록 장려하는 암호 경제 게임에 참여합니다. [20]
토큰 경제학
인터넷 컴퓨터 네트워크에는 두 가지 기본 토큰이 있으며, 여기에는 다음이 포함됩니다.
- ICP - 네트워크 관리를 위한 독점적인 제어 토큰
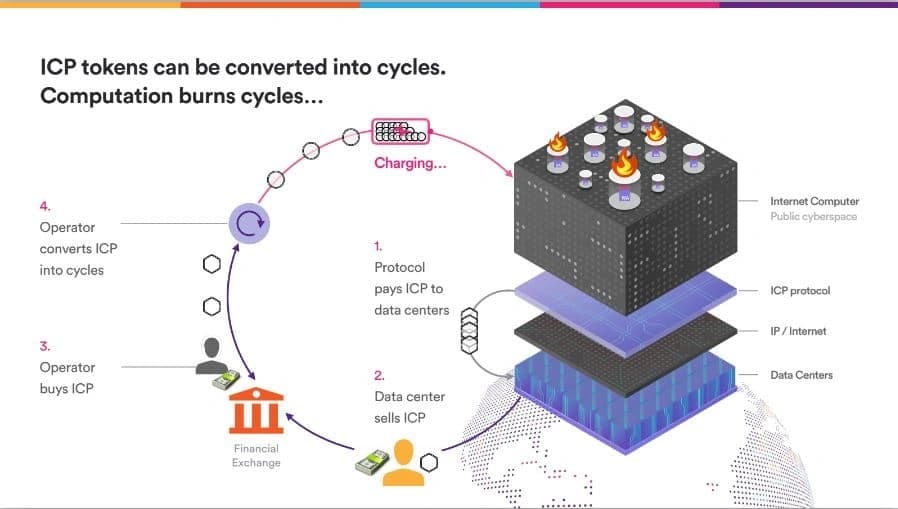
- 사이클 - 이더리움의 "가스비"와 유사하게 연산을 지원하는 데 사용되는 스테이블 코인입니다. 단, 트랜잭션이 관련되지 않는 한 사용자는 Canister를 사용할 때 가스비를 지불할 필요가 없습니다.
ICP 토큰은 네트워크를 실행하는 알고리즘 프로토콜 시스템인 네트워크 신경 시스템(NNS)에 잠글 수 있습니다. 또한 컨테이너를 사용하여 연산하기 위한 가스비인 사이클로 변환할 수도 있습니다. 이 프로세스에는 ICP 토큰을 소각하여 연산을 위한 사이클로 변환하는 것이 포함되며, 이는 디플레이션이라고 합니다.
ICP 기능
ICP 토큰은 인터넷 컴퓨터 블록체인 운영을 돕고, 다음은 핵심 사용 사례를 간략하게 설명합니다. [22]
- 노드 제공자 보상: 인터넷 컴퓨터 블록체인의 노드 제공자는 컴퓨팅/스토리지 인프라를 제공한 대가로 ICP 보상을 받습니다. 고정 월별 보상은 명목 화폐로 계산되어 ICP 토큰으로 지급되므로 노드 실행 비용이 일정하게 유지됩니다. 노드의 더 넓은 분산을 장려하기 위해 지리적 위치에 따라 보상이 약간씩 다릅니다. 노드 제공자는 적절한 서비스 품질을 유지하는 한 보상을 받으며, 보상은 새로운 ICP 토큰을 발행하여 지급되므로 인플레이션이 발생합니다.
- 거버넌스: ICP 토큰 보유자는 토큰을 스테이킹(잠금)하여 뉴런을 생성할 수 있습니다. 뉴런은 토큰 보유자가 온체인 개방형 거버넌스 시스템인 NNS(Network Nervous System)를 통해 투표권을 확보할 수 있도록 합니다. NNS를 통해 뉴런 보유자는 IC 프로토콜 및 소프트웨어 업그레이드, 새로운 노드 제공자 온보딩, 노드 머신 추가, 새로운 서브넷 블록체인 생성과 관련된 제안에 투표할 수 있습니다. 뉴런은 다른 뉴런을 팔로우하여 투표권을 위임할 수 있으며, 보유자는 투표 프로세스를 통해 거버넌스에 참여한 대가로 보상을 받습니다. 이러한 보상은 새로운 ICP 토큰을 발행하여 지급되므로 인플레이션이 발생합니다.
