Subscribe to wiki
Share wiki
Bookmark
Celo
The Agent Tokenization Platform (ATP):Build autonomous agents with the Agent Development Kit (ADK)
0%
Celo
Celo is an Ethereum Layer-2 and mobile-first blockchain network designed for fast, low-cost payments globally. The Celo ecosystem includes a proof-of-stake blockchain (the Celo Platform), the native CELO token, USDC and USDT as gas currencies, Mento stable assets (cUSD, cEUR, cREAL, eXOF), and integrations with infrastructure like Uniswap V3, Curve, Chainlink, and Rarible. Launched on Earth Day in 2020, Celo's open-source mainnet supports over 1,000 projects aimed at global prosperity. Rene Reinsberg and Marek Olszewski are the co-founders of Celo, the Celo Foundation, and cLabs. [1][2]
Overview
Celo is an Ethereum Layer-2 and mobile-first blockchain network designed for fast, low-cost payments globally. It was designed to create an accessible global financial ecosystem for mobile users, allowing entry with just a mobile number. Key features include a Layer-1 protocol, EVM compatibility, proof-of-stake, a carbon-negative approach, mobile-first identity, ultra-light clients, localized stablecoins (cUSD, cEUR, cREAL), and gas payable in multiple currencies. Celo facilitates easy payments by mapping phone numbers to wallet addresses using a decentralized identity layer, with mobile participants earning rewards for system security and maintenance. Using a novel address-based encryption algorithm and stable-value tokens pegged to fiat currencies, Celo makes sending payments as easy as sending a text by mapping phone numbers to wallet addresses and offering rewards for securing and maintaining the system. [1][2]
Dango Testnet
First proposed during EthCC 2023, The Dango Testnet is the first public test network for Celo Layer 2, aimed at developers working on Cel2. Launched on July 7th, 2024, its goals include demonstrating successful state migration and setting a solid foundation for future developments. Dango will run alongside the existing Alfajores testnet, allowing infrastructure providers to adapt to the L2 codebase before upgrading other testnets and, eventually, the Celo mainnet. Dango retains most of Celo’s features while adding new capabilities such as full Alfajores history and state, dual use of the CELO token, fee abstraction, native bridging to and from Layer 1, data availability via EigenDA, staking, and Ultragreen Money. [10][14]
Architecture
Celo Stack
Celo focuses on providing a simple user experience for those unfamiliar with cryptocurrencies and using low-cost devices with limited connectivity. It employs a full-stack approach, designing each layer with the end-user in mind while considering other stakeholders, such as network node operators, who support the user experience. [3]
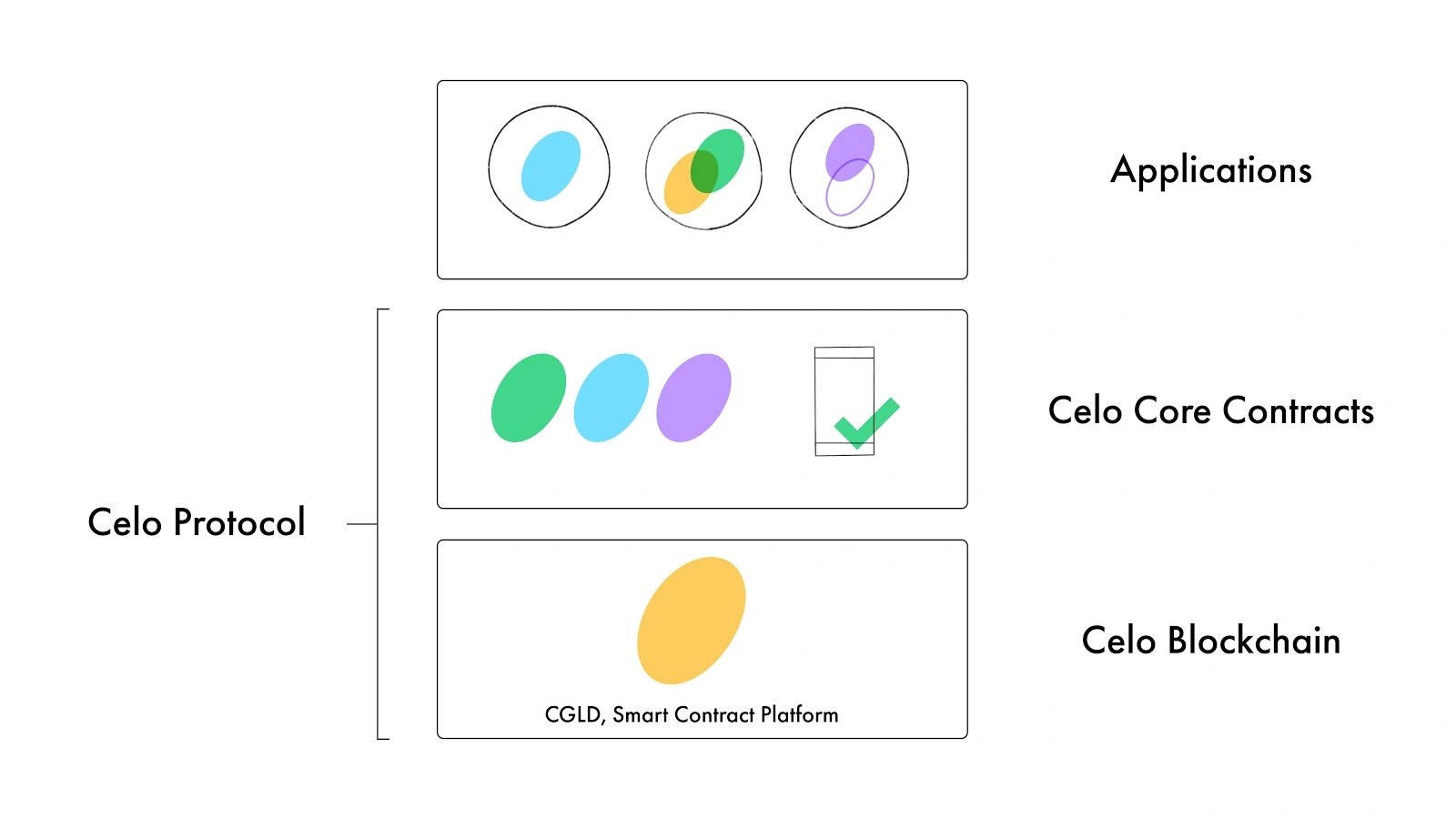
Celo Blockchain
Celo is an open cryptographic protocol that enables secure and decentralized transactions and smart contracts. While sharing ancestry with Ethereum and maintaining full EVM compatibility, Celo uses a Byzantine Fault Tolerant (BFT) consensus mechanism (Proof-of-Stake) instead of Proof-of-Work. It features unique block and transaction formats, client synchronization protocols, and gas payment and pricing mechanisms. [3]
Core Contracts
Celo Core Contracts consist of smart contracts on the Celo blockchain that handle platform features like ERC-20 stable currencies, identity attestations, proof-of-stake, and governance. A decentralized governance process manages these upgradeable contracts. Applications built on the Celo Platform, such as the Celo Wallet app, enable end-users to manage accounts and make payments by interacting with the Celo blockchain and invoking the Celo Core Contracts’ API. Third-party developers can deploy custom smart contracts to leverage these core contracts, and some application functionalities may use centralized cloud services. Combining the Celo blockchain and Celo Core Contracts forms the Celo Protocol. [3]
