Subscribe to wiki
Share wiki
Bookmark
0G Labs
The Agent Tokenization Platform (ATP):Build autonomous agents with the Agent Development Kit (ADK)
0%
0G Labs
0G Labs is a technology company developing a decentralized Layer 1 blockchain and modular infrastructure designed to support artificial intelligence (AI) and Web3 applications. The project aims to provide scalable and cost-efficient resources to address challenges related to data storage, computational power, and latency when integrating AI with blockchain technology. [1]
Overview
0G Labs develops a decentralized Layer 1 blockchain designed to support artificial intelligence applications. The project addresses challenges in combining AI and blockchain, including the high costs of storing large datasets, the significant computing power required for training and inference, and the need for low-latency systems for real-time use.
Its infrastructure includes four independent services: 0G Chain (a modular blockchain for AI-related transactions), 0G Storage (decentralized storage for large models and datasets), 0G Compute (resources for AI model training and execution), and 0G Data Availability (ensuring reliable access to data). These components can operate together or independently, and integrate with both EVM-based and non-EVM blockchains.
0G’s modular approach is intended to make AI workloads more accessible across decentralized environments, with potential applications in areas such as AI agents, decentralized knowledge tools, finance, healthcare, and large-scale machine learning. [2]
Technology
0G Chain
0G Chain is a modular, EVM-compatible Layer 1 blockchain designed as the execution and settlement layer for AI-related transactions. It is engineered to address the high costs and low throughput of general-purpose blockchains. The chain's architecture separates the Execution Layer, which handles smart contract processing, from the Consensus Layer, which manages validator coordination and network security. This separation enables independent upgrades, allowing the execution layer to adopt new EVM features without altering the core consensus mechanism.
The network operates on a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) model and utilizes a highly optimized version of the CometBFT (formerly Tendermint) for its consensus mechanism. This configuration allows the chain to support over 2,500 transactions per second (TPS) with sub-second finality. Validators stake the native 0G token to secure the network and are compensated through block rewards, transaction fees, and staking yields. To ensure fairness and prevent collusion, the system employs a Verifiable Random Function (VRF) for validator selection. The project's roadmap includes a future transition to a DAG-based consensus model, which will enable parallel transaction processing and further enhance scalability. [4]
0G Storage
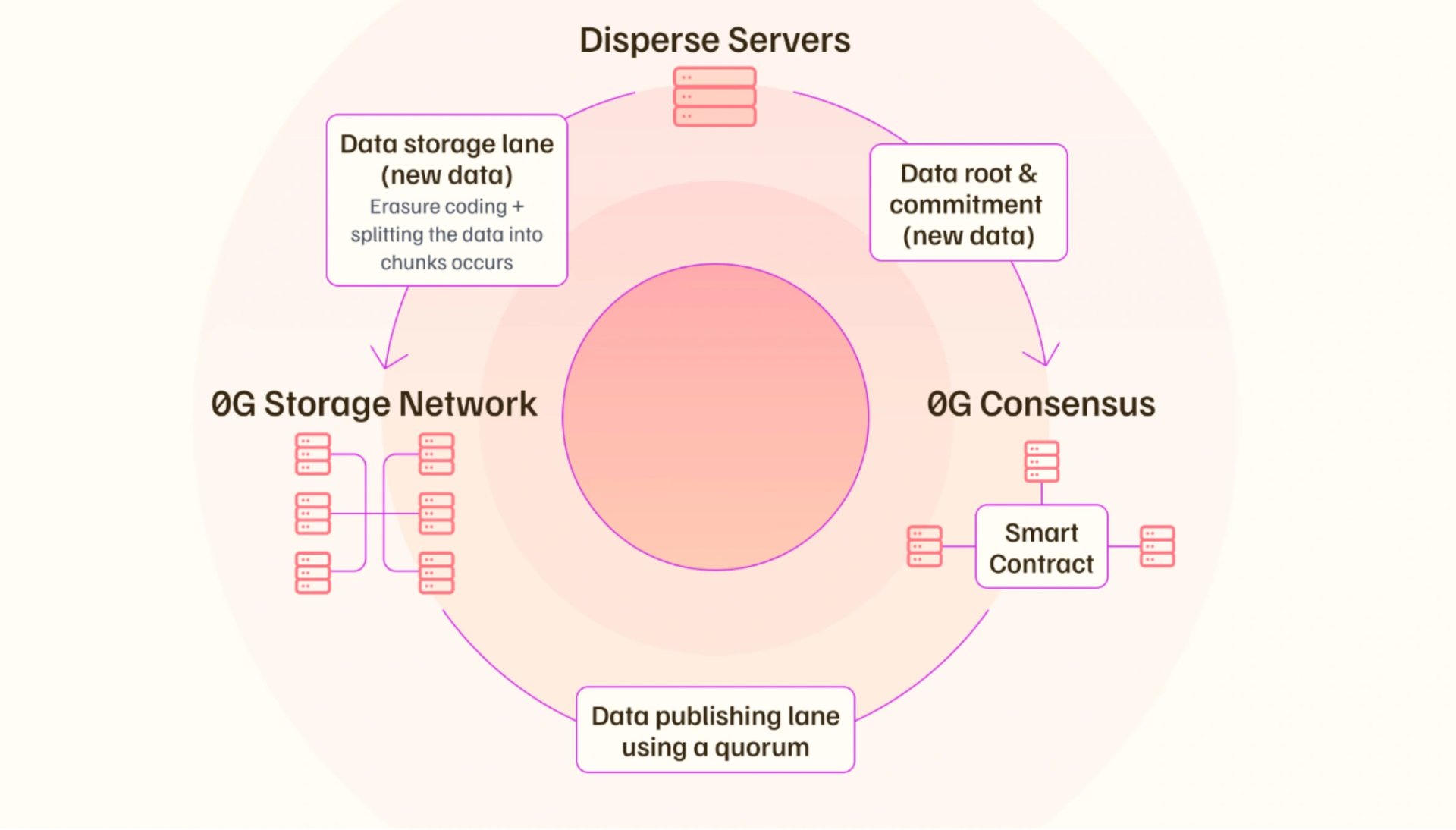
