Subscribe to wiki
Share wiki
Bookmark
IQ.wiki
The Agent Tokenization Platform (ATP):Build autonomous agents with the Agent Development Kit (ADK)
0%
IQ.wiki
IQ.wiki is the largest blockchain and cryptocurrency encyclopedia in the world with thousands of pages. IQ.wiki is powered by IQ token and all edits on the platform are recorded on-chain through Polygon and the InterPlanetary File System (IPFS). The encyclopedia is governed by IQ token stakers. The entire database of content from IQ.wiki is also integrated into AIDEN, an AI agent for blockchain knowledge.
IQ.wiki is one of the dApps that makes up the IQ AI ecosystem, which also includes Agent Tokenization Platform (ATP), a platform enabling users to create tokenized AI agents that can operate autonomously. [17] [18][30]
Sophia, an AI agent for editing, updating, and creating cryptocurrency-related content on IQ.wiki, was launched as one of the flagship tokenized agents through IQ's ATP platform.
Overview
Blockchain
All edits on IQ.wiki are recorded on the Polygon blockchain with the transaction hash for each edit stored on-chain. The data and images uploaded as part of each wiki are stored on IPFS and the hashes are included on each page for the users to verify. [18]
Ranked Lists
IQ.wiki added ranked lists to its functionality where the team covers not only the top cryptocurrencies but also their founders, date founded, and respective blockchains. IQ.wiki’s rankings combine CoinMarketCap’s price data, such as price as marketcap with in-depth wiki articles covering categories from stablecoins to AI.[21]
Events
IQ.wiki's interface features an Events page, providing detailed information about conferences, hackathons, and other crypto and blockchain-focused events around the world. [22]
IQ Token
The IQ token is integral to IQ.wiki. The IQ token is a cryptocurrency dedicated to building the next wave of decentralized finance with IQ AI ecosystem. Aside from IQ.wiki, IQ powers Agent Tokenization Platform (ATP), enabling users to create tokenized agents that can operate autonomously.[18] [17]
Language Support
To cater to the growing demand for IQ.wiki to expand beyond just the English language, BrainDAO announced the launch of IQ.wiki Korea and IQ.wiki China in February 2024. Users got the possibility to switch to the Korean or Chinese IQ.wiki interface and have any article translated into Korean or Chinese by AI.[23]
Integrations
The team continues to build on IQ.wiki’s database of thousands of articles and integrate its content across the cryptocurrency space. In 2023, IQ.wiki established a partnership with Bond Protocol to integrate the wikis into their bond marketplace. Furthermore, many DeFi protocols, including Ramses, Frax Finance, Lodestar Finance, and ZeroLiquid, have integrated their IQ.wiki page into their respective landing pages.[21]
ENS
IQ.wiki integrates Ethereum Name Service (ENS). If a user has resolved their ENS to their blockchain address, their ENS will automatically populate as their username when they log in. [18]
Market Data
IQ.wiki pages on cryptocurrencies, NFT projects, and exchanges automatically pull market data and statistics from Coingecko and other reliable APIs. [18]
Leadership
IQ.wiki is led by Chief Brain Navin Vethanayagam who leads IQ.wiki's Community, Content, and Growth team, and Chief Technology Officer Cesar Rodriguez who leads IQ.wiki's Engineering Department. Navin previously served as Everipedia's Chief Community Officer for several years. Cesar Rodriguez was previously Everipedia's Director of Engineering and led development for the IQ.wiki platform. [24] Cesar Rodriguez also manages the BrainDAO engineering team of project managers, backend engineers, front-end engineers, and UX designers.[20]
The managers of IQ.wiki's Community, Content & Growth team include Andy Cho who serves as IQ.wiki's Director of Business Development, Violetta Ziborova who serves as IQ.wiki's Content Manager, and Kevin Wang who serves as IQ.wiki's Director of China.
After the launch of the new IQ.wiki platform in October of 2011, Everipedia Co-founder and CEO Theodor Forselius as well as CFO and COO Suchet Dhindsa transitioned over to the parent company of IQ.wiki, Brainfund, which is dedicated to more broadly investing in the future of knowledge. Everipedia co-founders Sam Kazemian and Travis Moore have also joined the parent company as board members.
History
IQ.wiki began as Everipedia, the “encyclopedia of everything”, in 2014 and became the world’s first blockchain encyclopedia in 2018 after launching the IQ token. In 2022, Everipedia expanded to the Polygon blockchain and rebranded as IQ.wiki.
