DeAgentAI
DeAgentAI is a decentralized infrastructure project that develops a framework for autonomous AI Agents designed to operate securely and verifiably on blockchain networks. Its infrastructure enables AI entities, referred to as DeAgents, to maintain a persistent identity, interact with users and other agents, and execute actions within decentralized systems. [1]
Overview
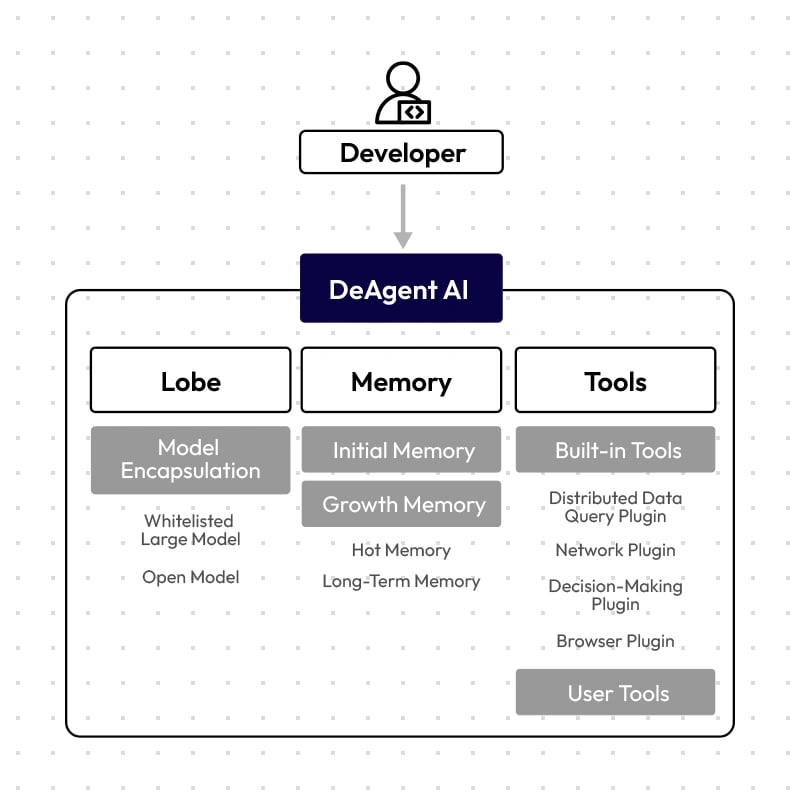
DeAgentAI is a decentralized infrastructure designed to allow AI Agents to function autonomously and reliably within Web3 ecosystems. The project aims to address core limitations of existing blockchain architectures, which it identifies as lacking the efficiency and structure necessary for AI-driven operations. The framework focuses on solving three critical challenges: achieving verifiable consensus on probabilistic AI outputs, ensuring unique and immutable agent identities, and maintaining a continuous, traceable on-chain memory. By addressing these issues, DeAgentAI seeks to provide a foundation for scalable and trustworthy AI participation in decentralized applications. [2]
The project's framework, known as the Autonomous Execution Network, defines the lifecycle for its AI Agents—called DeAgents—including their creation, interaction, and evolution on distributed systems. Each DeAgent consists of a cognitive engine (Lobe), a persistent record of its memory, and a set of tools for performing actions or accessing external data. The network involves several distinct roles: Creators deploy agents, Users interact with them, Executors process their computational logic, and Committers validate the outcomes to maintain network consensus. This structure is intended to enable agents to operate independently and predictably on-chain, supporting applications such as autonomous DeFi protocols, evolving blockchain-based games, and AI-assisted governance systems. [3]
Architecture
Lobe
