Subscribe to wiki
Share wiki
Bookmark
Ripple
The Agent Tokenization Platform (ATP):Build autonomous agents with the Agent Development Kit (ADK)
0%
Ripple
Ripple is a technology company that develops the Ripple Payment protocol and exchange network. Although XRP is often referred to as Ripple, it is important to know that XRP is an open-source digital asset independent of Ripple, which is a technology company. Founded in 2012 and originally named OpenCoin, the project was renamed Ripple Labs in 2013 and rebranded Ripple in 2015. Ripple is a global payment network with major international banks and financial services providers as its customers. [1]
Overview
Ripple is the company behind XRP, and it’s a payment settlement system and currency exchange network that can process transactions globally. Ripple is a money transfer network designed to serve the needs of the financial services industry. Ripple was designed from the very beginning to essentially be a replacement for SWIFT (a leading money transfer network) or to otherwise replace the settlement layer between major financial institutions. [2]
As the Ripple community expanded, Ripple created the XRPTalk, which spanned off from Bitcoiltalk. The XRP Talk forum was the main catalyst behind the growth of the XRP community and it was replaced by XRPChat, which has grown to become one of the largest in the cryptosphere. [2]
Ripple added Escrow and Payment Channels, which helped boost its scalability and performance. The new features enable companies to adopt the Ripple Consensus Ledger (RCL), and the Interledger Protocol (ILP). This allows them to benefit from XRP technology, as they experience faster and cheaper cross-border payments. [2]
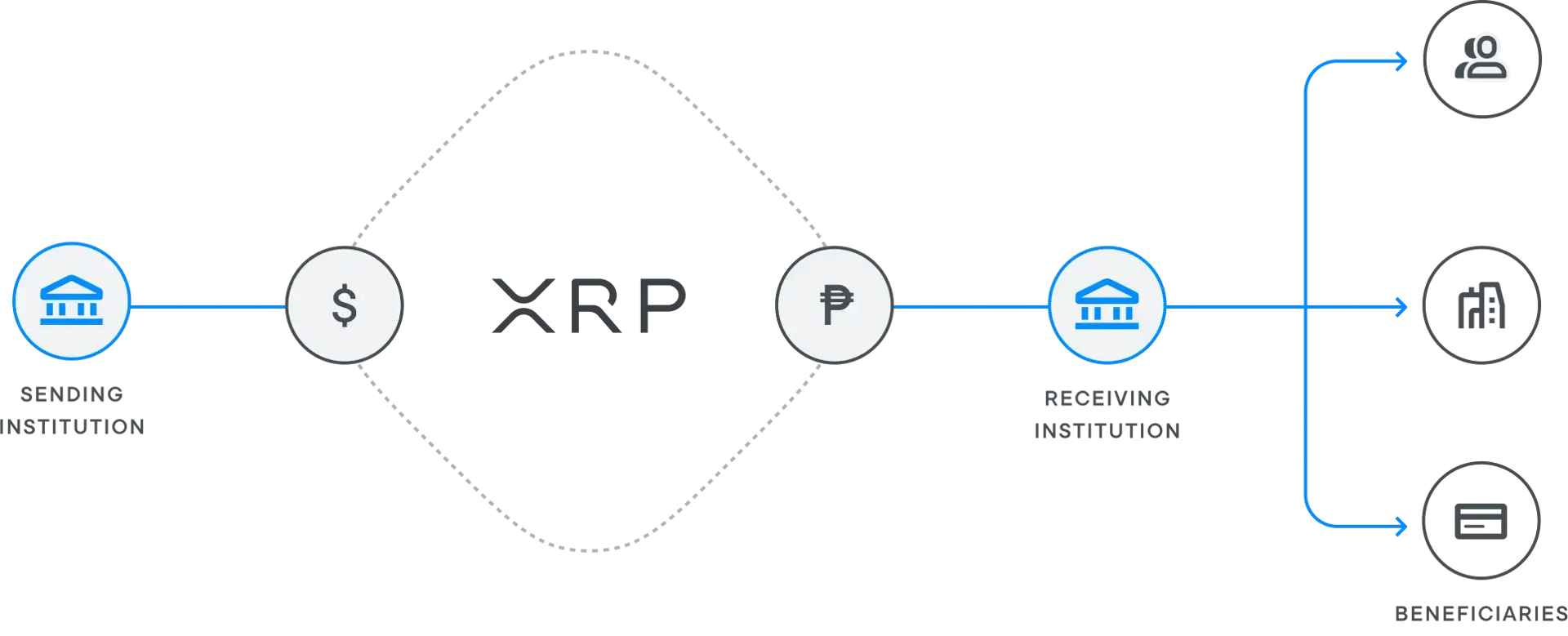
History
Ripple Project (Ripplepay.com) was founded by Ryan Fugger who is the predecessor of the current XRP ledger.