0G Storage is a decentralized storage system designed for large-scale AI datasets and models, offering high-speed data retrieval. It aims to provide a cost-effective alternative to both centralized cloud storage and slower decentralized options. The architecture is divided into two distinct lanes: a Publishing Lane that manages metadata and availability proofs on the consensus network, a Storage Lane that handles the actual data using erasure coding, replication for redundancy, and fault tolerance.
The system offers two storage tiers to accommodate different use cases. An Immutable Log Layer is designed for archival data and large AI training sets, while a Key-Value Layer supports dynamic data required by real-time applications. The network's consensus mechanism is known as Proof of Random Access (PoRA), where storage nodes must prove they can retrieve stored data segments quickly to earn rewards. This mechanism incentivizes both storage and rapid accessibility. [10]
0G Compute Network
The 0G Compute Network is a decentralized marketplace that connects developers requiring AI computing power with GPU providers. It is designed to function as an "Uber for AI computing," reducing the high costs, vendor lock-in, and complex setup associated with traditional cloud providers. The network operates on a pay-per-use model, allowing users to access on-demand GPU power for tasks such as model inference and training without incurring fixed commitments.
Transactions on the network are managed through smart contracts that hold payments in escrow, releasing funds only after service delivery is confirmed. To minimize transaction costs, the system employs compressed zero-knowledge proofs (ZK-proofs) for settlement. It also supports verifiable computation proofs, allowing users to confirm the results of their AI workloads without the provider retaining any user data. The network is accessible to developers through direct blockchain connections as well as traditional REST APIs and SDKs. It features built-in redundancy with automatic failover to other providers in its global network. [5]
0G Data Availability (DA)
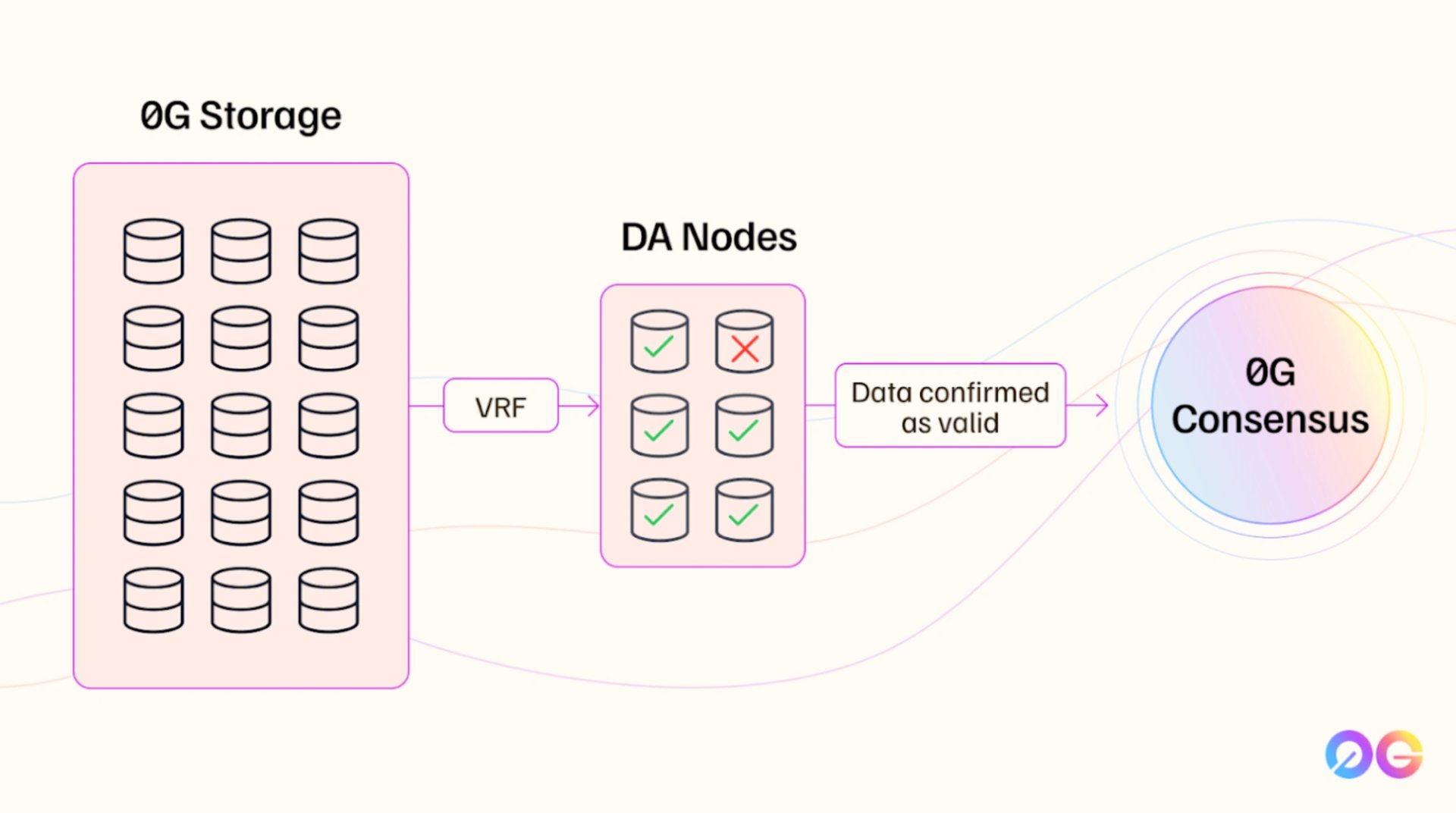
0G DA is a data availability layer designed to ensure that blockchain data remains accessible, verifiable, and secure while scaling to meet the demands of AI and decentralized applications. Traditional DA systems face limitations, including bottlenecks caused by slow nodes, reliance on external storage, and weaker security mechanisms compared to Ethereum. By contrast, 0G DA integrates built-in storage, a horizontally scalable consensus model, and inherits Ethereum’s economic security through shared staking, positioning it as a more robust and scalable option. Its architecture separates storage, availability, and consensus, enabling each to be optimized independently, while redundancy and cryptographic proofs guarantee data integrity.