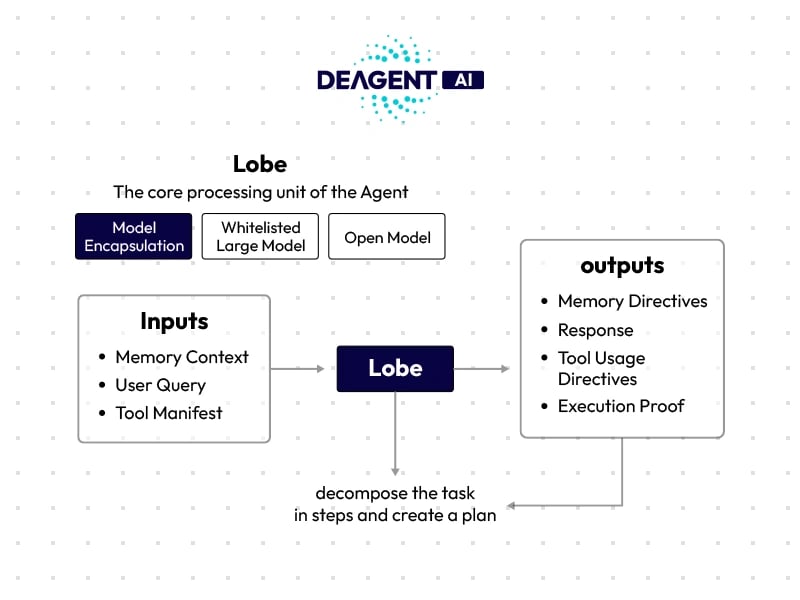
The Lobe functions as the Agent’s cognitive core — the component responsible for processing inputs, executing reasoning, and producing verifiable outputs. It integrates multiple data streams, including user queries, relevant memory context, and available tools, before invoking one or more foundational AI models. After processing, it generates structured outputs that may include user responses, memory updates, and execution proofs. Lobes can be locally optimized, remotely hosted, or developed by the broader community, with each instance identified by a specific Uniform Resource Identifier (URI) that tells Executors how to access and run it.
To maintain integrity and trust within decentralized agent systems, the DeAgent framework introduces Lobe Consensus, a mechanism ensuring that the Lobe’s execution is verifiable. This involves proving both model invocation and surrounding logic using different techniques: Zero-Knowledge Proofs for non-model logic, TLS-based proofs for closed-source APIs, and entropy-based selection for open-source models. The entropy method measures the similarity between input and output embeddings, selecting the most contextually relevant result while discouraging tampering or manipulation. Together, these methods establish a balance between security, transparency, and performance, ensuring each Lobe’s output can be trusted within a distributed AI ecosystem. [4]
Memory and Tools
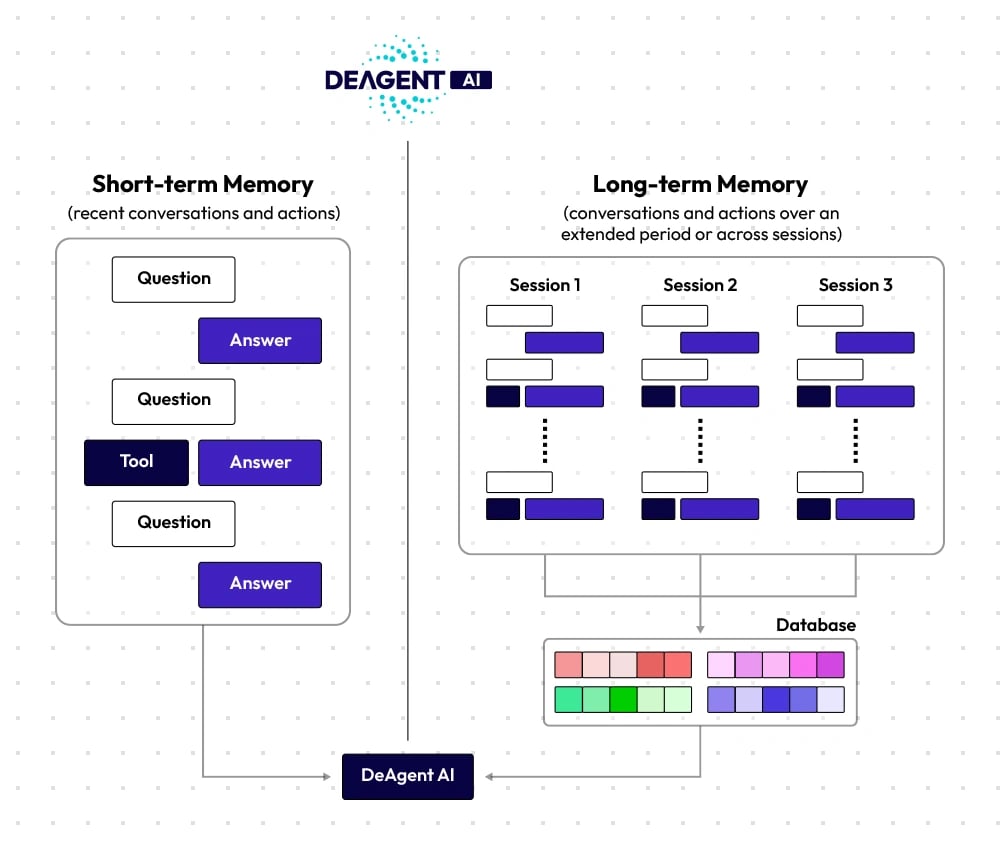
While the Lobe provides cognitive processing, an Agent’s individuality and functionality come from its Memory and Tools, which define its persistent state and abilities. Memory stores the Agent’s complete interaction history across the distributed system, creating a verifiable Long-term Memory. For each interaction, the Agent retrieves relevant portions through a combination of Short-term Memory (recent