Subscribe to wiki
Share wiki
Bookmark
Jito
The Agent Tokenization Platform (ATP):Build autonomous agents with the Agent Development Kit (ADK)
0%
Jito
Jito offers a liquid staking service for Solana that allocates maximum extractable value (MEV) rewards to participants. Users can stake their SOL through the Jito Stake Pool and receive JitoSOL tokens in return. These tokens offer liquidity while allowing holders to earn staking and MEV rewards. Lucas Bruder and Zano Sherwani are Jito's co-founders. [1]
Overview
Jito provides a liquid staking service for Solana, allowing users to stake their tokens and receive JitoSOL tokens in return. JitoSOL offers liquidity while earning both staking and MEV (maximum extractable value) rewards. This service stands out by providing additional rewards from MEV transactions and only working with validators that use software to enhance network performance and reduce congestion. JitoSOL accumulates value from these rewards and supports DeFi integrations, enabling users to earn yield from validators and lending or farming protocols. Jito aims to maximize yield for JitoSOL holders and improve the Solana network. [1]
Jito Foundation
The Jito Foundation, established in the Cayman Islands, supports the Jito Network's development and operates under its own Bylaws and governance documents. Tokenholders have decision-making power regarding the Foundation and the network. Governance of the Foundation is conducted through Tokenholder Votes, including the submission and voting on Jito Improvement Proposals (JIPs). [2]
Features
MEV Solution
Maximum Extractable Value (MEV) refers to the profit that can be gained from the specific order of transaction execution. For example, if a large swap on Orca alters a pool’s price, traders might exploit the price discrepancy for arbitrage, which is considered MEV. Similarly, liquidation bots compete to process liquidations when a price threshold is met. MEV is prevalent in traditional finance and everyday scenarios, such as fans rushing to buy concert tickets to avoid resale markups. [3]
The Jito Foundation aims to optimize the extraction and distribution of MEV to enhance Solana's security and decentralization. Solana has faced network congestion from traders attempting to capture MEV by resending transactions multiple times, similar to users repeatedly refreshing a ticket sales website that is under heavy load. To address this, Jito introduced a solution involving an auction system where traders bid for transaction sequences they believe are profitable. A block engine selects the highest-value combination of transactions, and the proceeds from these auctions are shared with stakers through JitoSOL. This mechanism reduces the incentive for spam while boosting rewards for stakers, and JitoSOL benefits from these MEV rewards without being exposed to the risks of MEV trading. [3]