Ripplepay.com launched.
Jed McCaleb started developing a digital currency system (XRP Ledger) together with David Schwartz and Arthur Britto.
- Chris Larsen and Jessie Powell joined Jed McCaleb to discuss the concept of the digital currency system.
- Ryan Fugger passed over the ownership of Ripplepay to Jed MeCaleb's team.
- Jed McCaleb's team founded OpenCoin Inc. in September 2012.
Opencoin was rebranded to Ripple Labs in September 2013.
Ripple Lab was rebranded to Ripple in October 2015.
- Launched the Global Payment Steering Group to oversee the creation and maintenance of Ripple payment transaction rules, formalize standards for activity using technology, and other actions to promote the implementation of Ripple payment capabilities.
- Santander became the first bank in the United Kingdom to use Ripple for cross-border payment.
- Ripple signed with 10 new banks including Axis Bank and Yes Bank in India, Akbank in Turkey, and BBVA Bank in Spain.
- A 47-bank consortium from Japan joined Ripple and other 57 major customers from America and other regions joined the platform.
- Received a boost from Kraken adding four different XRP trading pairs, including XRP/CAD, XRP/JPY, XRP/EUR, and XRP/USD.
XRP Ledger (XRPL) Foundation was established in September 2020 and raised $5.5 million from Ripple, Coil, and GateHub. XRPL Foundation is an independent and nonprofit entity with a mission to accelerate the development and adoption of the decentralized XRP Ledger.[10]

Ripple announced a plan to launch its Liquidity Hub in 2022 to help financial services firms offer their customers the ability to buy and sell. Liquidity Hub is a turn-key liquidity and global payout platform, built specifically for enterprise needs supporting a variety of digital assets and connecting organizations to a rich set of liquidity venues to source optimized pricing via smart order algorithms.[9][10]
Ripple buys crypto custody firm Metaco for $250 million.
Ripple buys digital asset custody firm Standard Custody & Trust. Standard Custody & Trust Company offers custody and escrow services under a charter granted by the New York State Department of Financial Services and is a qualified custodian in accordance with federal legislation.[20] Standard Custody was previously a subsidiary of PolySign and partnered with Digital Ascension Group[21], led by Jake Claver to provide digital asset custody solutions to end users.
Ripple launches RLUSD
On December 17, 2024. Ripple launched its stablecoin, RLUSD. RLUSD was first introduced in June 2024 and in August 2024, the stablecoin was announced to be in private beta testing on XRP Ledger and Ethereum mainnet. [23]
RLUSD is valued 1:1 to the US dollar (USD) and 100% backed by US dollar deposits, short-term US government treasuries, and other cash equivalents. A third-party accounting firm will audit these reserve assets, and Ripple will publish monthly attestations. [23]
"Ripple USD (RLUSD) is now live on global exchanges. An enterprise-grade stablecoin built for everyone, $RLUSD combines fiat stability with blockchain efficiency.
Technology
The XRP Ledger (XRPL) is a decentralized public blockchain that allows for the fast, low-cost, real-time transfer of XRP, fiat currencies, and other digital assets. It is also open source, meaning anyone can participate in its development. XRP Ledger was created in 2012 by Ripple co-founder and CEO Chris Larsen. Initially, it was used to power the Ripple payment network, but it has since been adopted by other companies such as Coil and Omni to innovate upon diverse Web3 implications.XRP Ledger is a decentralized platform allowing for peer-to-peer asset transfer. A consensus algorithm validates connections on the network, which makes the network incredibly fast and secure.