exchanges) and Long-term Memory (context fetched via Retrieval-Augmented Generation). This structure allows Agents to recall prior experiences and respond continuously, while Committers verify the authenticity of referenced historical data in the ledger. Although the retrieval and scoring process for RAG is not fully consensus-verified, Executors are incentivized to provide accurate and relevant context to ensure consistent performance.
Tools extend the Agent’s capacity beyond reasoning into direct interaction with data, systems, and environments. Built-in tools enable secure blockchain queries, verifiable data retrieval via web access, and system-level operations via the Decision Plugin. The Decision Plugin, in particular, allows Agents to evaluate and authorize actions such as contract execution or governance votes through a structured approval process verified by Committers. This mechanism transitions Agents from static reasoning entities to autonomous actors capable of executing verified, consequential decisions within decentralized systems. Through the combined use of Memory and Tools, each Agent develops a distinct personality—rooted in its experiences, capabilities, and decision-making logic. [5]
Agent-to-Agent (A2A) Protocol
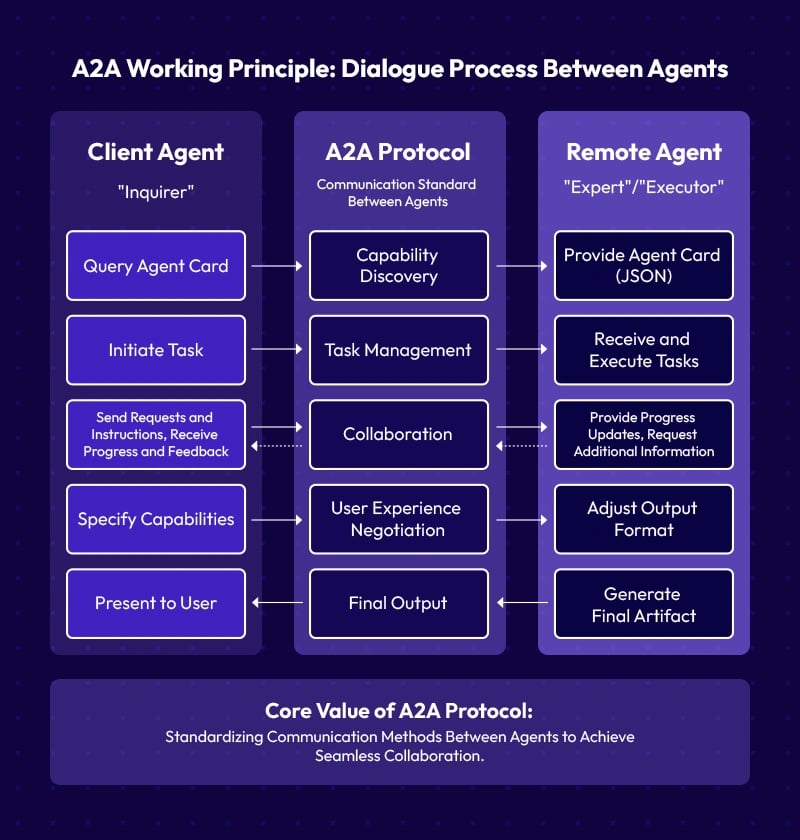
The Agent-to-Agent (A2A) Protocol enables autonomous agents within the DeAgentAI framework to communicate, collaborate, and coordinate directly with one another. This protocol operates via standard on-chain transactions, where one agent sends a transaction containing a structured payload to another agent’s address. The receiving agent processes this payload using its own Lobe, Memory, and Tools, producing a response that may include state updates, decisions, or additional A2A messages. Once verified and accepted by Committers, these exchanges are recorded on-chain, ensuring transparency and continuity across interactions.
