Subscribe to wiki
Share wiki
Bookmark
Taiko
The Agent Tokenization Platform (ATP):Build autonomous agents with the Agent Development Kit (ADK)
0%
Taiko
Taiko is an open-source and permissionless ZK-Rollup network equivalent to Ethereum. The network functions without centralized control, with all operations being community-driven and permissionless. [1][2][3]
Overview
Taiko Network, founded by Daniel Wang in March 2022, comprises a suite of smart contracts on Ethereum, offering a permissionless ZK-Rollup solution. It mirrors Ethereum's user experience and operates without centralization, managed by the community. With a ZKP development history since 2018, Taiko aims to be Ethereum's primary scaling solution, focusing on simplicity and security.
The Alpha Testnet launched December 2022, emphasizing security, simplicity, decentralization, and permissionless participation. Taiko aims to resolve the blockchain trilemma by prioritizing decentralization, security, and scalability, ensuring Ethereum compatibility while enhancing scalability.[1][4][5][12]
History
2022
In October 2022, Taiko was first introduced on Mirror. On December 28th of the same year, the Taiko Alpha-1 testnet (a1), codenamed Snæfellsjökull, went live, marking the project's first public testnet release. Taiko aims to develop a Type-1 ZK-EVM with the objective of scaling Ethereum securely and seamlessly for developers and users.
Further developments were annolunced leading up to the mainnet release originally set for 2023 but later postponed to 2024.[13][4]
2023
In 2023, Taiko made significant progress in its development and community engagement. The launch of four public testnets provided valuable insights and attracted a diverse community of participants. Key rollup designs, including the Based Contestable Rollup (BCR) and Based Booster Rollup (BBR), were developed, promising to enhance the platform's functionality.
Community growth was notable, with substantial increases in members and followers across various channels. Events worldwide facilitated face-to-face interactions, while the Taiko ecosystem expanded to include nearly 80 dapps.
The introduction of the Taiko Grants program and educational initiatives underscored the project's commitment to community involvement and learning. Fundraising efforts secured $22M in funding, supporting ongoing development and community building.[14]
Taiko Protocol
The Taiko Protocol governs the rules and participation criteria for the Taiko rollup system, emphasizing security, decentralization, and permissionlessness.
Smart contracts on Ethereum Layer 1 verify ZK-SNARK proofs, while Layer 2 smart contracts manage key protocol functions.
Participants include proposers, who create rollup blocks; provers, who validate blocks with ZK-SNARK proofs; and node runners, who maintain network synchronization.
The protocol operates in three stages: block proposal, validation, and proving, ensuring block integrity and transaction validity.
Provers generate proofs for block transitions, with an Oracle Prover overseeing state transitions for added security.
Overall, the Taiko Protocol aims to provide a secure, decentralized, and permissionless scaling solution for Ethereum.[1][3][4][5][15]
Based Sequencing
Based Sequencing is a fundamental concept in Taiko's design, distinguishing it from other rollups. In Taiko, sequencing relies on Ethereum Layer 1 (L1) rather than a centralized sequencer. This means that Ethereum L1 validators determine the sequence of transactions on Taiko, eliminating the need for a centralized sequencer within the network.[16]
Based Contestable Rollup (BCR)
Taiko's Based Contestable Rollup integrates contestation and based sequencing. In this system, participants propose blocks, which can then be contested by others. This process requires higher-tier proofs to resolve disputes, ensuring the integrity of the blockchain.
Each proof requires a validity bond, and if contested, a contestation bond is also required. Contestation involves financial stakes, discouraging frivolous challenges, and maintaining system efficiency. However, this mechanism may disincentivize the submission of invalid yet verifiable proofs, posing a challenge for bug detection.
Overall, the BCR system aims to balance security and efficiency while providing a robust framework for block verification and dispute resolution in the Taiko protocol.[17][18]
Boosted Based Rollup (BBR)
Based rollups delegate sequencing to Ethereum Layer 1 (L1), maintaining decentralization. Booster rollups amplify this by providing native Ethereum L1 dapp scaling, akin to adding extra processing power to a computer.
BBRs retain the advantages of based rollups while enabling direct Ethereum scaling. They address fragmentation issues by facilitating atomic cross-rollup transactions within the booster network.
For users, BBRs ensure accessibility to favorite dapps across the network, reducing transaction costs and enhancing throughput. For developers, BBRs streamline scaling by enabling dapps to be boosted without redeployment to individual Layer 2s.[19][20]
Multi-Proofs
In Taiko, nodes can act as provers, generating proofs for proposed blocks on the TaikoL1 contract to validate state transitions. The first valid prover receives rewards, potentially including TKO tokens. Taiko blocks progress through proposed, proved, and verified states.