Consensus algorithms are solutions designed to address something known as the “Byzantine Generals’ Problem. In the case of Bitcoin, it uses the Proof-of-Work consensus algorithm, while Ethereum uses the Proof-of-Stake consensus algorithm to address the problem. The Ripple Consensus Algorithm helps the protocol address the issues faced by the current system of cross-border transfers. Current systems take days to settle a transfer and are opaque, which means the receiver has no idea when they will receive the funds in their account. On the other hand, Ripple addresses transactions in mere seconds. The Ripple Protocol Consensus Algorithm relies on nodes that verify transactions by reaching a consensus. However, the consensus algorithm makes it impossible for validators to agree to a malicious transaction.[9]
Use Cases
Liquidity Hub is a turn-key liquidity and global payout platform, built specifically for enterprise needs. With Liquidity Hub and Ripple’s suite of products, businesses can access optimized crypto liquidity and an extensive payout rail network to power crypto payments, crypto treasury operations, and a variety of other solutions.[4]
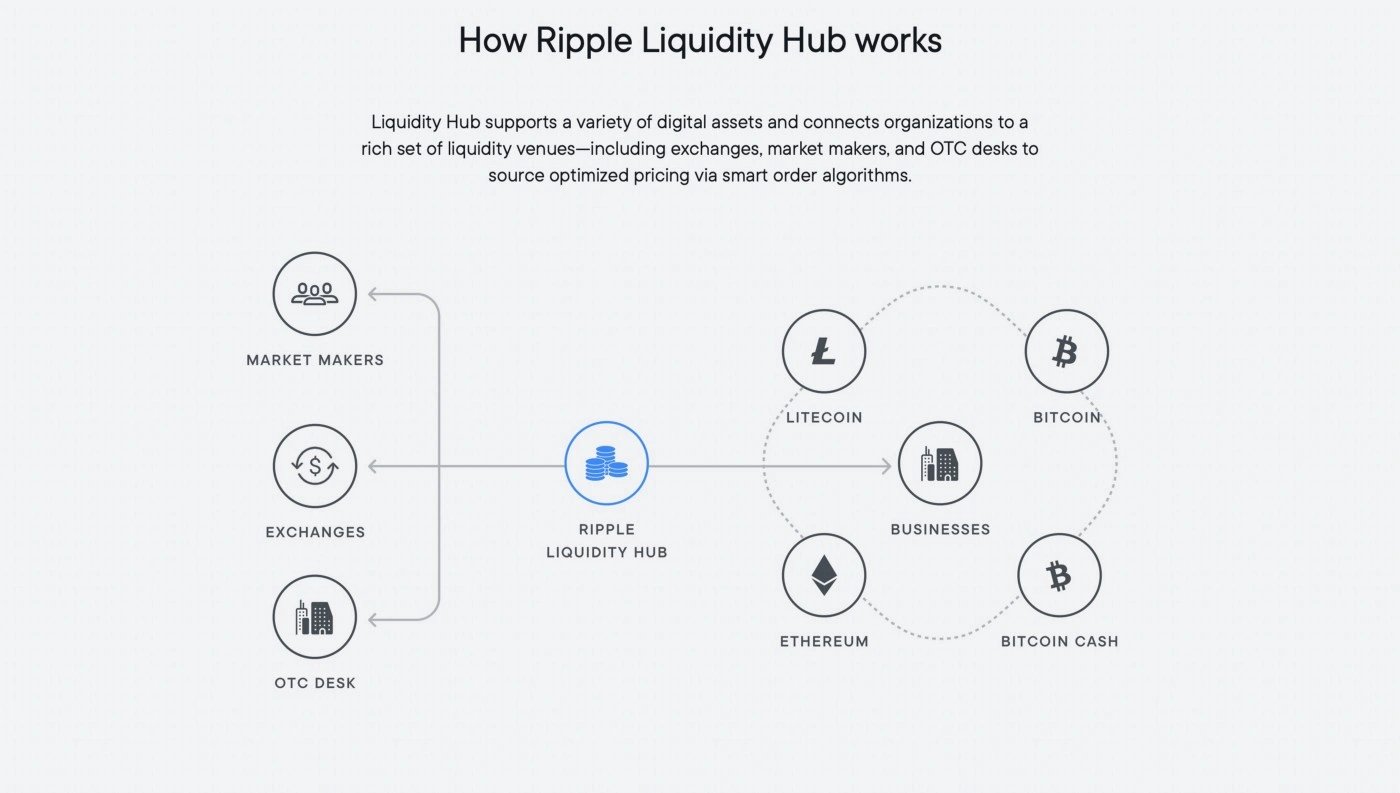
Complete platform for minting, managing, transacting, and destroying CBDCs. Each solution is built on a private ledger that is based upon XRP Ledger technology—a proven blockchain that has transacted over 70 million times over the course of 10 years and is trusted by financial institutions around the world.[5]
Partnership / Collaboration
- Novatti: Novatti uses Ripple's payment solution to drive customer growth. Novatti is a leading digital payments company that enables businesses across 58 countries from corner stores and startups to global organizations - to pay and be paid from any device, anywhere.[1]
- Modulr: Molulr is a leading embedded payments platform in the UK and Europe, enabling customers to make payments 24/7, 368 days a year in seconds. Ripple enables Modulr to deliver seamless payments.[2]
- Tranglo: Tranglo is one of Asia's leading cross-border payments hubs providing 25 countries with technology that makes cross-border transactions faster, affordable, and more secure. Tranglo partnered with Ripple to provide accessible and equitable financial services to the public.[3]
- I-Remit: I-Remit is the largest Filipino-owned non-bank remittance service provider in partnership with more than 100 financial institutions in 30 countries across the globe. Ripple helps I-Remit provide low-cost, real-time cross-border payments around the world. [4]
- MoneyMatch: MoneyMatch is a Malaysia-incorporated FinTech company focused on delivering a more efficient cross-border payment service by providing same-day, low-cost global payments to both SMEs and individuals. MoneyMatch and Ripple make it cheaper and faster for Malaysian small and medium enterprises to pay global suppliers.[5]
- Siam Commercial Bank (SCB): SCB is Thailand’s longest-established bank and one of the largest banks in terms of market capital assets, offering four models for inbound services with more than $300M. Ripple helps SCB drive innovation with instant cross-border remittances.[6]
- Sentbe: Sentbe is a financial services firm based in Korea and Singapore offering online international remittances across Southeast Asia and beyond. Ripple helps Sentbe provide faster, cheaper, and convenient remittances for migrant workers in Korea.[7]
- MoneyNetint: MoneyNetint is a financial services company based in the U.K. providing cross-border receipts and payments to corporate clients around the world. RippleNet gives MoneyNetint easy access to new corridors.[8]
