Subscribe to wiki
Share wiki
Bookmark
Forta
The Agent Tokenization Platform (ATP):Build autonomous agents with the Agent Development Kit (ADK)
0%
Forta
Forta is a decentralized, community-based monitoring network used to detect threats and anomalies on DeFi, NFT, governance, bridges and other Web3 systems in real-time. [1]
History
Forta began in early 2021, incubated by the leading risk management and blockchain security company OpenZeppelin with a $23 million fundraise led by Andreessen Horowitz. [3] Forta is backed by world-class, leading entities in the Web3 venture capital sphere, with the major investment round being led by Coinbase Ventures, Blockchain Capital, a16z, Blueyard, Placeholder, North Island Ventures, the Digital Currency Group and OpenZeppelin, among others. It is exploring a DAO to become more decentralized. In November 2021, Forta went public to a global audience with the launch of the Forta App and Explorer.[3][2]
In the beginning of 2022, governance over Forta was endowed to the Forta Foundation, an independent, non-profit organization that will facilitate Network governance by Forta’s community members. Since then, Forta has seen major adoption and growth from leading organizations and developers in the Web3 ecosystem.
Overview
Forta is a real-time detection network designed for security and operational monitoring of blockchain activity. It provides alerts about the security and health of owned or dependent systems and protocols, allowing investors to respond to threats and minimize the risk of fund loss. The Forta Network actively monitors on-chain activity in real-time, identifying threats, security incidents, and significant events. This network comprises detection bots created by a community of Web3 developers and security professionals. Each bot operates as a specialized security tool, focusing on specific on-chain elements. Some bots track general threats, like phishing attacks and rug pulls, while others are customized to monitor protocol-specific activities. [5]
Forta's decentralized network of independent node operators scans all transactions and block-by-block state changes for outlier transactions and threats. When an issue is detected, node operators send alerts to subscribers of potential risks, which enables them to take action. Developers can build detection bots and machine learning models and run them on the decentralized Forta network to uncover anomalous activity on every blockchain transaction. [2][4]
Detection Bots
Detection Bots serve as surveillance tools created by developers and deployed on the network. The functionality of each bot is determined by the logic implemented by its developer. These bots vary in complexity, with some monitoring for specific conditions, such as a multi-sig transaction surpassing a predefined amount threshold, while others use advanced heuristics and machine learning models to detect various factors like scam activity. When a bot identifies the specified criteria, it issues an alert. [9]
To prevent spam and malicious bots from consuming network resources, developers must stake a minimum of 100 FORT on each detection bot they deploy. Bots lacking this minimum stake will remain inactive. [9]
Scan Nodes
Scan Nodes constitute the other essential component of the network, similar to servers contributing capacity to the Forta Network. Scan nodes are responsible for executing detection bots, supplying them with blockchain data, and disseminating any alerts. [9]
Anyone can operate a scan node by staking the required amount of FORT tokens. Each scan node monitors blocks and transactions from a blockchain, with the Forta Network currently supporting scan nodes for EVM blockchains like Ethereum, Polygon, and BNB Chain. Each scan node is assigned a specific set of detection bots by the Forta Network. [9]
Upon the publication of a new bot, it is randomly allocated to one or more scan nodes and begins running shortly afterward. The scan node collects alerts reported by the detection bots and publishes them. To ensure accountability and incentivize responsible network operation, each scan node must be staked with a minimum of 2,500 FORT. [9]
Network Intelligence
The Forta Network's detection bots collectively generate alerts and other data points every hour. Users can subscribe to alerts from a specific detection bot using the Forta App, browse and search the latest alerts, and, for more technical users, query alerts using the Forta API to integrate alert feeds into their own applications. [9]
FORT Token
FORT is an ERC-20 token in the Ethereum network, it is the native token of Forta. FORT Token is an incentive structure to secure Forta's monitoring network, allowing Forta to grow and secure the Web3 ecosystem as a whole. Forta adopts a work token model, where both scan node pools and detection bots must have FORT staked above a minimum requirement. This acts as an economic security mechanism of their actions in their network, as the stake can be slashed if participants act maliciously. [7]
Use Cases
FORT has the following use uses: [8]
- Owners of scanner pools deposit FORT tokens to make their pools discoverable in the network and to secure their economic contributions. Staked FORT faces potential slashing if nodes fail to perform their assigned tasks or engage in malicious behavior. Withdrawal of staked FORT is subject to a designated thawing period, allowing time for verification and dispute resolution.