While proved blocks demonstrate state transitions, verified blocks additionally confirm the validity of parent blocks' proofs, ensuring the integrity of the block sequence. Taiko operates an off-chain proof market where proposers engage proof service providers to optimize network efficiency.
Providers commit to delivering proofs within agreed timeframes, with rewards typically in TKO tokens or other assets. Taiko advocates for the use of multiple proof systems to enhance security and diversity. This approach mitigates potential vulnerabilities by incorporating various cryptographic implementations, including ZK proofs and SGX, fostering robustness in the rollup ecosystem.[21]
Taiko Nodes
Taiko nodes, comprising taiko-geth and taiko-client, execute and manage transactions in the Taiko network. Taiko-geth, a modified version of go-ethereum, executes L2 transactions, while taiko-client facilitates consensus and transaction handling.
The driver in taiko-client synchronizes local chains with verified L2 blocks and inserts new blocks by listening to TaikoL1 protocol contract events. The proposer fetches pending transactions and proposes them to the TaikoL1 contract, ensuring adherence to protocol rules. The prover validates proposed blocks and generates validity proofs to ensure block integrity.
The synchronization process ensures local chains are updated with verified L2 blocks, while proposing and proving blocks maintains the integrity of the network.[22]
Bridging
Bridges on Taiko facilitate secure asset transfers between different blockchains using merkle proofs. The Taiko protocol stores block hashes of each chain on smart contracts, enabling verification of values across chains. Taiko's signal service utilizes merkle proofs for secure cross-chain messaging, allowing reliable communication between chains. The bridge, comprising smart contracts and a web app, enables users to transfer assets between Ethereum and Taiko.
Users interact directly with the Bridge contract for Ether bridging, while for ERC-20 tokens, a BridgedERC20 contract is deployed on the destination chain. Transferring tokens involves sending a message, generating merkle proofs, and executing methods to mint or transfer tokens between chains.[23]
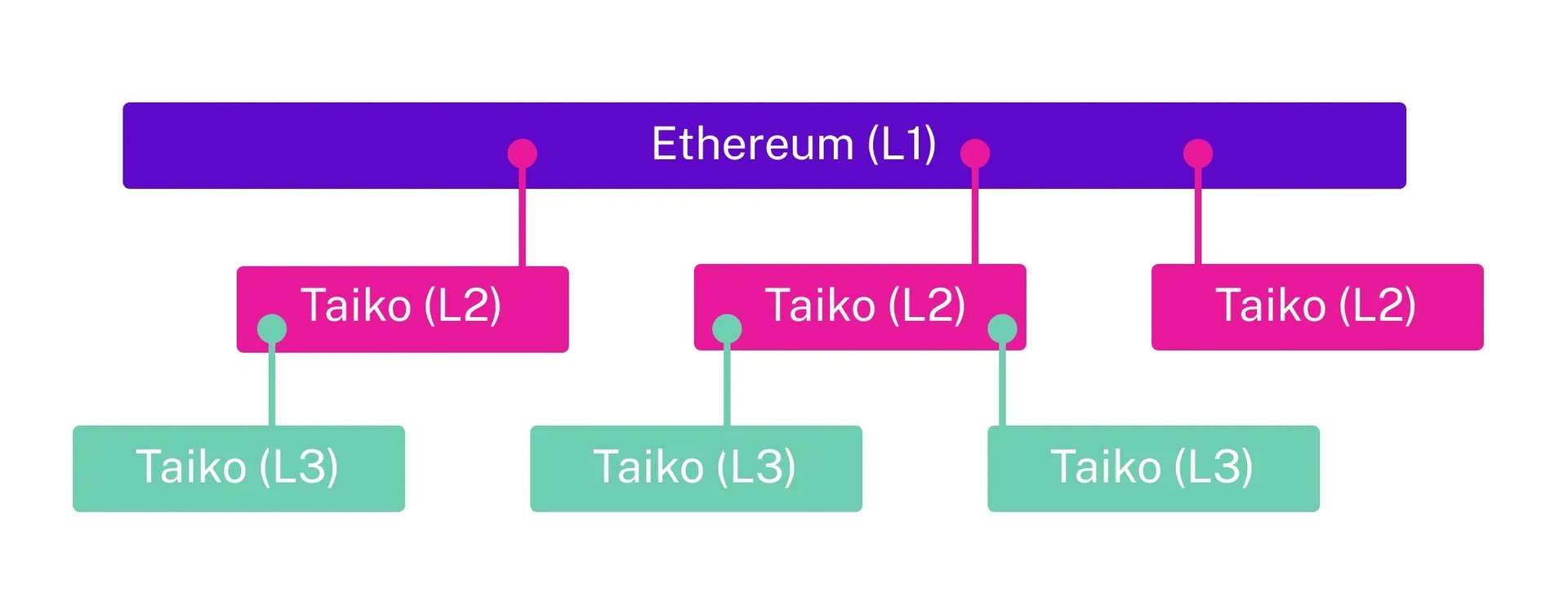
Inception Layers
Inception layers in Taiko enable horizontal scaling for Ethereum by deploying multiple Taiko instances as parallel L2s or as L3s on top of existing L2s. This flexibility, stemming from Taiko's Ethereum-equivalent design, permits codebase reuse across layers. Inception layers involve deploying Taiko as an L2 and replicating the exact codebase as an L3, maximizing reusability and simplicity while addressing scalability challenges.