- DIFC Innovation Hub: In August 2024, Ripple partnered with the DIFC Innovation Hub, the innovation ecosystem of the Dubai International Financial Centre (DIFC), to accelerate blockchain and digital assets innovation in the UAE. The partnership will connect the next generation of developers with the DIFC Innovation Hub, the largest innovation community in the region and home to more than 1,000 growth-stage tech firms, innovation companies, digital labs, venture capital firms, regulators, and educational entities. [22]Brad Garlinghouse, Ripple CEO, said:
“The UAE is one of the most advanced jurisdictions globally when it comes to offering regulatory clarity for licensed firms to offer virtual asset services and fostering an environment in which the next generation of financial innovation can flourish.“Our partnership with the DIFC Innovation Hub promises to drive the adoption of blockchain technology in the region as the XRPL continues to be a leading blockchain for the region’s start-ups and scaleups building real use cases.”
Issues / Criticism
Legal Issues
Ripple Labs Inc. resolves criminal investigation
May 2015 - Ripple Labs Inc. and its wholly-owned subsidiary, XRP II LLC, formerly XRP Fund II LLC, agreed to resolve a criminal investigation in exchange for a settlement agreement calling for a series of substantial remedial measures, including migration of a portion of Ripple’s virtual currency business to a separate entity, the company’s ongoing cooperation in other investigations, an extensive remedial framework to ensure future compliance with federal laws and forfeiture and penalties totaling $700,000, announced U.S. Attorney Melinda Haag of the Northern District of California, Director Jennifer Shasky Calvery of the U.S. Treasury Department Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) and Chief Richard Weber of the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) Criminal Investigation Division.[7]
SEC charges Ripple and two executives
December 2020 - The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) announced that it filed an action against Ripple Labs Inc. and two of its executives, who are also significant security holders, alleging that they raised over $1.3 billion through an unregistered, ongoing digital asset securities offering. The complaint alleged that Ripple raised funds, beginning in 2013, through the sale of digital assets known as XRP in an unregistered securities offering to investors in the U.S. and worldwide. Ripple also allegedly distributed billions of XRP in exchange for non-cash consideration, such as labor and market-making services.[11]

December 2022 - Ripple and U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) accused one another of stretching the law, as they argued for a ruling on whether the XRP, the world's seventh-largest cryptocurrency, is a security. The SEC sued Ripple and its current and former chief executives in December 2020, alleging they have been conducting a $1.3 billion unregistered securities offering since the token's creation. The final round of briefs seeking summary judgment brings the case closer to a ruling that could further define what digital assets are considered securities in the U.S. Ripple argued that the SEC was seeking a ruling that XRP was in an investment contract, but without any contract, any investor rights, and any issuer obligations.[12][13]
SEC drops lawsuits against Ripple Executives
The cryptocurrency community has finally witnessed the end of the long-running courtroom standoff in which the United States Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) sued Ripple over the issuance and selling of XRP – with the SEC retreating from the case.