- Delegators can also stake on a pool, with similar withdrawal restrictions. In case of a pool being slashed, Delegators may experience a proportionately smaller deduction from their stake.
- Developers stake FORT tokens on bots, signaling bot quality to the network and providing a sybil resistance mechanism to enhance network integrity.
- Users purchasing Forta's General Plan for data consumption from the network pay a monthly fee, denominated and settled in FORT.
- Premium feeds may be denominated and paid in either FORT or USDC, depending on the decision of the feed owner.
Token Distribution
The total supply of FORT tokens has been capped at 1,000,000,000 FORT. The FORT Community Allocation is held by the Forta Foundation and is not subject to a specific vesting or distribution schedule. [6]
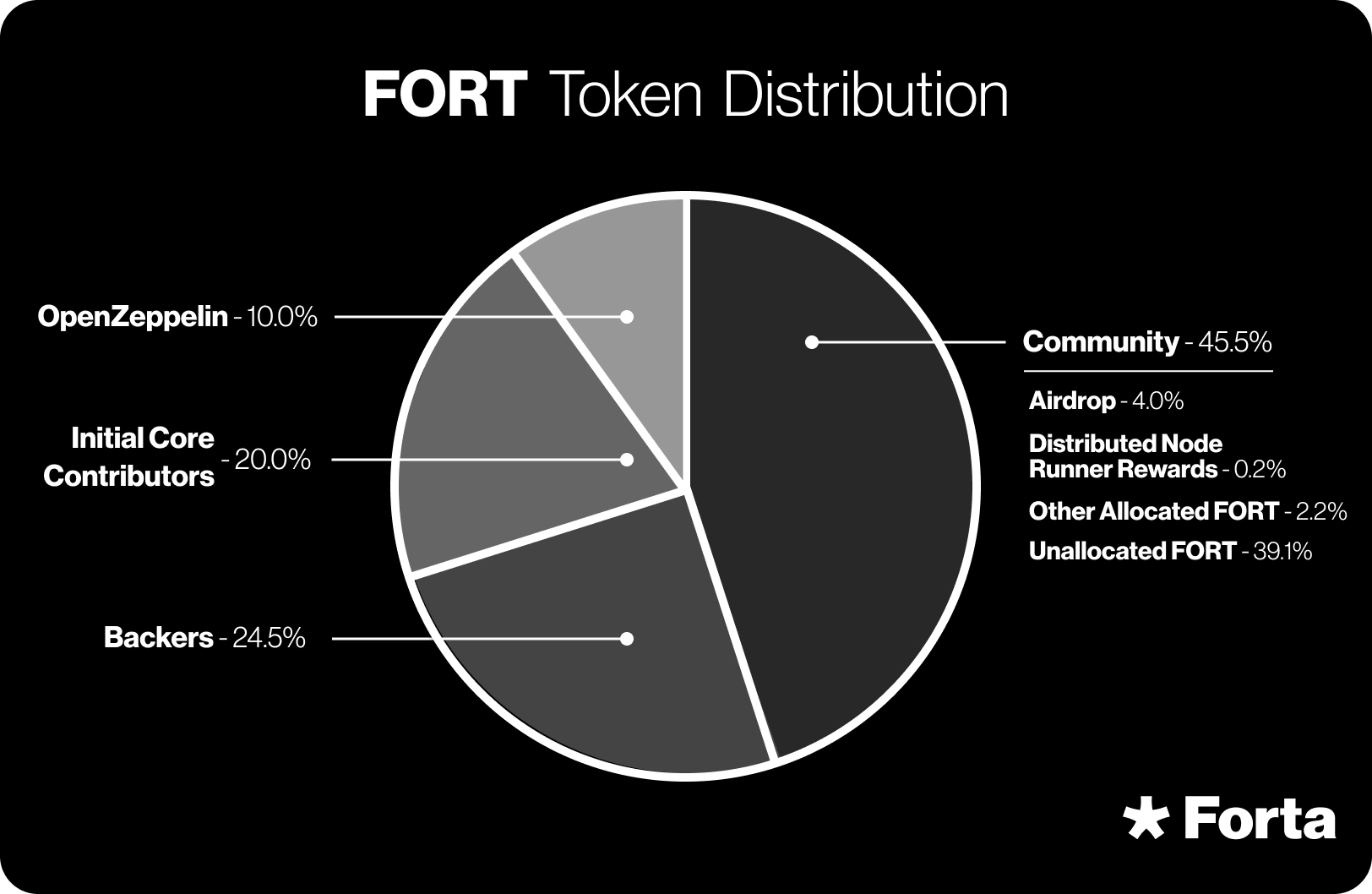
- Community Allocation: The FORT Community Allocation is held by the Forta Foundation and is not subject to a specific vesting or distribution schedule.