Celo Protocol
Celo's blockchain reference implementation is based on go-ethereum, the Go implementation of the Ethereum protocol. While recognizing Ethereum as an independent project with its trajectory, the Celo team hopes to contribute changes, where applicable, indebted to the Geth community for their foundational work. Core components of the Celo protocol are implemented at the smart contract level and off-chain. Celo employs a Byzantine Fault Tolerant (BFT) consensus protocol to agree on new blocks. The software instances participating in this consensus protocol are known as validators, specifically active or elected validators, distinguishing them from registered validators who are not actively selected. Celo’s consensus protocol is based on Istanbul (IBFT), an implementation developed by AMIS and proposed as an extension to go-ethereum. Though IBFT was never merged into go-ethereum, variants exist in both the Quorum and Pantheon clients. Celo has updated Istanbul to align with the latest go-ethereum releases, addressing correctness liveness issues and enhancing scalability and security. [4]
Validator Elections
In Celo's Validator Elections, holders of the native asset, CELO, may participate and earn rewards. Accounts do not vote for validators directly but instead for validator groups. Before voting, CELO holders move balances into the Locked Gold smart contract. Locked Gold can be used concurrently to place votes in Validator Elections, maintain a stake for registering as a validator or validator group, and vote on on-chain Governance proposals. This allows validators and groups to vote and earn rewards with their stake. [5]
Ultralight Sync
In addition to Ethereum's full, fast, and light sync modes, Celo supports an ultralight sync mode. Ultralight nodes compute the validator set for the current epoch by downloading the last header of each previous epoch and applying the validator set diff. They then download the latest block header, verifying that at least two-thirds of the validator set for the current epoch signed it. Ultralight nodes download approximately 17,000 times fewer headers than light nodes to sync the latest block on the Celo mainnet with 5-second block periods and 1-day epochs. [6]
Governance
Celo employs an on-chain governance mechanism to manage and upgrade the protocol, including changes to smart contracts, adding stable currencies, or modifying reserve asset allocation. All changes require approval from CELO holders, with a quorum threshold determining the necessary number of votes for a proposal to pass. [7]
Celo Network
The Celo network's topology consists of machines running the Celo blockchain software in different configurations. Validators collect transactions from other nodes, execute related smart contracts to form new blocks, and use a Byzantine Fault Tolerant (BFT) consensus protocol to advance the network's state. Due to the scalability and security limitations of BFT protocols, only a limited set of nodes can act as validators through a proof-of-stake mechanism. Full Nodes, which are not configured or elected as validators, primarily serve requests from light clients and forward transactions in exchange for transaction fees. They maintain at least a partial blockchain history and can join or leave the network anytime. Light Clients, such as those running on user devices for the Celo Wallet, connect to full nodes to request account and transaction data and to sign and submit new transactions without retaining the full state of the blockchain. [3]
Celo Wallet