On October 19, 2023, The U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) dismissed its aiding and abetting claims against Ripple Labs executives Chris Larsen and Brad Garlinghouse in its lawsuit alleging the blockchain company violated U.S. securities law, according to a court filing in New York on Thursday. Ripple Labs Chief Legal Officer Stuart Alderoty wrote on X: [14][30]
"The SEC made a serious mistake going after Brad & Chris personally – and now, they’ve capitulated, dismissing all charges against our executives. This is not a settlement. This is a surrender by the SEC."
Larsen also had a comment on X about the SEC withdrawing from the case:[15]
"The last 3 years we’ve seen a rogue administrative state that needs to be held accountable for its actions – not just an investigation into the conflicts of interests that led to these baseless claims, but how the US actively demolished its global standing as the home for innovation, with thousands of jobs moving overseas."
Garlinghouse pointed out that this was his company’s third victory against the regulator, arguing that the SEC targeted him and Larsen in a “ruthless attempt to personally ruin us and the company so many have worked hard to build over a decade.” As he added:[15]
“The SEC repeatedly kept its eye off the ball while secretly meeting with the likes of SBF – failing again and again to protect US consumers & businesses. How many millions of taxpayer $ were wasted?! Feels good to finally be vindicated.”
The SEC’s actions on Ripple began in December 2020 when the commission filed a lawsuit against Garlinghouse, Larsen, and the company largely over sales of its XRP tokens, which the commission also claimed were securities. It’s unclear why the SEC chose to drop the charges after almost three years, with a trial scheduled to begin in April 2024. [16]
Criticism
March 2019 - A Forbes author and IT expert, after his in-depth analysis, brought up various points that lead to the conclusion that the Ripple business model, at its core, is a pump and dump scheme, as it undergoes numerous activities to increase the value of the XRP cryptocurrency. Unlike most crypto pumps and dumps, however, Ripple takes numerous steps to obscure this basic fact.
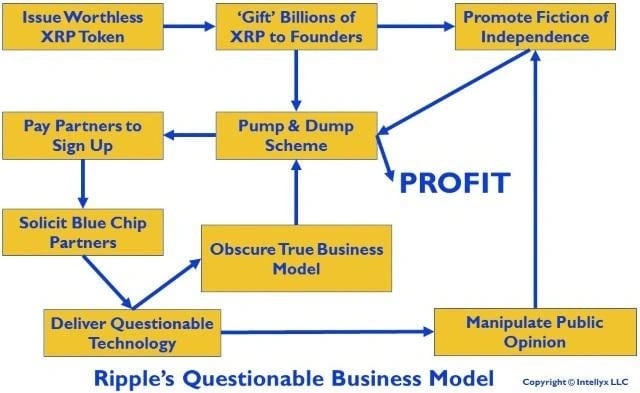
The starting point in the chart above is the issuance of many billions of XRP tokens printing Monopoly money out of thin air. To obscure Ripple founders' intention, however, an open source 'community' - not technically Ripple itself - issued the tokens. Many people in the crypto community don't even consider XRP to be a cryptocurrency at all, because it's not decentralized. One of the strongest indicators that Ripple is a going concern is the dozens of customers it touts. Look more closely, however, and most such companies are 'partners', not customers. Pump and dump schemes leverage the perceived value of the asset in question, not its intrinsic value separate from the speculative interest in the asset. [6][16]
Ripple Executive Hack
On January 31, 2024, Chris Larsen, Ripple's Executive Chairman, posted on X (formerly Twitter) about a breach of his "personal XRP accounts". He wrote the post to confirm that the breach was on his account, not Ripple. [17]
"Yesterday, there was unauthorized access to a few of my personal XRP accounts (not @Ripple) – we were quickly able to catch the problem and notify exchanges to freeze the affected addresses. Law enforcement is already involved." Larsen wrote.
