Subscribe to wiki
Share wiki
Bookmark
Botanix Labs
We've just announced IQ AI.
Botanix Labs
Botanix Labs is a protocol that aims to transform Bitcoin into a programmable layer for the future of finance by building the first fully decentralized EVM-equivalent Layer 2 solution on Bitcoin, Spiderchain. This combines the ease of EVM with Bitcoin's decentralization and security.[1][2]
Overview
Botanix Labs, established in 2022 by Willem Schroe, Alisia Painter, and Armin Sabouri, aims to redefine Bitcoin's role in finance by positioning it as a programmable layer. Their objective is to integrate Bitcoin's security features with Ethereum's user-friendly interface. With the Botanix Labs Testnet having launched November 29th, 2023, they are working on developing the initial fully decentralized EVM-equivalent Layer 2 solution on Bitcoin to facilitate decentralized application (dApp) development.
Utilizing Bitcoin's Proof-of-Work (PoW) as a Layer 1 for foundational settlement and decentralization, the Botanix Protocol incorporates a Proof-of-Stake consensus model. This enables stakeholders to securely store their bitcoin on the Spiderchain, facilitating staking for all Bitcoin holders.
Botanix Labs aims to overcome challenges faced by Bitcoin in dApp development by integrating Ethereum's infrastructure with Bitcoin's security features. By merging Ethereum onto Bitcoin, Botanix leverages Bitcoin's security while tapping into Ethereum's capabilities. Through its Spiderchain technology, Botanix achieves complete decentralization.
The journey to founding Botanix Labs began with Willem Schroe's firsthand experience of hyperinflation in Lebanon. Driven to protect families from economic crises, Schroe embarked on a mission to create a platform that combines Bitcoin's security with Ethereum's applications.[1][2][3][4][5][19][6]
Transaction Fees
Transaction fees on Botanix are akin to Ethereum rather than Bitcoin, with three main types: Layer 2 transactions, Layer 1 to Layer 2 (bridge-ins), and Layer 2 to Layer 1 (bridge-outs). Fees, denominated in bitcoin, follow Ethereum's gas fee formula. For bridge-ins, users pay standard bitcoin transaction costs based on the mempool. Bridge-outs, involving transactions on both Layer 2 and Layer 1, are slightly pricier due to their dual nature. The cost of initiation follows standard Layer 2 fees, while finalization depends on the mempool and Layer 1 congestion.[10]
Products
Spiderchain
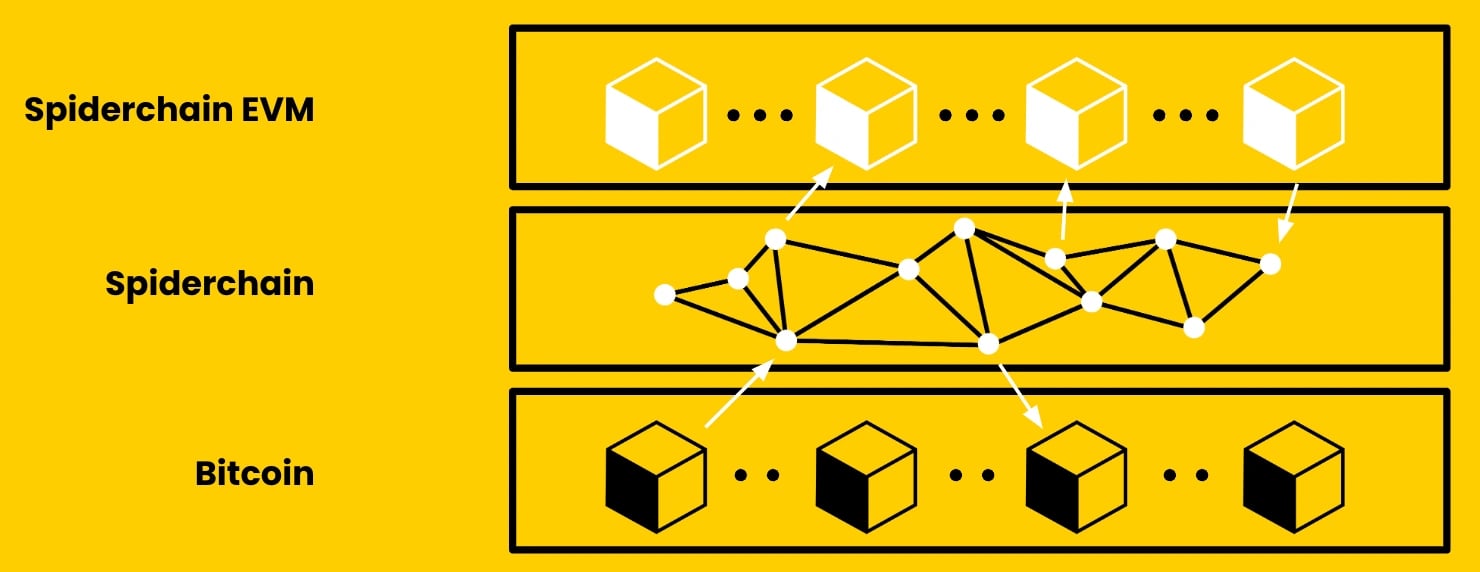
Botanix Labs introduces the Spiderchain, a novel component for second-layer blockchains, managed by Botanix Orchestrators. Each 'leg' of the Spiderchain represents a multisig wallet, ensuring security through decentralization. Linked to every Bitcoin block, it separates Bitcoin assets from the Bitcoin blockchain to the EVM, enabling a transition from the UTXO model to the EVM's account model.
Engineered with rigorous security standards, the Spiderchain ensures asset protection against potential attacks. Its forward security design locks bitcoin securely within established multisig wallets, preventing theft. Operating on two core components, the Spiderchain EVM leverages the Ethereum Virtual Machine and the Spiderchain, comprising a dynamic network of multisigs, aligning with Satoshi Nakamoto's vision for decentralized blockchain networks.[7][8]
Forward Security
The Spiderchain's "Forward Security" feature aims to safeguard Botanix's Proof-of-Stake protocol from attacks. It ensures that even if an attacker gains control of 2/3rds of the stake, they cannot steal Bitcoin due to the protocol's design. New multisigs are generated with each bitcoin block, distributing the stored bitcoin across multiple wallets. Fresh bitcoin is stored in new multisigs, enhancing security. Liveness Epochs and a Last-In-First-Out (LIFO) system further protect older wallets. These measures aim to prevent retroactive compromise, preserving Botanix's value integrity.[11][12]
