Subscribe to wiki
Share wiki
Bookmark
ISO 20022
The Agent Tokenization Platform (ATP):Build autonomous agents with the Agent Development Kit (ADK)
0%
ISO 20022
ISO 20022 is an international standard that regulates the digital transfer of financial information between financial institutions. Developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), ISO 20022 improves the interoperability and efficiency of banking and financial transactions by providing a consistent and adaptable approach to financial messaging.[1]
Overview
ISO 20022 is an international standard that provides a uniform framework for electronic data interchange between financial institutions. Originally created for traditional finance, ISO 20022 is now being used in cryptocurrency applications.
By standardizing financial communications, ISO 20022 improves the orderliness and interoperability of the cryptocurrency sector, enabling reliable interaction between different platforms and networks. This standard meets the financial sector's need for a universally recognized communication language. It enables these organizations to interact with partners and conduct business on a global platform.
ISO 20022 offers applications for financial institutions such as banks, cryptocurrency companies and brokerage firms by promoting direct communication between different departments and organizations. This reduces the cost of maintaining different communication networks. In addition, ISO 20022 is compatible with current protocols, enabling various financial operations.
The primary goal of ISO 20022 is to provide an international standard to replace the variety of message formats and protocols used by different financial systems. By implementing ISO 20022, financial organizations can increase accuracy and security of data transmission and simplify operations. [1][2]
ISO 20022
ISO 20022, also known as the Universal Financial Language (UFL), serves as a standard language for financial communications, facilitating communication between financial institutions and global payment networks such as SWIFT. This standard improves the efficiency, accuracy, and interoperability of financial transactions.
Compatibility with ISO 20022:
-
Traditional Financial Institutions: Banks, brokers and other financial institutions must comply with ISO 20022 by 2025 to ensure secure and seamless communication with customers and partners.
-
Cryptocurrency companies: Integration with ISO 20022 enables interoperability with banks and other financial systems, encouraging wider market adoption and acceptance of cryptocurrencies.
-
Fintech companies: Fintech companies offering innovative financial services need to ensure compatibility with ISO 20022 to integrate into the global financial system.
New business models in the evolving financial landscape must be compatible with ISO 20022. Integration with this standard supports the creation of new financial solutions and contributes to a more efficient, inclusive, and interoperable financial future. [2][3]
An example of this growing demand for adaptation is Ripple, the company behind the XRP cryptocurrency, has joined the ISO 20022 standards body.
Implementation Options
-
New Financial Services and Products: The combination of ISO 20022 and blockchain technology fosters the creation of new financial services and products, including more accessible and faster international payments, safer and more effective digital asset custody solutions and new financing options.
-
Financial Inclusion: By providing more accessible financial services to individuals and business that are not yet part of the traditional financial system, the adoption of ISO 20022 helps to drive economic growth and financial inclusion.
-
Interoperable Finance: More integrated and interoperable financial systems and platforms are possible through global standardization of financial communications.
Impel's Blockchain API
Impel is a financial technology company that utilizes blockchain technology to provide financial messaging in compliance with ISO 20022 standards. The platform offers optional collateral for instant settlement and includes a bridge to the R3 Corda platform, catering to banks and fintech organizations.
The implementation of Impel's API, based on ISO 20022 and blockchain technology, aims to improve the efficiency of transactions and data transfers.
Traditional formats such as SWIFT's MT and SEPA are being replaced by the more comprehensive and detailed ISO 20022 universal financial messaging language. Introduced in 2004, ISO 20022 is currently used in more than 70 countries and will be mandatory by November 2025 when SWIFT retires MT.
Impel's API supports all 733 categories of ISO 20022 data description messages, providing backward compatibility. It provides speed, security, and scalability and is based on the XDC network. It uses distributed ledger technology and the proof-of-stake (XDPoS) consensus method.
The collaboration with Fluent Finance integrates the US+ stablecoin into the XDC network, enabling a transparent and instant settlement solution supported by a consortium of federated banking partners.
Impel is providing a demonstration adapted to the generating and transmission of real-time financial messages, stored on the main network of the XDC network. It also provides a pilot program and a sandbox for testing.
For national and international payments, Impel's ISO 20022 API offers a solution that can improve interaction and speed up payments for corporates and financial institutions. [4][5]
ISO 20022 in 2024
The list of the first cryptocurrencies to adhere to the ISO 20022 standard includes:
XRP (Ripple)
- Focus: Facilitating global payments through RippleNet, a network connecting banks and financial institutions.
- Benefits: Fast and cost-efficient transactions, high throughput (1,500 transactions per second), established institutional adoption..
- Focus: Providing secure and sustainable infrastructure for financial applications.
- Benefits: Supports complex smart contracts, growing DeFi ecosystem and security with Ouroboros protocol.
Quant (QNT)
- Focus: Interoperability between various blockchain networks and traditional financial systems.
- Benefits: Enables communication across diverse blockchain environments, facilitates development of interoperable decentralized solutions.
- Focus: Building a scalable, secure, and user-friendly blockchain platform for real-world applications.
- Benefits: Fast and affordable micropayments, supports advanced smart contracts, environmentally friendly consensus mechanism.
