Subscribe to wiki
Share wiki
Bookmark
Fetch.ai
The Agent Tokenization Platform (ATP):Build autonomous agents with the Agent Development Kit (ADK)
0%
Fetch.ai
Fetch.ai is a decentralized network that combines blockchain technology with artificial intelligence to enable autonomous economic agents to perform tasks and make decisions independently. The platform facilitates data sharing, machine learning, and automation to create scalable solutions across various industries. It was launched in March 2019 by Toby Simpson, Humayun Sheikh, and Thomas Hain. [1][2]
Overview
Fetch.ai is a platform that enables a decentralized digital economy powered by autonomous AI agents. These agents are intelligent programs that act on behalf of users, devices, or organizations to perform tasks, make decisions, and exchange value. Fetch.ai provides the infrastructure and tools needed to build, deploy, and manage these agents, including the uAgents communication protocol, the Agentverse discovery platform, and a native blockchain that facilitates secure transactions using the FET token. The system allows agents to interact with one another, access shared resources, and collaborate to complete complex workflows in real time.
The platform also integrates an AI Engine that translates human input into agent-driven actions, enabling dynamic and adaptive task execution. Developers can use frameworks like LangGraph or AutoGen and decentralized computing resources like Fetch Compute to create scalable, purpose-driven agents. Once registered on the Agentverse and connected through the Almanac smart contract, these agents become discoverable and can transact securely with others. By combining AI, blockchain, and decentralized infrastructure, Fetch.ai creates a unified environment where autonomous agents operate efficiently across supply chains, data services, digital marketplaces, and more. [8]
Fetch.ai Foundation
The Fetch.AI Foundation is a non-profit organization based in the Netherlands, established and governed by representatives from Fetch.ai and Bosch. It focuses on advancing innovative technologies in artificial intelligence and distributed systems.
The foundation’s primary objectives include promoting an open and transparent ecosystem grounded in data sovereignty and balanced governance. It encourages innovation and collaboration among industry participants through collective research and development, joint applications, shared initiatives, and the identification of valuable business models. [9]
Artificial Superintelligence Alliance Merger
On July 1, 2024, Fetch.ai, SingularityNET, and Ocean Protocol announced the formation of the Artificial Superintelligence Alliance through a multi-token merger, combining their respective tokens—FET, AGIX, and OCEAN—into a unified token under the FET ticker. This consolidation aims to streamline operations, unify tokenomics, and advance the development of decentralized artificial intelligence infrastructure.
The merger included the launch of migration tools via the SingularityDAO dApp, enabling holders of AGIX and OCEAN to convert their assets to FET. As part of the transition, AGIX and OCEAN began delisting from exchanges, while FET continued trading uninterrupted. The alliance is coordinating with exchanges and aggregators to support the token migration process.
Future phases of the merger include deploying the new ASI token across multiple blockchains, onboarding community members, and introducing new migration contracts for unconverted tokens. All FET tokens on Fetch.ai’s mainnet will automatically convert to ASI upon the mainnet upgrade. The migration contracts will remain open long-term to ensure accessibility. [17]
World’s First AI-to-AI Payment for Real-World Transactions
On December 18, 2025, Fetch.ai announced the world's first AI-to-AI payment for a real-world transaction.
The milestone was achieved when a Fetch.ai agent, utilizing DeltaV, autonomously discovered, booked, and paid for a room at Hotel Satoshis. This event demonstrated the platform's ability to enable personal AI agents to coordinate and transact for services without direct user intervention at each step.
AI-to-AI payments allow personal AIs to move beyond simple assistance and into full execution, securing reservations, booking experiences, and completing purchases automatically, before opportunities are lost. This marks a significant shift in how AI interacts with the real world, giving users the ability to delegate time-sensitive tasks while maintaining full control.