Stake Delegation
The Jito Foundation's Liquid Staking aims to enhance Solana's decentralization and performance. Validators meeting specific criteria can qualify for stake delegation. The goals are to support high-quality network operators, improve decentralization by avoiding the superminority, provide high yields to JitoSOL holders, and promote the adoption of the Jito-Solana validator client, which helps increase yields and reduce spam. [4]
Validators must meet certain requirements, including running an MEV-enabled client with a commission rate of 10% or less, not being part of the superminority, and not using unsafe consensus modifications. They are ranked based on their performance, measured by average epoch credits over the last 20 epochs and adjusted for commission rates. [4]
Delegation is given to the top 200 performing validators. If fewer than 200 meet the criteria, the delegation is distributed among those who do. Pool churn is limited to 7.5% of the total value locked per 10-epoch cycle to minimize the impact on JitoSOL yields. Validators may be immediately excluded for zero epoch credits, exceeding the 10% commission rate, or engaging in malicious behavior. Performance rebalancing involves unstaking up to 7.5% of the pool from lower-scoring validators and reallocating it to higher-performing ones. [4]
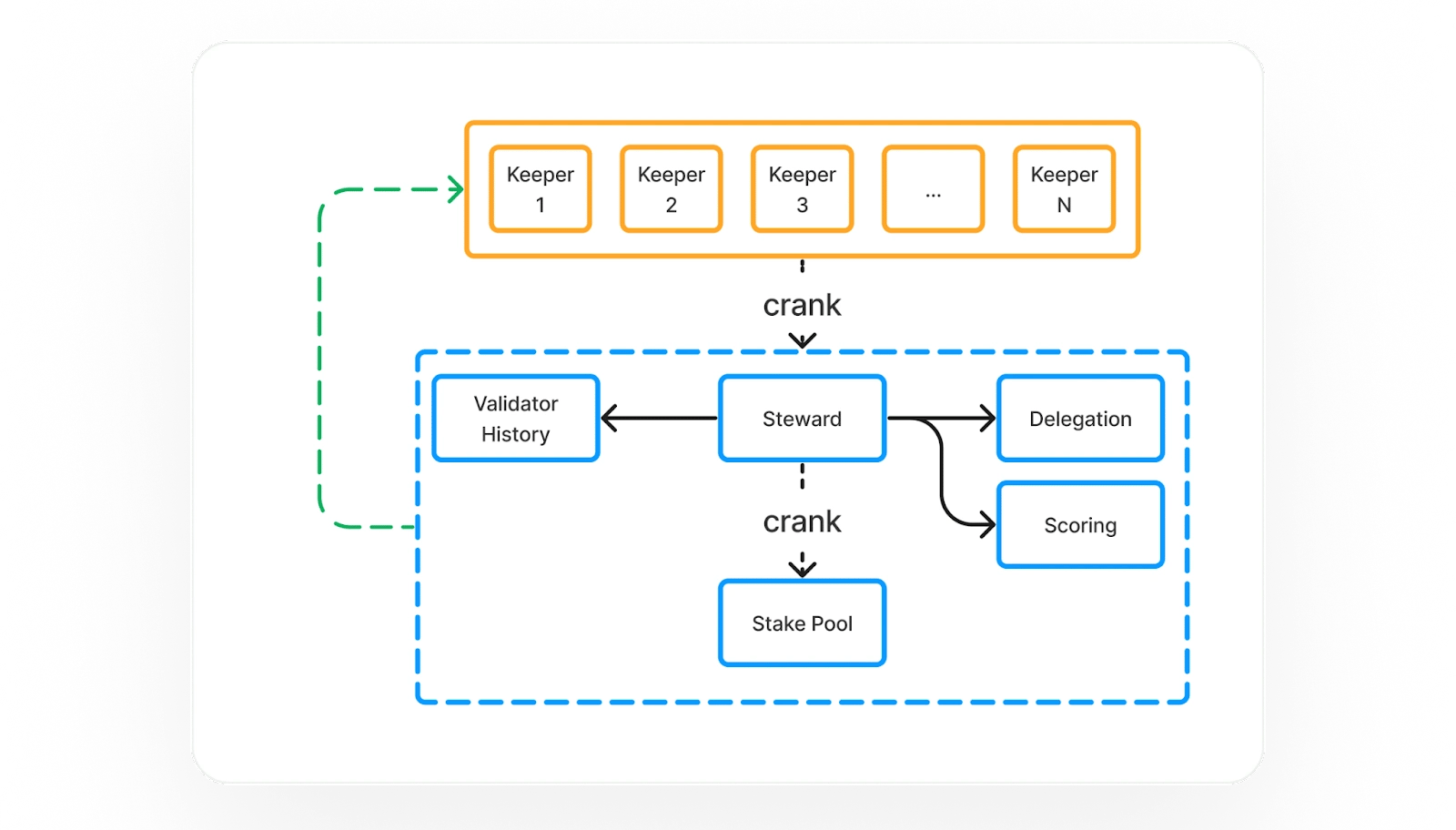
StakeNet
StakeNet consists of keepers and on-chain programs with two main components. The Validator History Program maintains a record of up to three years (512 epochs) of validator activity, offering a transparent and cryptographically verified history. This allows users and on-chain programs to assess validator performance. [5]
The Steward Program uses this historical data and other on-chain information to compute scores and determine stake delegation amounts for each validator. Keepers manage a state machine to ensure stakes are allocated to the highest-performing validators. This system operates autonomously and facilitates a transparent, efficient stake delegation process based on validated historical data. The operations of the stake pool are permissionless and accessible to anyone with a small amount of SOL for transaction execution. [5]
Validator Scoring
Since September 6, 2023, StakeNet has used on-chain data for validator scoring, which includes: [5]
- Vote Credits: Measures a validator's participation and accuracy in consensus.
- Commission: Reflects the fees charged by validators, affecting stakeholder rewards.
- MEV Commission: Additional earnings from efficient Maximum Extractable Value (MEV) extraction.
- Validator Version and Client Type: Provides insights into software reliability and operational status.
- Total Stake and Stake Rank: Shows each validator's total stake and ranking to identify those above the superminority line.