The Celo Wallet application is an unmanaged wallet enabling users to self-custody their funds using their keys and accounts. Critical functions like sending transactions and checking balances are executed trustlessly using a peer-to-peer light client protocol. However, the wallet employs a few centralized cloud services to enhance user experience, such as Google Play Services for pre-loading invitations, Celo Wallet Notification Service for sending push notifications, and Celo Wallet Blockchain API for providing a GraphQL API to query transactions and implement a user's activity feed. Users downloading the Celo Wallet from platforms like the Google Play Store are trusting cLabs (or the entity that has made the app available) and Google to deliver the correct binary, with many users finding this reliance on centralized services acceptable for the additional functionality provided. [3]
Initiatives
Bloom
Bloom is an advisory program for ecosystem token generation events (TGEs) designed to guide projects through TGE preparation and product roadmap development. The program offers support with launchpads, accelerator programs, exchange support, marketing, investor networks, strategic advisory on token structure and distribution, audit services, and access to key opinion leaders. Bloom aims to provide hands-on assistance to enable founders to concentrate on long-term product development and strategy. [8]
Connect the World
In April 2022, The Celo Foundation launched the $20M "Connect the World" campaign to promote the development of high-quality on
- and off-ramps for Celo globally. This initiative includes introducing FiatConnect, an open-source API specification to simplify and scale integrations. The campaign offers $50K to the first payment provider in each country to integrate FiatConnect and meet quality standards. It will also subsidize up to $100K on-ramp fees for all providers to reduce user access costs. [9]
CELO
CELO is the native asset of the Celo blockchain, supporting its growth and development. CELO holders can earn rewards, stake with validators, and vote on proposals that influence the future of the Celo ecosystem. The token has a maximum supply of 1B. [2][11]
Mento
Mento (formerly CP-DOTO) adjusts the supply of Celo stable assets based on user demand. Users can create a new Celo Dollar by depositing an equivalent amount of CELO or redeem a Celo Dollar for CELO. The system relies on an accurate oracle for the CELO to US Dollar exchange rate. When demand for Celo Dollar exceeds supply, users can profit by buying CELO at market price, exchanging it for Celo Dollars, and selling at a higher market price. Conversely, when demand falls, users can buy Celo Dollars at a lower price, exchange them for CELO, and sell them at market value. Mento aims to prevent reserve depletion through two virtual buckets of CELO and Celo Dollars, inspired by the Uniswap model. [12]
Granda Mento
Granda Mento facilitates the exchange of large amounts of CELO for Celo stable tokens, addressing the limitations of Mento and over-the-counter (OTC) transactions. While Mento effectively maintains stable token stability, its constant-product market maker can cause significant slippage in large transactions, where slippage refers to the price movement during a trade. Granda Mento operates similarly to Mento by using the reserve to mint or burn tokens: purchased stable tokens are created, and sold tokens are destroyed. For instance, exchanging 50,000 CELO for 100,000 cUSD would transfer the CELO to the reserve and mint the cUSD. Granda Mento aims to provide institutional-grade liquidity for minting or burning large volumes of stable tokens, handling millions at a time. [13]
Stablecoins
Celo Dollars (cUSD), Celo Euros (cEUR), and Celo Reals (cREAL) are Mento stablecoins designed for fast, cheap, and easy mobile transactions. These stablecoins facilitate low-cost remittances, cross-border payments, global charitable aid distribution, online payments, and value transfers within exchanges, especially in markets with currency volatility. [2]
Partnerships
- Safe
- Chainlink
- Animoca Brands
- Google Cloud
- Circle
- Rarible API
- Tether
- Optimism
- Brave
- EthicHub
- Toucan
- ZeroSwap
- Minipay
See something wrong?
The Agent Tokenization Platform (ATP):Build autonomous agents with the Agent Development Kit (ADK)