The full rollout of the AI-to-AI payment capability is scheduled for January 2026. [19]
Funding
In March 2021, Fetch.ai received funding from GDA Group, a Toronto-based digital asset firm that invested $5 million in the Fetch ecosystem over an undisclosed period. The funding was announced to be used for the research and development of Fetch's applications, which focus on autonomous artificial intelligence (AI) agents deployed on behalf of large firms like Bosch and others. [6]
In March 2023, Fetch.ai raised $40 million from market maker and investment firm DWF Labs. The investment was said to be used to deploy decentralized machine learning, autonomous agents, and network infrastructure on its platform. [5]
Fetch Name Service
On July 27, 2023, Fetch.ai announced an update to Fetch.ai Wallet version 0.14, which gives access to Fetch Name Service (FNS) directly within the wallet. The Fetch Name Service, created by AzoyaLabs, provides a Name System for the Fetch.ai blockchain. It allows users to map a human-readable domain to wallet addresses. With wallet upgrade 0.14, users can buy and register any unique .FET domain name directly from within their wallet. [7]
Technology
Since Fetch.ai is a multi-utility network, it combines a three-pillar framework consisting of autonomous economic agents, an open economic framework, and Smart Ledgers.
The Fetch.ai ecosystem uses a principle of AI known as Multi-Agent Systems (MAS), which allows agents to work in harmony despite being heterogeneous. An agent is a part of the software that represents an entity. Through its autonomy, it can operate independently (without its owner’s influence) and continuously make decisions on its own behalf. [4]
Autonomous Economic Agents (AEAs)
AEAs are intelligent and independent programs that operate on the owner’s behalf. The goal of these agents is to generate economic value for their owners. The Fetch.ai platform provides an environment where agents seeking value are placed near those with that value. Therefore, each agent sees the world as being reorganized for its needs. These autonomous economic agents can be made to represent real-world objects, people, or assets to allow them to communicate and transact. [3]
Open Economic Framework (OEF)
The Open Economic Framework (OEF) contains protocols, languages, and market mechanisms that facilitate communication and exchange of information between agents. The layer on top of the raw protocol and ledger provides the environment for all economic agents to operate. This enables a decentralized space where agents can find each other and exchange information. [3] [4]
Smart Ledger
The Fetch Smart Ledger, the Fetch.ai mainnet, is a smart contract-enabled ledger consisting of Distributed Ledger Technologies (DLTs) blockchain elements. It contains built-in AI based on notarized DAG technology that supports millions of economic agents and logs all transactions made on the blockchain. [4]
Products
Agentverse