- Focus: Creating a global financial network for fast, affordable, and accessible cross-border transactions.
- Benefits: Faster and cheaper remittances, unique Stellar Consensus Protocol, focus on financial inclusion.
- Focus: Providing a high-performance, secure distributed ledger platform for building compliant decentralized applications.
- Benefits: Fast transactions (over 10,000 per second), security architecture, and energy-efficient consensus mechanism.
IOTA (MIOTA)
- Focus: Enabling secure and scalable transactions specifically designed for the Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem.
- Benefits: Fee-less microtransactions, quantum-proof cryptography, lightweight and scalable architecture optimized for data and value transfer within the IoT.
XDC Network (XDC)
- Focus: Facilitating global trade and supply chain finance through a hybrid blockchain platform.
- Benefits: Combines public and private blockchain features, high transaction throughput (2,000 transactions per second), regulatory compliance, and efficient cross-border transactions.
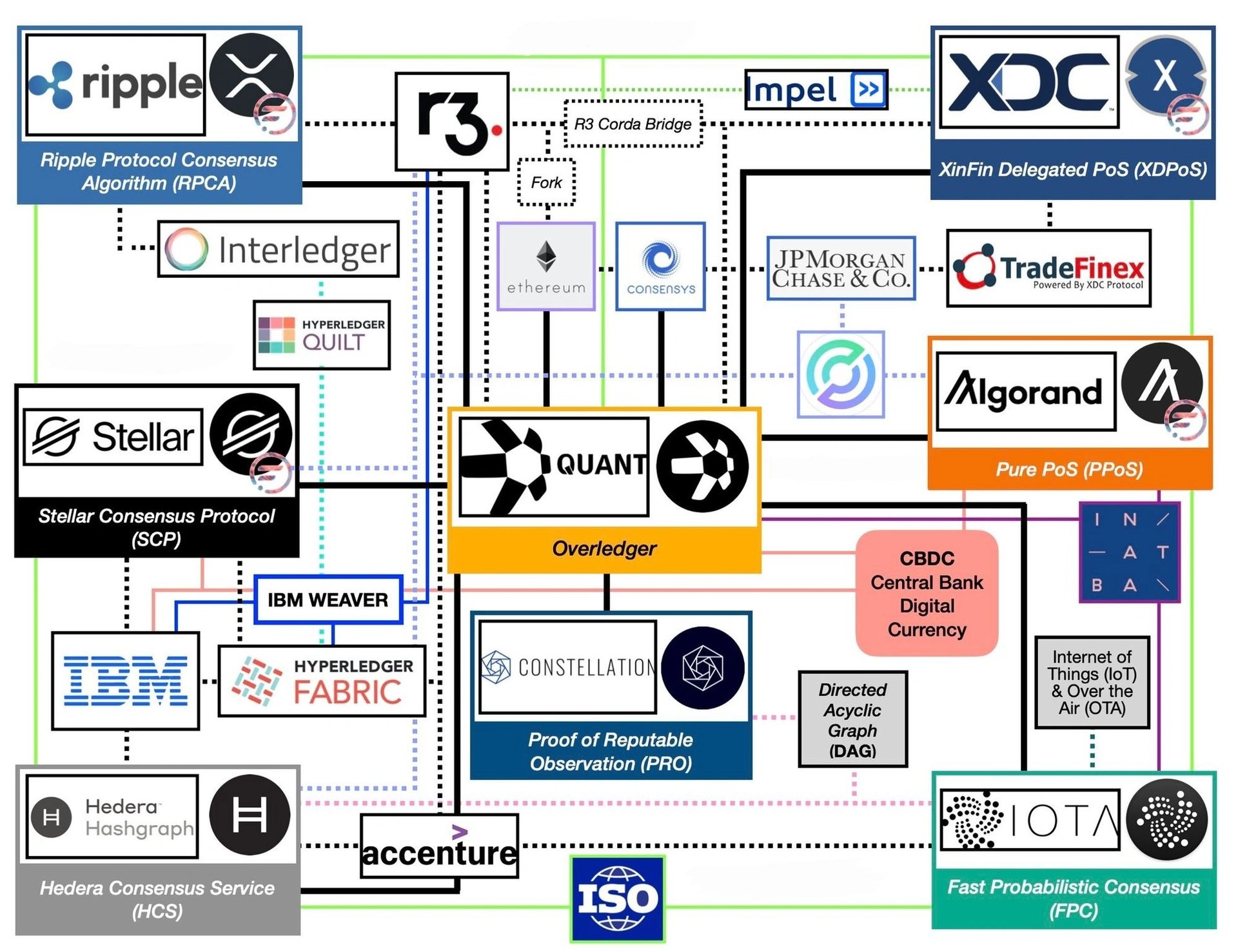
The adoption of ISO 20022 by these cryptocurrencies demonstrates their capacity to bridge the gap between traditional finance and blockchain technology. This facilitates cross-border financial transactions that are faster, more secure, and more cost-effective. [1][2][7]
See something wrong?
The Agent Tokenization Platform (ATP):Build autonomous agents with the Agent Development Kit (ADK)