Pre-blockchain Origins
Everipedia was founded by Sam Kazemian and Theodor Forselius at UCLA in December 2014. The website was created as a side project out of Kazemian's dorm room. [4][5]
Originally, Everipedia started with a mission to build a more modern and inclusive version of Wikipedia. Sam and Theodor were inspired by Y Combinator's co-founder Paul Graham's blog post published in 2008 entitled "Startup Ideas We'd Like to Fund." In his list of ideas, he called for "more open alternatives to Wikipedia". [3]
In April 2015, Travis Moore joined Everipedia's team as a co-founder and their CTO. In September 2017, Suchet Dhindsa joined as Everipedia's COO and CFO.
In July 2015, Everipedia received seed funding from Mucker Capital. Shortly after, Everipedia received its first outside investment from angel investor Kami Parsa. It also received funds from multiple other angel investors that year, including David Segura and David Petersen, the co-founder and CEO of Buildzoom. In 2016, Everipedia received $130,000 on Wefunder, a crowdfunding service that connects start-ups with investors online.
Everipedia becomes the first Blockchain Encyclopedia
On December 6, 2017, Everipedia announced they were building "the first encyclopedia on the blockchain." They stated they are working on a cryptocurrency token called IQ which would be used to govern the platform and incentivize editors. Prior to expanding onto the blockchain, Everipedia had an IQ points system where editors would get non-tradable points to signify how many contributions they had made to the site. [14]
On the same day, Wikipedia co-founder Larry Sanger joined the team serving as Everipedia's Chief Information Officer until he launched the non-profit Knowledge Standards Foundation in 2019. [14][15]
On February 8, 2018, Everipedia announced that it had received $30 million of funding from a group of strategic investors in a Series A led by Galaxy Digital to build Everipedia into the world’s first blockchain encyclopedia. [6]
On July 12, 2018, Everipedia moved onto the EOS blockchain and launched the IQ token airdropping 51% of the IQ token supply to EOS holders. Everipedia Co-Founder and CTO Travis Moore explained that by doing an airdrop Everipedia would ensure the widest possible distribution of IQ tokens with every EOS holder receiving tokens. [16]
"The airdrop will play a significant role in helping Everipedia accomplish as wide of a distribution as possible for IQ tokens."
After Everipedia became a blockchain encyclopedia in 2018 the readership and editorship on Everipedia moved toward crypto content. [20]
IQ OraQles with The Associated Press
2020 US Presidential Election