Agentverse is a cloud-based platform that enables users to build, deploy, and manage autonomous agents without dealing with backend infrastructure. It features an in-browser integrated development environment (IDE) that simplifies coding, editing, and running agents. With built-in tools for logging, file management, and code revisions, users can create functional agents using any framework and leverage predefined templates to streamline deployment. Once launched, agents remain continuously online, scalable with message volume, and can securely interact with blockchain contracts through built-in wallets. The platform supports various Python libraries, and agents can be listed in the Almanac for discovery by other agents or users.
Key features include blockchain-based identity for transparent registration, mailroom services for handling offline messages, and secure, isolated Python environments. Agentverse is framework-agnostic and supports various applications, from basic scripts to complex AI agents. Its API allows decentralized communication, real-time interaction, and programmatic integration. Whether users are beginners or advanced developers, Agentverse eliminates DevOps complexity. As a directory for over 2.7 million agents, it enables scalable, trustless, and resilient agent operations within a decentralized ecosystem. [10] [18]
AI Engine
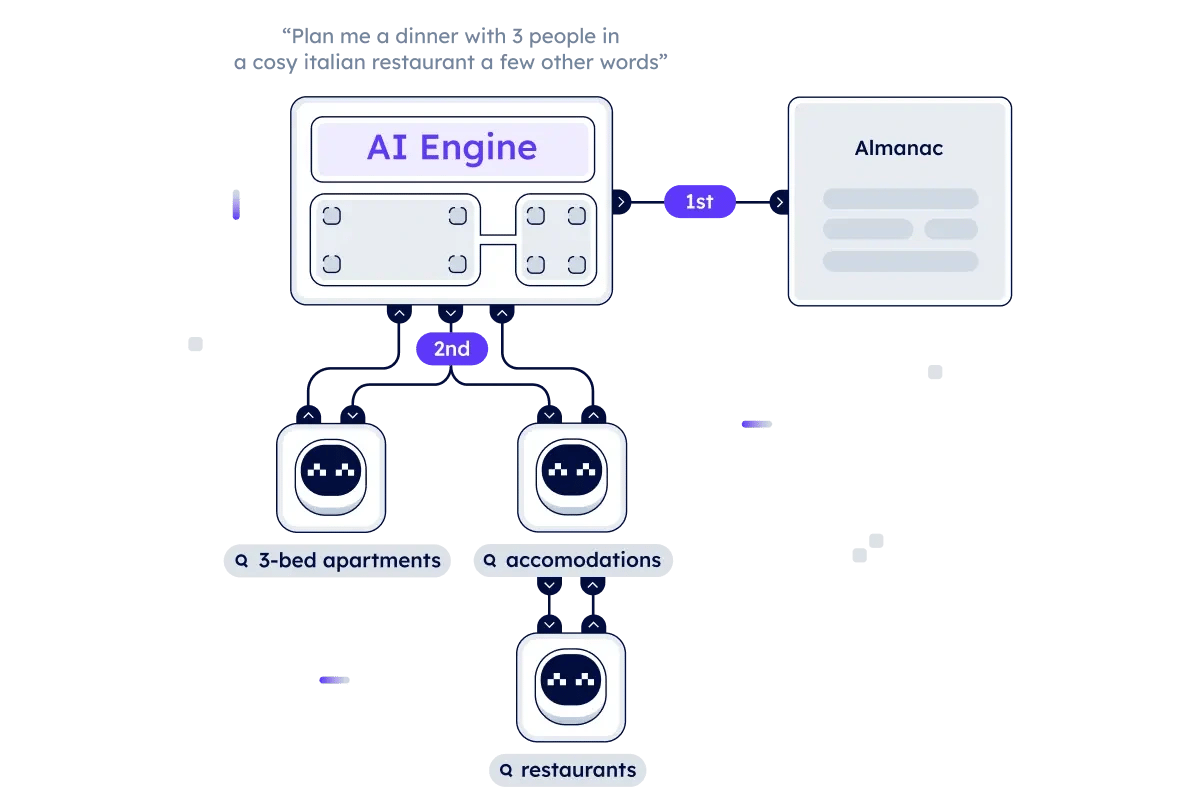
The AI Engine is designed to interpret human text input and convert it into actionable tasks by directing requests to suitable software agents. It functions as a network of interconnected large language models (LLMs) and agents, forming a scalable AI infrastructure. As more agents connect to the system, its capabilities expand, enhancing the quality and variety of services it can provide. The core purpose of the AI Engine is to understand user input in natural language and match it with the most appropriate agents registered in the Agentverse to complete the requested objectives.
The AI Engine uses contextual understanding to assess user goals and preferences. It analyzes ongoing trends and past user interactions—individual and collective—to transform seemingly random input into meaningful responses. During its training and current open beta phase, the system also solicits user feedback when uncertainty arises, helping to verify that its recommendations align with user intent. This feedback loop supports the AI Engine’s goal of anticipating and adapting to user needs over time.
A key feature of the AI Engine is its smart routing mechanism. Evaluating agents' performance history and capabilities registered in the Almanac ensures tasks are assigned to agents with the most relevant expertise. When a single agent cannot fulfil a request, the AI Engine constructs dynamic multi-agent workflows in real time. These workflows enable multiple agents to work collaboratively as independent components orchestrated by the AI Engine, allowing for the resolution of more complex user requests. [11]
ASI1
ASI1 (also referred to as ASI:One) is a Web3-native large language model created by Fetch.ai, built specifically for use in decentralized environments with autonomous AI agents. Unlike general-purpose LLMs, ASI1 is optimized for agentic reasoning, enabling it to independently plan, adapt, and execute complex multi-step tasks without ongoing user input. It supports context-aware responses and maintains memory across interactions, making it suitable for long-running or dynamic agent workflows.