The incident was first reported by a Blockchain expert named ZachXBT. According to him, a massive wallet on the XRP Ledger blockchain was compromised and around 213 million XRP tokens were stolen. The stolen funds were then laundered through multiple exchanges, including Binance, Kraken, and OKX. [17][18]
On February 2, 2024, CEO of Binance, Richard Teng said in an X post that Binance froze $4.2 million worth of XRP tokens tied to the exploit. Teng said XRP Ledger developers, who maintain the blockchain that uses XRP, had flagged the exploit to exchanges and asked them to look out for deposits related to exploiter wallets. [19]
"We appreciate both the communities efforts in flagging it to exchanges - as always@zachxbt did a great job - and the Ripple team’s work in collaborating with us. We will continue to support Ripple in their investigations and their efforts to retrieve back the funds, including closely monitoring the majority of funds still in the exploiter's external wallets in case they deposit to Binance.Our team is firmly dedicated to supporting a safe ecosystem, so we always encourage projects and users to reach out to us in instances like this." - Richard tweeted
Developments
Ripple Acquires Hidden Road
On April 8, 2025, Ripple agreed to buy prime brokerage firm Hidden Road for $1.25 billion, in the crypto startup’s biggest acquisition to date. [25]
"Together, Ripple and Hidden Road are bringing the promise of digital assets to institutional customers at scale, bridging traditional finance and decentralized finance in ways never seen before." - the Ripple team tweeted
Founded in 2018, Hidden Road offers clearing, prime brokerage, and financing services across foreign exchange, digital assets, derivatives, swaps, and fixed income. It currently clears more than $3 trillion annually across markets with over 300 institutional customers, including hedge funds. [24]
“Ripple’s acquisition of Hidden Road is a defining moment for the XRP Ledger and XRP,” Schwartz said on social media on April 8.
“Now imagine even a portion of that activity on the XRP Ledger — and that’s exactly what Hidden Road plans on doing — not to mention future use of collateral and real-world assets tokenized on the XRPL,”
Ripple Made $4-5 Billion Offer to Acquire Circle
In April 2025, Ripple made a multi-billion-dollar offer to acquire USDC stablecoin issuer Circle, citing people familiar with the matter.The offer was said to be in the range of $4 billion to $5 billion, but was reportedly rejected as being too low. At the start of April, Circle filed paperwork with the SEC to go public. [26]
A Circle spokesperson told Bloomberg news that the company was “currently in a quiet period with the SEC,” meaning its ability to comment on corporate financial plans is restricted. Circle did not immediately respond to a request to comment from Decrypt.
Ripple's Philanthropy
On May 5th, 2025, Ripple announced a donation totaling $25 million to U.S. educational non-profit organizations DonorsChoose and Teach For America. [27]
The donation will primarily be distributed in the form of Ripple's stablecoin, Ripple USD (RLUSD). This initiative aims to enhance access to educational resources, improve academic outcomes, and bolster economic resilience for teachers and students across the United States. [27]
Ripple highlights that the collaboration will fund thousands of teacher projects and classroom needs, supporting Teach For America's Ignite tutoring program.
Additionally, both organizations will work to advance financial literacy education, helping students and educators build a solid academic foundation and economic capability in a rapidly changing job market. [27]
Ripple Expands to UAE
According to a statement released on May 19, 2025, two new United Arab Emirates-based (UAE) firms have adopted the Ripple Payments solution.
Ripple announced a partnership with Zand Bank and Mamo to expand its platform on the UAE market. [28] [29]
This functionality, paired with the new DFSA license, enables Ripple to manage payments end-to-end on behalf of its customers, moving funds across the globe 24/7/365, and settling payments in a matter of minutes – reducing time and friction, and making the movement of value in and out of the UAE dramatically more efficient. [29]
“Securing our DFSA license enables Ripple to better serve the demand for solutions to the inefficiencies of traditional cross-border payments, such as high fees, long settlement times, and lack of transparency, in one of the world’s largest cross-border payments hubs.
Our new partnerships with Zand Bank and Mamo are testament to the momentum that the license has created for our business,” said Reece Merrick, Managing Director, Middle East and Africa, at Ripple.
“As the global cross-border payments market grows, the leadership demonstrated by authorities in the UAE to create a supportive environment for crypto innovation has positioned the nation and its native companies to benefit from the transformative power of blockchain technology to drive efficiency and innovation in payments."
Ripple Acquires GTreasury
On October 16, 2025, Ripple announced its acquisition of GTreasury, a global provider of treasury and risk management software. The acquisition is intended to integrate Ripple's crypto-based payment solutions into standard corporate treasury workflows. This will enable GTreasury's customers to leverage Ripple's global network for more efficient and faster international payments. Ripple CEO Brad Garlinghouse commented on the deal, stating, “Ripple’s and GTreasury’s capabilities together bring the best of both worlds, so treasury and finance teams can finally put their trapped capital to work, process payments instantly, and open up new growth opportunities.” [31]
See something wrong?
The Agent Tokenization Platform (ATP):Build autonomous agents with the Agent Development Kit (ADK)
