Subscribe to wiki
Share wiki
Bookmark
Bitcoin Ordinals
The Agent Tokenization Platform (ATP):Build autonomous agents with the Agent Development Kit (ADK)
0%
Bitcoin Ordinals
Bitcoin Ordinals are a form of non-fungible tokens (NFTs) that are inscribed on a satoshi, the smallest unit of Bitcoin. Some of the notable collections in the Bitcoin Ordinals space are Ordinal Punks, Taproot Wizards, Bitcoin Rocks, and TwelveFold.
Overview
On January 21st 2023, the Bitcoin Ordinals protocol was launched on the Bitcoin mainnet by software engineer and bitcoiner, Casey Rodarmor. He began working on the project in 2022, after the Bitcoin Taproot upgrade in November 2021 which made it possible to create programmable smart contracts on the blockchain, thus enabling the concept of Ordinals. [1][2]
NFTs on Ethereum references off-chain data on IPFS, a decentralized file storage system. This data can be modified through dynamic metadata, as demonstrated by some NFT projects that update individual NFTs' metadata to enhance image quality. This feature highlights a flaw in NFTs that the Rodarmor aims to address. In comparison to NFTs, Ordinals are "complete" since all data is stored on-chain, and therefore addressed as “digital artifacts” rather than Bitcoin NFTs. Furthermore, NFTs often have royalties attached to them, whereas digital artifacts do not. [3]
History
There were several NFT projects and updates to the Bitcoin ecosystem that laid out the foundation for the Bitcoin Ordinals protocol to be launched successfully.
Bitcoin NFT History
The first attempt at creating NFTs on Bitcoin was through a project called Colored Coins, which were created in 2012 to represent non-Bitcoin assets on the blockchain. However, this method proved to be inefficient as Colored Coins were not easily distinguishable from regular Bitcoins. [4][5]

In 2014, Counterparty was launched as a derivative of Bitcoin and allowed the creation, buying, and selling of digital assets through its XCP token. The platform introduced the concept of Rare Pepes, which were NFTs inspired by the Pepe the Frog meme. Rare Pepes were a popular use case for Counterparty and far predated the NFTs of Ethereum that we know today. [4][6]
Bitcoin Upgrades
There were also a few upgrades that laid out the foundation for this project to be launched. One of the most significant upgrades is the Segregated Witness or SegWit, launched in 2017. The SegWit upgrade fixed several bugs in Bitcoin Core, allowing more transactions per block and laying the groundwork for Layer 2 payment channels such as the Lightning Network. However, SegWit was controversial, leading to a hard fork of the network that resulted in the launch of rival blockchains, Bitcoin Cash and Bitcoin SV. [7]
In 2021, the introduction of the Taproot upgrade promised to bring more privacy to Bitcoin transactions and reduce the amount of data needed to make them, which in turn lowered transaction costs. This upgrade also allowed for more complex transactions to look like standard, person-to-person transactions, making it more challenging to identify transaction inputs on Bitcoin’s blockchain. These previous attempts as well as updates to the Bitcoin ecosystem gave Rodarmor the inspiration and knowledge needed to successfully launch the recent Ordinals protocol. [7]
Notable Ordinals Projects
Some of the notable collections in the Bitcoin Ordinals space are Ordinal Punks, Taproot Wizards, Bitcoin Rocks and TwelveFold.