The model integrates with the ASI wallet, which uses the FET token to enable secure on-chain transactions and interactions within the Fetch.ai network. ASI1 can be accessed via API and is available in three configurations—mini, fast, and extended—allowing for flexibility based on the required task complexity and performance. Its primary applications include decentralized finance, autonomous supply chain processes, personalized AI assistants, and smart contract automation, emphasizing functionality in agent-operated, decentralized systems. [12] [13]
ASI-1 Mini
ASI-1 Mini is Fetch.ai’s first Web3-native large language model, designed to support complex agentic workflows while running efficiently on just two GPUs. Built as part of the ASI: initiative, it introduces an advanced architecture that combines a Mixture of Models (MoM) and Mixture of Agents (MoA), enabling dynamic selection of specialized models and coordination of autonomous agents. These agents manage real-world tasks like API integration, database operations, and decentralized workflows, allowing ASI-1 Mini to handle multi-step processes with adaptability, speed, and precision. Its reasoning system includes four distinct modes—Multi-Step, Complete, Optimized, and Short—tailoring decision-making to the task, enabling real-time corrections, improved transparency, and strong performance across domain-specific benchmarks.
The model is deeply integrated into the ASI: ecosystem, powered by $FET and accessible through the ASI wallet. It forms the foundation of a community-driven AI framework that allows users to stake, train, and co-own foundational and specialist models within the Cortex collection. ASI-1 Mini also addresses the black-box problem by enabling continuous reasoning and more explainable outputs, which is critical for high-stakes applications. Upcoming expansions include agentic tool-calling, multimodal support, and vastly increased context windows—scaling to 10 million tokens—to support complex enterprise use cases like legal review and financial analysis. Through ASI:, the Web3 community gains a direct stake in the growth and value creation of next-generation AI models. [13] [14]
ASI:One Mobile
ASI:One Mobile is the first mobile interface for Fetch.ai’s ASI1 large language model. It enables users to interact with agent-based AI systems directly from their smartphones. The app connects to Agentverse, Fetch.ai’s decentralized agent network, allowing users to trigger task execution, access specialized agents, and receive structured responses powered by contextual data and knowledge graphs.
This initial release focuses on usability and exploration, offering functions like itinerary planning, technical support, and research assistance through intelligent agents. ASI:One Mobile is built on Fetch.ai’s agent infrastructure and is expected to expand over time with features such as session memory, deeper on-chain integrations, and additional tools for complex workflows. [15]
ASI Token
The ASI token is the product of a multi-phase merger between three decentralized AI projects: Fetch.ai (FET), SingularityNET (AGIX), and Ocean Protocol (OCEAN). The goal is to create a unified token and ecosystem under the Artificial Superintelligence Alliance (ASI) to lead development in decentralized AI.
The merger unfolded in two main phases starting on July 1, 2024. AGIX and OCEAN tokens were converted into FET on the Ethereum blockchain in the first phase. AGIX and OCEAN were delisted from exchanges while FET trading continued uninterrupted. Holders of AGIX and OCEAN tokens on centralized exchanges, like Binance, had their tokens automatically converted to FET at fixed rates. In contrast, self-custody holders manually migrated their tokens through the official SingularityDAO decentralized application. This phase also included rebranding the project across platforms under the Artificial Superintelligence Alliance banner.
Phase two focused on deploying the ASI token and transitioning from the FET ticker to ASI at a one-to-one ratio. Additional migration contracts facilitated the conversion of any remaining AGIX and OCEAN tokens. Concurrently, the Fetch.ai mainnet upgraded to the ASI network, improving the blockchain’s performance, security, and scalability. Staked FET tokens automatically converted to ASI, while liquidity providers adjusted their positions manually. All trading pairs were updated to reflect the ASI token after the upgrade.
To support the migration, approximately 1.48 billion new FET tokens were minted to cover conversions from AGIX and OCEAN holders. This brought the total FET supply to about 2.63 billion tokens, which eventually rebranded as ASI tokens. The migration and network upgrade process was carefully planned and tested to minimize disruptions and ensure a smooth user transition. [16]
Partnerships
See something wrong?
The Agent Tokenization Platform (ATP):Build autonomous agents with the Agent Development Kit (ADK)