Through A2A communication, agents can exchange information, delegate specialized tasks, coordinate complex operations, and negotiate to achieve shared goals. Each interaction adheres to the system’s core principles of consensus, identity, and continuity, which is intended to enable multi-agent collaboration in a verifiable and deterministic manner. This protocol forms the foundation for emergent system behavior, where interconnected agents can collectively reason, act, and evolve within a decentralized environment. [6]
Multi-Party Computation (MPC)
Multi-Party Computation (MPC) is utilized to enable trustless execution within the DeAgentAI framework, allowing decentralized participants to collectively authorize and perform sensitive actions without relying on a single point of control. When an agent issues an approved decision through its Decision Plugin, the Committers—who collectively manage cryptographic key shares—initiate an MPC process to generate the necessary authorization signature. This process ensures that no individual participant ever reconstructs or accesses the full private key, maintaining confidentiality and integrity. The resulting signature is then broadcast to carry out the approved on-chain action, such as executing a transaction.
By distributing authority among multiple participants, MPC enhances security and decentralization. It is designed to remove single points of failure, ensure cryptographic operations are verifiable, and enable agents to perform critical tasks autonomously and securely. This mechanism is foundational for allowing agents to act as reliable custodians, decision-makers, and participants in decentralized governance without compromising system integrity. [7]
Implementations
AlphaX
AlphaX is an autonomous AI agent operating within the DeAgentAI framework, utilizing the principles of consensus, identity, and continuity to ensure reliable and verifiable outputs. It is designed to generate predictive signals for cryptocurrencies such as BTC, ETH, and SUI over time horizons of 2 to 72 hours. Its accuracy is intended to be enhanced through user feedback and continuous model refinement. AlphaX uses persistent memory to adapt its decision-making over time. In its autonomous mode, it can execute trading strategies in real-time in response to market conditions, allowing for both predictive analysis and fully automated trading. The project has reported a prediction accuracy rate exceeding 70% and an annualized return of 455% during a testing period. [8]
AIA
The $AIA token is the foundational currency of the DeAgentAI ecosystem, designed to power a network of autonomous AI Agents that act as independent, on-chain economic entities. Instead of serving merely as a governance or payment token, $AIA provides the economic bandwidth that enables AI Agents to make decisions, exchange value, and evolve collaboratively. It establishes a shared incentive structure aligning creators, users, validators, and trainers toward the collective growth and intelligence of the system.
Functionally, $AIA underpins all core activities within the ecosystem. It is used as the medium of exchange for services such as Agent creation, interaction, and access to premium features. Participants can stake $AIA to enhance network security and data validation, earning rewards for their contribution. Additionally, token holders have governance rights that allow them to vote on key parameters and strategic decisions, embedding decentralized oversight into the system’s long-term development. [9]

Tokenomics
AIA has a total supply of 1B tokens and has the following allocation:
- Investors: 21%
- Ecosystem: 20.2%
- Team: 18%
- Community: 16.5%
- Community Airdrop: 13.5%
- Advisor: 5%
- Staking Rewards: 5%
- Liquidity: 0.8%