Orchestrator Node
Botanix Labs employs Orchestrator nodes to facilitate its protocol and validate transactions. These nodes ensure liquidity on both the Bitcoin and Botanix sides and oversee the safe storage of bridged Bitcoin in multi-signature wallets. Orchestrator nodes also play a crucial role in block construction and managing BTC operations on the Botanix EVM.
Individuals can operate an Orchestrator node by staking a certain amount, with the understanding that malicious behavior may lead to stake slashing. The Spiderchain's security follows Proof-of-Stake models, ensuring resilience against adversarial collaboration. Those interested are encouraged to consult available documentation.
Each Bitcoin block generates a new multi-signature wallet, with Orchestrators chosen randomly from a decentralized network.[9]
Botanix Blockchain
The Botanix blockchain process operates in a steady state with three primary functions. Initially, it detects incoming transactions from users to Orchestrators on the Bitcoin parent chain (peg-in). Subsequently, it executes state transitions to create new blocks. Finally, it manages the transfer of assets from the Spiderchain back to the parent chain (peg-out).
- Detect incoming transactions to Orchestrators and process them via peg-in.
- Execute the Botanix consensus and state progression, akin to Ethereum block progression.
- Manage asset transfers from the Spiderchain to the parent chain through peg-out.
Due to differing blockchain speeds (Bitcoin operates at approximately 10 minutes per block, while Botanix runs at 2-3 seconds per block), tasks primarily involve updating the UTXO "mempool." Orchestrator O, chosen randomly in a Proof of Stake system, constructs the blocks. Upon a Bitcoin block's arrival, Orchestrator O executes the Botanix operation, finalizing the EVM chain.[13]
Funding
In May 2024, Botanix Labs completed an $11.5 million funding round for its BTC L2 solution Spiderchain, with investors like Polychain Capital, Placeholder Capital, Valor Equity Partners, ABCDE, and several notable angels. The funds will support the development of Spiderchain.[14][15]
Partnerships
Botanix Labs x Palladium Labs
On March 19, 2024, Botanix Labs forged a partnership with Palladium Labs to introduce a Bitcoin-native stablecoin on the Botanix EVM. This collaboration enhances the Bitcoin DeFi ecosystem by addressing common risks in DeFi infrastructure. Palladium's stablecoin, PUSD, operates on an over-collateralized basis, aiming for resilience and reliability through its algorithmic monetary policy. By leveraging the Botanix EVM and Spiderchain, Palladium seeks to fortify self-sovereign financial applications on Bitcoin.
This stablecoin will be integrated into the Botanix EVM, which has undergone testing since November 2023 with over 5,000 experimental token projects. Willem Schroe, Botanix Labs co-founder, emphasizes the significance of native stablecoins for Bitcoin's technological evolution and expresses support for Palladium's initiative.[16]

Botanix Labs x Yala Labs
On March 21, 2024, Botanix Labs partnered with Yala Labs to enhance the Yala protocol's decentralized financial (DeFi) services using the Botanix EVM. Yala's stablecoin (YU) aims to increase stability and liquidity across ecosystems without needing bridges or relocating Bitcoin collateral. Together, they aim to accelerate the development of Bitcoin-native DeFi applications and services.[17]

Botanix Labs x Vertex
On May 13th, 2024, Botanix announced a partnership with the Vertex Protocol team to introduce Vertex to the Bitcoin ecosystem. Vertex, initially deployed on Arbitrum, aims to provide an all-in-one decentralized exchange for Bitcoin users within the Spiderchain ecosystem.[18]

See something wrong?