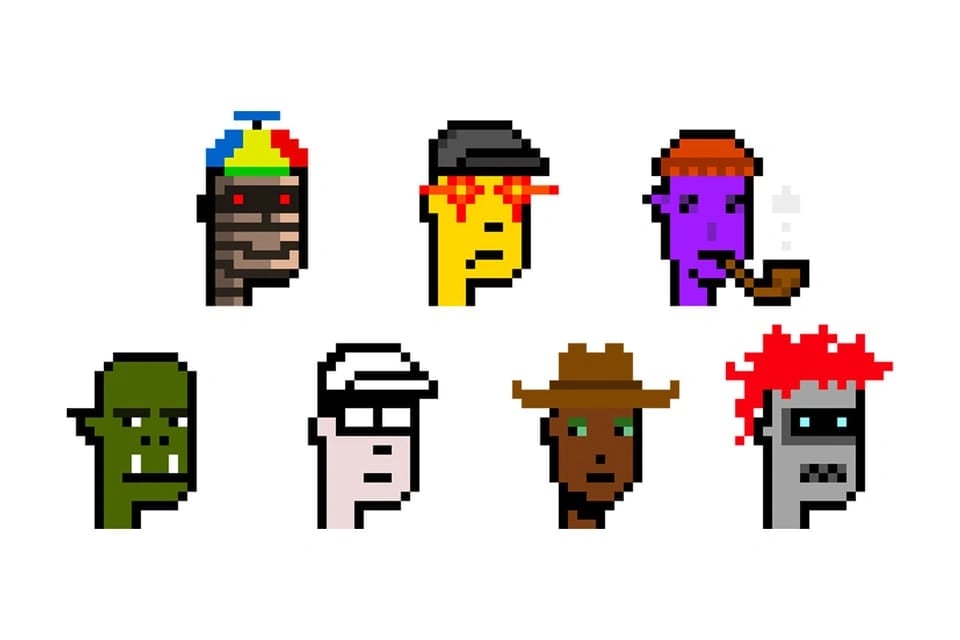
Ordinal Punks
Ordinal Punks is a collection of only 100 Bitcoin NFTs paying homage to the popular CryptoPunks project. The NFTs were created through a generative PFP collection of 192x192 pixel images using an open-source algorithm. The project's infrastructure requirements meant that bids and asks for the NFTs are managed on a Google Sheet, with the project's creator serving as an escrow on Discord. [8][9]
 Taproot Wizards
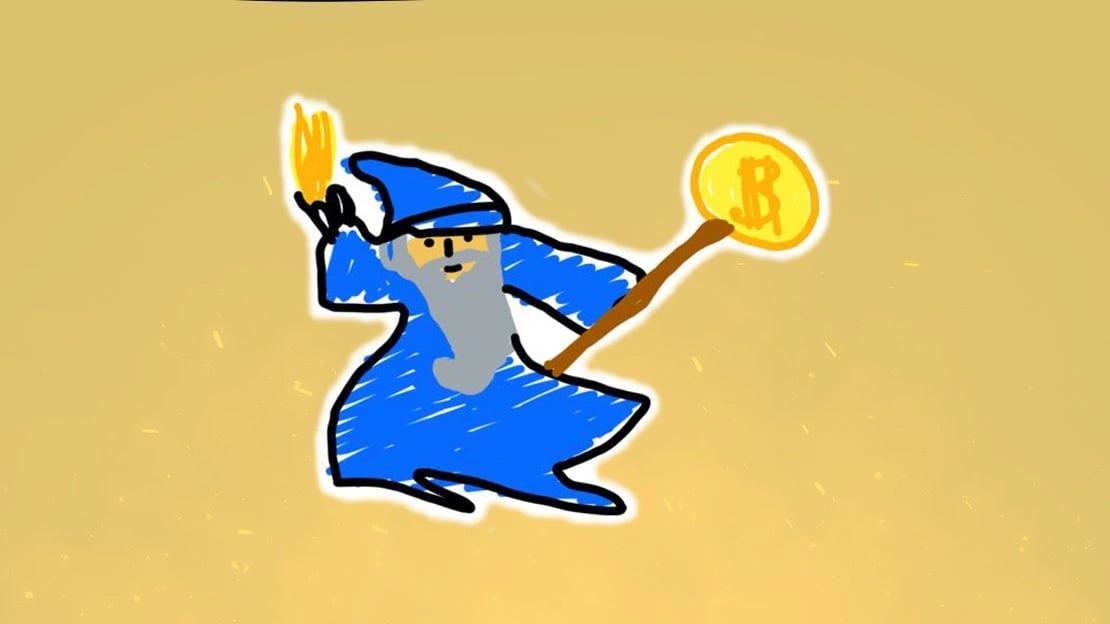
Taproot Wizards

Taproot Wizards is another notable Ordinals collection on the Bitcoin chain, consisting of hand-drawn NFT wizards inscribed on the Bitcoin chain, starting from Inscription 652. The first Ordinal in the collection holds the distinction of being the largest block and transaction in Bitcoin's history, clocking in at 4MB. [9][10]
 Bitcoin Rocks
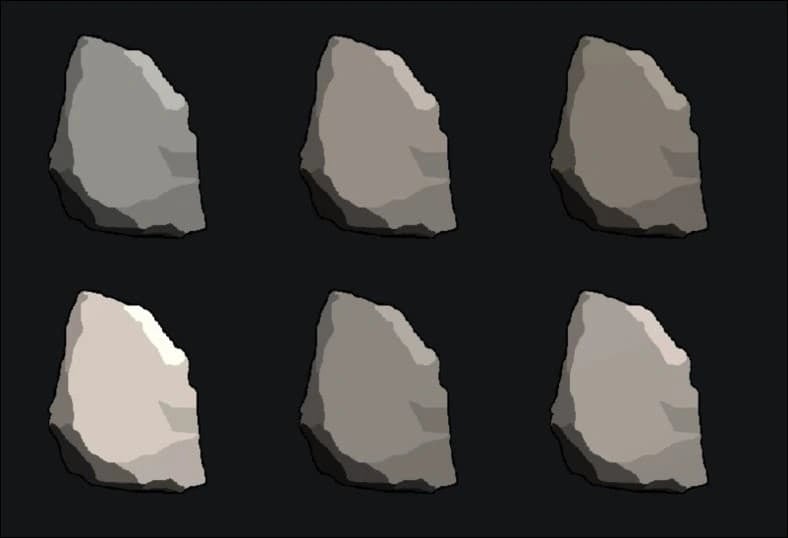
Bitcoin Rocks