Data sources include on-chain accounts, which offer proof of authenticity, and gossip data, which provides real-time updates. StakeNet plans to expand the data set to include additional metrics such as geographical location and validator skip rates in the future. [5]
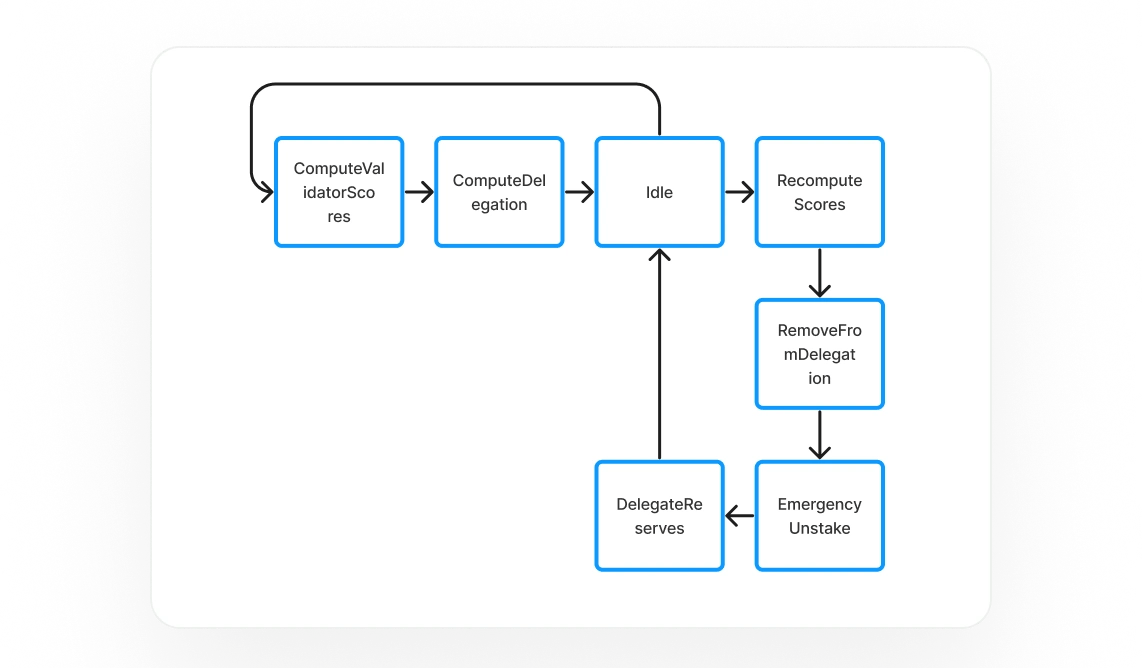
Stake Movement
Traditionally, stake pool management relies on a hot wallet controlled by the managing team, posing risks if compromised, as it could move all stakes to a single validator. To address this, StakeNet has shifted authority to an on-chain steward program. The hot wallet authority, or "Staker," is now managed by a Program Derived Address (PDA) controlled by the Steward. This change ensures that only stake movements calculated by the on-chain scoring algorithm can occur, enhancing security by preventing external manipulation. The Steward Program automates and aligns stake delegation with network health, rewarding high-performing validators and penalizing underperformers. [5]
JitoSOL
JitoSOL is a liquid staking derivative on the Solana blockchain that allows users to exchange their SOL for JitoSOL, maintaining liquidity and DeFi opportunities while earning staking yield. It also offers rewards from maximum extractable value (MEV) extraction on Solana. Users can trade JitoSOL on decentralized exchanges like Jupiter or withdraw SOL via Jito’s website after a 2-3 day cooldown. The token starts with a 1:1 exchange rate with SOL, which appreciates as rewards are accrued. [7]