- 계산/저장 연료: 인터넷 컴퓨터 블록체인의 카니스터 스마트 계약 계산은 ICP 토큰을 소각하여 얻는 "사이클"에 의해 구동되며, 이는 이더리움의 "가스"와 유사합니다. 그러나 이더리움의 "사용자 지불" 모델과 달리 인터넷 컴퓨터는 카니스터 스마트 계약에 사이클이 미리 충전되어 자체 계산 비용을 지불할 수 있도록 하는 "스마트 계약 지불" 또는 "역방향 가스" 모델을 사용합니다. 이를 통해 사용자는 각 거래마다 가스 비용을 지불해야 하는 책임에서 벗어날 수 있습니다. ICP 유틸리티 토큰을 소각하면 사이클이 생성되어 디플레이션이 발생합니다.
- 거래/제안 수수료: ICP 보유자는 지갑 간에 토큰을 전송할 때 ICP로 소액의 거래 수수료를 지불하고, NNS에 제안을 제출할 때 소액의 수수료를 지불합니다. 이러한 수수료는 거래의 일부로 소각되어 디플레이션에 기여합니다.
ICP 소각 주기 분석
BTC<>ICP 메인넷 통합
비트코인과 인터넷 컴퓨터의 통합은 비트코인의 유동성을 IC의 스마트 계약 기능과 결합합니다. 메인넷에서 출시된 후, 이 통합은 비트코인에 고급 스마트 계약 기능을 제공합니다. 이러한 개발을 통해 인터넷 컴퓨터는 비트코인을 위한 레이어 2 플랫폼 역할을 할 수 있으며, IC의 스마트 계약이 블록체인 브리지나 제3자와 같은 중개자 없이 비트코인을 기본적으로 보유, 전송 및 수신할 수 있도록 합니다. [23]
인터넷 컴퓨터 발자국
인터넷 컴퓨터(IC) 생태계는 최근 지속 가능성 정책과 블록체인의 탄소 발자국을 설정하는 것을 목표로 하는 커뮤니티 작성 제안인 NNS 제안 #55487을 구현했습니다. 그 결과, Carbon Crowd 팀은 인터넷 컴퓨터의 기본 디지털 인프라의 탄소 발자국을 줄이는 것을 목표로 하는 인터넷 컴퓨터 발자국 프로젝트 개발을 시작했습니다. [24]
자금 조달
이 프로젝트는 Andreessen Horowitz, Polychain Capital, SV Angel, Aspect Ventures, Electric Capital, ZeroEx, Scalar Capital 및 Multicoin Capital을 포함한 다양한 기여자로부터 재정적 지원을 받아 총 1억 2,100만 달러를 모금했습니다. DFINITY 재단은 2018년에 50,000명 이상의 등록 참가자에게 ICP 토큰을 에어드랍했습니다. [21]
2020년 12월 18일, 인터넷 컴퓨터의 알파 메인넷이 DFINITY에 의해 출시되었고, 이후 2021년 5월 10일에 공개되었습니다. 그 결과, 인터넷 컴퓨터의 소스 코드가 공개되었고, ICP 유틸리티 토큰의 거래 및 거버넌스 기능도 도입되었습니다. [21]
최근 개발 상황
코스모스와의 ckBTC 통합
2024년 9월, 인터넷 컴퓨터 블록체인과 코스모스 생태계 간에 크로스체인 연결이 구축되었습니다. 이 개발에는 인터넷 컴퓨터에서 발행된 비트코인 지원 토큰인 ckBTC와 탈중앙화 거래소 Osmosis가 관련됩니다. 이 통합은 서로 다른 블록체인 네트워크 간의 통신을 가능하게 하도록 설계된 상호 운용성 프로토콜인 Omnity에서 지원합니다.
이 통합을 통해 ckBTC는 Osmosis를 통해 코스모스 생태계로 전송될 수 있습니다. 커스터디언 또는 합성 표현에 의존하는 기존 브리징 메커니즘과 달리, 이 구현은 크로스체인 트랜잭션을 검증하기 위해 인터넷 컴퓨터의 스마트 계약(캐니스터라고 함)을 사용합니다. Omnity는 중앙 집중식 인프라 없이 네트워크 간의 합의 상태를 검증하여 이를 용이하게 합니다.