Bitcoin Rocks is a limited collection of only 100 NFTs inspired by the early Ethereum NFT collectible project, Ether Rocks. The collection pays tribute to the early days of NFTs and is an example of the intersection between the Bitcoin and NFT communities. Some of the NFTs in the collection have been listed for as much as 1,000 BTC. [9][11]

TwelveFold
Twelvefold is an experimental 300-piece collection from Yuga Labs on the Bitcoin blockchain. The generative pieces were crafted by Yuga Labs’ Chief Content Officer Figge. The collection features a base 12 grid, with each of the 144 points on the grid being a shiny ball of differing in color and size. The auction ended on March 6th, 2023 with 288 successful bids, raising a total of $16.49 million in BTC. [12][13]
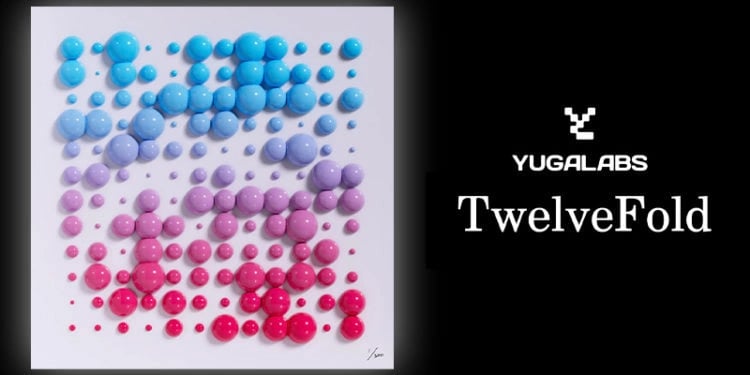
See something wrong?
The Agent Tokenization Platform (ATP):Build autonomous agents with the Agent Development Kit (ADK)