JitoSOL and ETFs
The Jito Foundation has advocated for the inclusion of LSTs like JitoSOL in exchange-traded funds (ETFs) as a more flexible alternative to direct staking, especially in light of regulatory constraints around staking within traditional ETFs. LSTs offer benefits aligned with ETF architecture, such as collateral utility, in-kind redemption, and improved yield management. JitoSOL’s structure and classification as a non-security commodity position it as a candidate for ETF inclusion, enabling both long-term and short-term holders to gain yield exposure to Solana without operational staking complexity. [8]
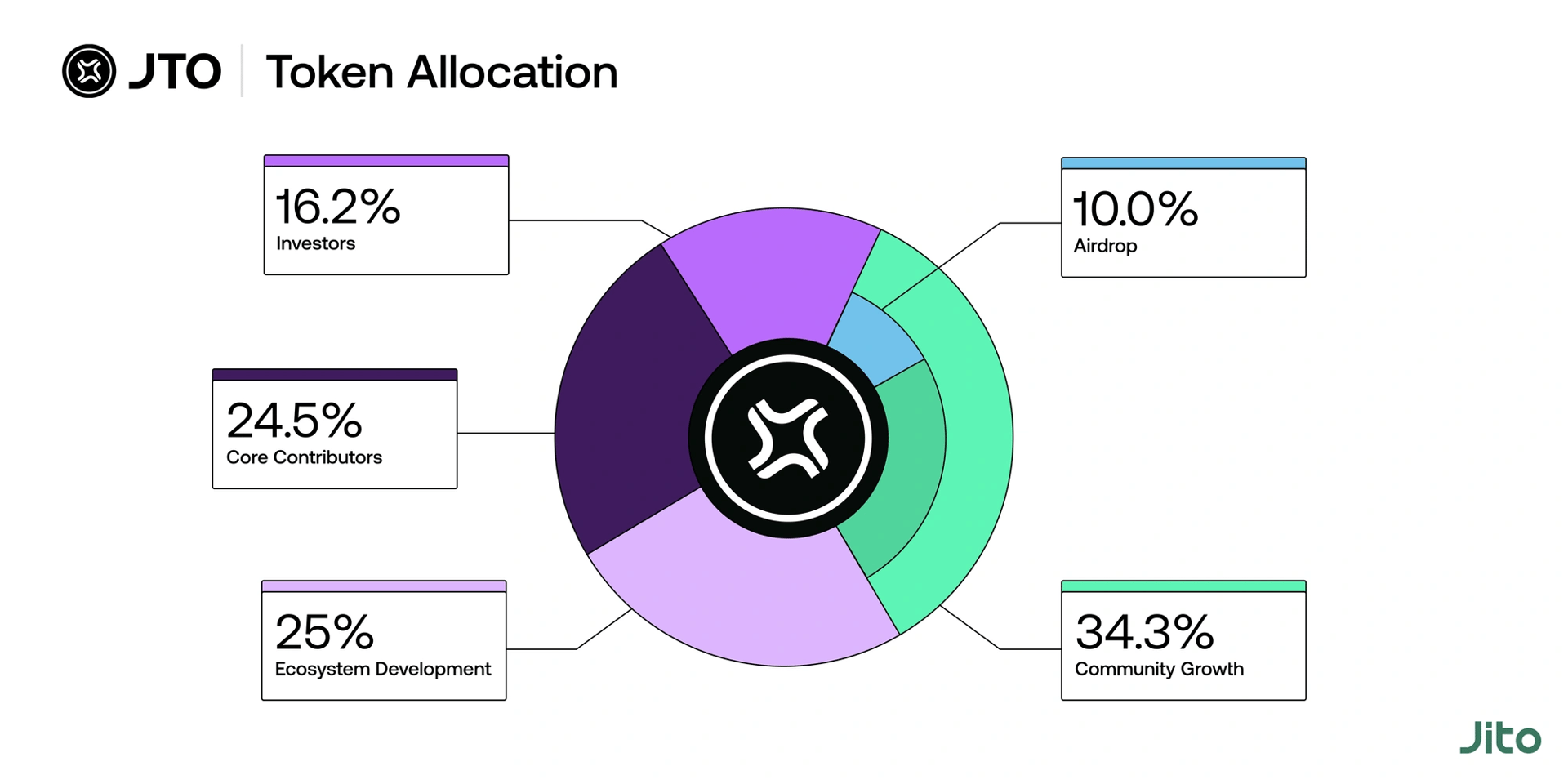
JTO Token
The JTO governance token enables community members to influence the decision-making and direction of the Jito Network directly. JTO has a total supply of 1B and has the following allocation: [6]
- Community Growth: 34.2%
- Ecosystem Development: 25%
- Core Contributors: 24.5%
- Investors: 16.2%
- Airdrop: 10%
Partnerships
- Maple Finance
- Midcurve
- Phantom
- Infinex
- Drift
- Mango
- MarginFi
- Solend
- Orca
- Kamino Finance
- Raydium
- Meteora
- Invariant
See something wrong?
The Agent Tokenization Platform (ATP):Build autonomous agents with the Agent Development Kit (ADK)