In 2020, IQ.wiki known as Everipedia at the time developed IQ OraQles, a service that allows verified first parties to bring real-world information on-chain. In 2020, The Associated Press used the IQ OraQles system to publish U.S. election race calls on Ethereum. AP signed the data with their own Ethereum address 0x436Ee8cB3a351893b77F8B57c9772DAEc3a96445 which is listed on their website. This marked the first time a US election was called on the blockchain. The historic moment was covered by publications including Forbes, CoinDesk, and Nasdaq News. The on-chain results from the election were also used to resolve a Yield Wars prediction market which saw over $200,000 in volume. [9][8][7][2][1] [10]
The system was later used by the Associated Press to record events including the 2020 US Senate Election Races, Super Bowl LV, and March Madness 2021. [19]
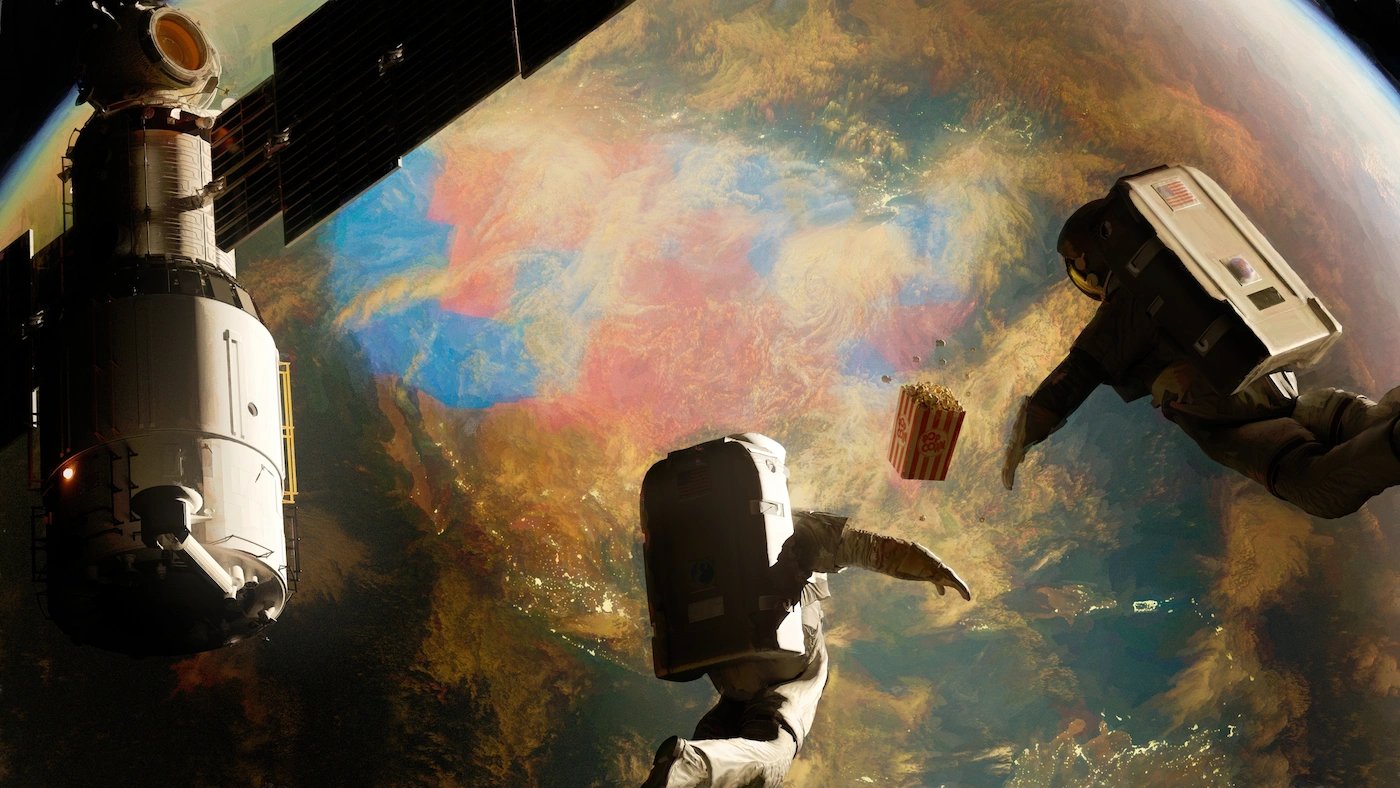
AP's First NFT
In March 2021, AP collaborated with Everipedia to create a one-of-one NFT artwork commemorating the first US election recorded on the blockchain titled The Associated Press calls the 2020 Presidential Election on Blockchain - A View from Outer Space. The NFT artwork was created and published on Ethereum by AP using their Ethereum address 0x436Ee8cB3a351893b77F8B57c9772DAEc3a96445. AP used this same address to declare the winner of the United States 2020 Presidential Election. AP’s unique Ethereum address acts as a cryptographic signature for The Associated Press calls the 2020 Presidential Election on Blockchain - A View from Outer Space and shows that AP has verified the historic election data displayed in the piece as well as the metadata in the NFT. Within the NFT’s metadata AP has included the exact date and time that AP called the election, the electoral college votes won by Republicans and Democrats, the names of both candidates, and the number of votes received by each candidate. [13][12][11]
On March 11, 2021, The Associated Press calls the 2020 Presidential Election on Blockchain - A View from Outer Space sold for 100.888 ETH in an auction on OpenSea.

Rebranding to IQ.wiki
IQ.wiki was previously known as Everipedia. On October 11, 2022, Everipedia rebranded as IQ.wiki. The original Everipedia name came from the original vision of creating an encyclopedia of everything. However, after Everipedia became a blockchain encyclopedia in 2018 the readership and editorship on Everipedia moved toward crypto content. The new name was chosen to reflect the central role of the IQ token and blockchain technology in the platform. Along with the rebrand, IQ.wiki added several Web3 features and integrations to better serve the crypto community. [20] [18]
See something wrong?
The Agent Tokenization Platform (ATP):Build autonomous agents with the Agent Development Kit (ADK)