이 계약의 일환으로 Osmosis는 코스모스 생태계 내에서 ckBTC를 목록에 포함하는 최초의 탈중앙화 거래소가 됩니다. 이를 통해 자산을 거래하고 플랫폼의 유동성 풀에 포함할 수 있습니다. 이 통합은 원래 네트워크를 넘어 ckBTC의 운영 범위를 확장하여 IBC(Inter-Blockchain Communication) 프로토콜을 사용하는 탈중앙화 애플리케이션 및 프로토콜과의 상호 작용을 가능하게 합니다. 브리징 프로세스는 인터넷 컴퓨터의 기본 비트코인 통합과 스마트 계약 자동화를 결합하여 중개자 없이 자산 전송을 지원합니다. 이 구성은 분산화 원칙을 유지하면서 블록체인 환경을 연결하려는 광범위한 노력을 반영합니다. [29] [30] [31]
캄보디아 파트너십 및 스마트 시티 협력
2024년 9월, DFINITY 재단은 캄보디아 우정통신부(MPTC)와 양해각서(MOU)를 체결했습니다. 이 협약은 블록체인 및 인공지능 기술을 캄보디아의 디지털 인프라 이니셔티브에 통합하는 것을 지원하기 위한 협력 프레임워크를 개략적으로 설명합니다.
이 파트너십에는 잠정적으로 "캄보디아 블록체인 허브"라고 명명된 국립 블록체인 센터 설립 계획이 포함됩니다. 이 시설은 소프트웨어 개발 워크숍, 교육 프로그램, 분산 기술 공동 연구와 같은 활동을 통해 개발 및 교육 환경으로 사용될 예정입니다.
명시된 목표 중 하나는 신원 확인 메커니즘, 디지털 서비스 제공 및 관리 상호 운용성을 포함하여 공공 부문 환경에서 블록체인 시스템을 구현하는 것입니다. 인터넷 컴퓨터(ICP) 프로토콜은 실험 및 시스템 배포를 위한 기본 레이어로 사용됩니다.
이 협력에는 특히 온체인에서 작동하는 자율 에이전트의 배포와 같은 AI 애플리케이션에 대한 탐색도 포함됩니다. 이 이니셔티브의 추가 구성 요소에는 해당 지역의 기술 참여를 늘리는 것을 목표로 하는 해커톤 및 역량 강화 이벤트와 같은 커뮤니티 중심 노력이 포함됩니다.
이 협력 노력은 분산 기술의 거버넌스 및 도시 계획 사용 사례를 조사하기 위한 국가 정부와 DFINITY 재단 간의 공식적인 참여를 나타냅니다. [32] [33] [34]
Elliptic과의 파트너십
2025년 2월, DFINITY 재단은 암호화폐 자산 규정 준수 및 위험 모니터링 전문 기업인 Elliptic과 파트너십을 체결했습니다. 이 협력의 목표는 인터넷 컴퓨터 생태계 전반에 걸쳐 보안 및 규정 준수 인프라를 확장하는 것입니다. 이 통합을 통해 ICP가 Elliptic의 모니터링 제품군에 추가되어 거래 추적 및 규제 심사가 가능해졌습니다. 이 파트너십은 기관 투자자들이 ICP의 스마트 계약 프레임워크를 기반으로 구축된 애플리케이션과 상호 작용하면서 관할 구역 요구 사항을 충족할 수 있는 도구를 제공합니다.
Validation Cloud 통합
2025년 4월, Web3 인프라 제공업체인 Validation Cloud는 DFINITY 재단과 파트너십을 맺고 인터넷 컴퓨터 프로토콜(ICP)에 블록체인 분석 서비스를 도입했습니다. 협업의 일환으로 Validation Cloud는 ICP Rosetta 노드에 대한 액세스를 통합하여 ICP 원장 및 NNS(Network Nervous System) 거버넌스 캐니스터와의 상호 작용을 용이하게 했습니다. 이러한 노드는 거래 분석, 규제 보고, 자동화된 규정 준수 워크플로를 포함한 블록체인 관련 운영에 필요한 기능을 제공합니다. 이번 통합은 고객 알기 제도(KYC) 및 자금세탁 방지(AML) 표준과 같은 규제 프레임워크 준수, 분석 및 기업 수준의 사용 사례를 지원하기 위한 것입니다.
운영 보안 상태
2025년 6월 현재, 인터넷 컴퓨터 프로토콜은 2021년 초기 배포 이후 알려진 네트워크 침해 사례가 없습니다. 이 프로토콜은 완전한 온체인 인프라에서 운영되며, 데이터와 애플리케이션 로직은 분산 네트워크 내에서 직접 호스팅됩니다. 이는 일반적으로 중앙 집중식 취약점에 더 취약한 기존의 오프체인 스토리지 서비스에 대한 의존성을 제거합니다. 이 아키텍처는 하이브리드 또는 클라우드 기반 블록체인 솔루션과 일반적으로 관련된 외부 위협에 대한 노출을 줄이는 것을 목표로 합니다. [26] [27] [28]
잘못된 내용이 있나요?