This approach facilitates extensive scalability for Ethereum and ensures seamless communication across layers, combating fragmentation concerns using Merkle proofs.[24]
Taiko Organizations
Taiko Labs
Taiko Labs is a research & development group that works on the Taiko protocol. [5][11]
Taiko Treasury
This is a treasury that is funded by the income generated by the Taiko protocol (L2 EIP-1559 congestion MEV). [5]
Taiko DAO
Taiko decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) is a group of Taiko Token (TKO) holders that have the voting rights to govern various parts of the Taiko Protocol including smart contract upgrades, TKO parameters, and more. The Taiko DAO effectively controls everything. [5]
Taiko Foundation
This is an entity that stewards the growth and development of the Taiko protocol and the wider ecosystem. The foundation works solely for, and on behalf of, the Taiko DAO and token holders. Its responsibilities include, but are not limited to, financing of technical developments, ecosystem growth, and maintenance, partnerships with service providers, events management, etc — either through grants or other means. The foundation does so with full transparency to the Taiko community and DAO. [5]
Taiko Security Council
Taiko Security Council is an N-member council of individuals and entities elected by the Taiko DAO to undertake emergency actions on the Taiko protocol, as and when needed. The Security Council’s core responsibility is to ensure the safety and soundness of the Taiko protocol, and as such it has the power to implement upgrades or changes in pursuit of that objective. The Security Council also controls the Guardian Provers within the Taiko protocol. [5]
Tokenomics
Taiko Token ($TKO)
The Taiko token is essential in the contestable rollup design, supporting bond systems in BCR and BBR. These bonds, denominated in Taiko tokens, ensure network integrity and efficiency, with forfeited bonds redirected to Taiko’s Treasury on L1.
Additionally, the token enables decentralized governance, allowing holders to influence upgrades and manage the treasury across L1 and L2s. With a fixed supply of 1 billion TKO tokens and strict governance over minting and burning, Taiko emphasizes decentralized control and token integrity.[25]
Funding
In June 2023, Taiko Labs raised $22 Million across two funding rounds and launched its testnet (Alpha-3) with a mission to build a decentralized and Ethereum-equivalent (Type 1) ZK-EVM. The rounds were led by Sequoia China and Generative Ventures respectively, with participation from BAI Capital, GGV Capital, GSR Markets, IOSG Ventures, Kucoin Ventures, Mirana Ventures, OKX Ventures, Skyland Ventures, Token Bay Capital, Yunqi Partners, plus other investors and prominent contributors & community members from across the Ethereum ecosystem.[6]
“Thanks to recent advancements in zero-knowledge algorithms, hardware acceleration and leading industry research, we believe that we are now on the cusp of having a truly decentralized Ethereum-equivalent ZK-rollup. This is our core mission at Taiko and we are incredibly proud to partner with leading investors who share our uncompromising vision.” - Daniel Wang, CEO & Co-founder of Taiko[6]
On March 2, 2024, Taiko Labs announced a Series A raise of $15 Million led by Lightspeed Faction, Hashed, Generative Ventures, and Token Bay Capital, with participation from Wintermute Ventures, Presto Labs, Flow Traders, Amber Group, OKX Ventures, GSR, WW Ventures, and more. This latest funding round brought Taiko's total capital raised to $37 million across three rounds. [9]
“Building the first Ethereum-equivalent-based rollup is something we knew was going to be a multi-year adventure,” Wang said. “Now, as we approach main net launch, we realize what a ride it has been. We’re determined to ship our products as soon as they’re ready and show the industry that what had been thought of as impossible, is indeed possible.” - Daniel Wang commented[9]

Ambassador Program
The Taiko Ambassador Program aims to increase awareness about Ethereum's scalability through ZK-EVMs. Ambassadors focus on developer advocacy, educational content creation, or community organization. They assist, advocate, and educate within the Ethereum/Taiko community, helping shape the program's direction.
Applicants with expertise or interest in Ethereum and ZKPs, strong communication skills, and a desire to contribute are encouraged to apply. Benefits include collaboration with the Taiko team, monthly rewards, and potential progression to a full-time role within Taiko Labs.[26]
Founding Team
See something wrong?
The Agent Tokenization Platform (ATP):Build autonomous agents with the Agent Development Kit (ADK)