- Backers: The Forta Network received early support from backers who provided funding for its development and became early members of the community. These backers also functioned as some of the initial node operators in the Forta Network, and their transfer restrictions are enforced through on-chain vesting smart contracts.
- Initial Core Contributors: The Forta Network was developed and introduced by a team from OpenZeppelin. A portion of 20% of the total FORT token supply is allocated to these individuals as Initial Core Contributors, subject to a 4-year linear vesting period with a 1-year cliff, overseen by OpenZeppelin. The earliest vesting commencement date for Initial Core Contributors' FORT token allocations was September 1, 2021, aligning with the transfer restrictions for the Backers.
- OpenZeppelin: OpenZeppelin, a prominent blockchain security company, founded and incubated the Forta Network. A portion amounting to 10% of the total FORT token supply has been designated for OpenZeppelin. This allocation is subject to a 4-year linear vesting period with a 1-year cliff. The vesting of OpenZeppelin's FORT token allocation commenced on September 1, 2021.
Governance
The Forta Foundation is a non-profit organization responsible for holding assets, such as public and open-source intellectual property, Github repositories, and FORT tokens within the Network. It facilitates Forta's governance by community members. To decentralize governance, the Foundation introduced a framework with two components: [10]
- Forta Proposal Process: A formal framework for the community to organize proposals and express support through FORT token holder voting.
- Forta Governance Council: Decision-making authority is delegated by the community to a council elected by FORT token holders. This allows ongoing community involvement through the Forta Proposal Process.
Forta Proposal Process
The Forta Proposal Process (FPP) is designed to establish a formal framework for the Forta community to contribute to the development of the Forta Network and its ecosystem. The Forta Forum serves as a public space for governance-related discussions and idea sharing. Detailed information about the FPP can be found on the Forum. [10]
Forta Governance Council
The Forta Governance Council oversees the development of the Forta Network, facilitating collective action within the community. Composed of early community members and experts, the initial council is elected through FORT token holder votes. [10]
The Council aims to simplify governance matters, reducing the burden on individual voters to prevent fatigue. While the Council handles certain decisions, any community member can express sentiment, propose changes, or signal support by voting with FORT tokens in the Forta Proposal Process. This doesn't exclude other forms of community participation, such as direct outreach to fellow community members or the Council. [10]
Defined by the Council Bylaws, the governance authority allows the Council to:
- Support initiatives for Forta's growth and sustainability.
- Facilitate the development of features and changes in the Network.
- Enable security programs for the Network's long-term security.
- Educate the Web3 ecosystem on decentralized runtime security.
- Attract and retain community members through community-building and marketing initiatives.
- Carry out actions aligning with the Council's mission.
Decisions within the Council are generally made on a majority vote basis. The community has the option to lobby for the removal of a council member if they don't represent the community's interests well. [10]
Members
The current members of the Forta Governance Council were elected through FP-1 on June 5th, 2022. The members are: [10]
- Demian Brener - Founder & CEO at OpenZeppelin, the company that founded and incubated Forta.
- Hart Lambur - Co-Founder at UMA, a proven Web3 protocol, and active Forta user.
- Jeremy Sklaroff - General Counsel at Celestia, a seasoned crypto lawyer passionate about decentralized technology.
- Jonathan Alexander - CTO at OpenZeppelin, the company that founded and incubated Forta.
- Juan Garre - Director at the Forta Foundation, a serial entrepreneur overseeing operations for the Forta Foundation since its inception.
- Mat Travizano - Founder at Rewilder, a serial entrepreneur now dedicated to addressing environmental issues with blockchain technology.
- Tomasz Stańczak - Founder at Nethermind, one of the earliest members of the Forta community involved in developing detection bots, contributing to core development, and running scan nodes within the ecosystem.
See something wrong?
The Agent Tokenization Platform (ATP):Build autonomous agents with the Agent Development Kit (ADK)