The system uses erasure coding to split and distribute data across nodes, with availability confirmed through randomly selected DA nodes using verifiable random functions. These nodes validate data in small quorums and submit availability proofs, which are finalized by validators in the 0G consensus network. This sample-based verification process significantly reduces overhead while maintaining strong guarantees of security and availability. With demonstrated throughput of 50 Gbps in testing, parallel data processing, and infinite scalability through expandable consensus networks, 0G DA supports workloads like training large language models and managing AI agents, making it a foundational layer for decentralized AI infrastructure. [6]
AI Alignment Nodes
AI Alignment Nodes are specialized participants in the 0G ecosystem designed to oversee the safe and reliable functioning of decentralized AI systems. They address key challenges associated with centralized AI—such as lack of transparency, limited accountability, and potential misalignment—by providing distributed monitoring and oversight. Their role includes tracking model drift, verifying AI outputs, monitoring performance, and flagging anomalies to ensure that AI behavior remains consistent with intended objectives and community standards.
Beyond AI monitoring, these nodes contribute to network integrity by detecting protocol violations, reporting malicious activity, and supporting governance processes with data-driven insights. They represent a scalable framework for decentralized AI safety, combining automated monitoring with distributed governance to ensure transparency and accountability. By embedding ethical oversight directly into the network, AI Alignment Nodes enable faster and safer AI development, foster user trust, support compliance with evolving regulations, and promote sustainable ecosystem growth. [7]
Intelligent NFTs (INFT)
INFTs are a token standard designed to encapsulate an entire AI agent, including its models and data, within a single token. This contrasts with traditional NFTs, which typically only link to off-chain metadata. Built on ERC-7857, an extension of the ERC-721 standard, INFTs enable true ownership of a functional AI. When an INFT is transferred, the complete, encrypted AI agent is securely moved to the new owner.
This standard prioritizes privacy by using encrypted metadata storage and secure re-encryption for ownership transfers, protecting proprietary models and sensitive data. The persistence of the AI agent is ensured by leveraging 0G's decentralized storage system. Potential use cases for INFTs include AI-powered trading bots, personalized AI assistants, intelligent game characters, and specialized research tools. [8]
0G
The native token of the 0G ecosystem is 0G. The total supply is fixed at 1 billion tokens. The allocation is structured to support long-term development and community growth.
The distribution of the 1 billion 0G tokens is as follows: [3]
- Community & Ecosystem Growth (56%):
- Ecosystem: 28%
- AI Alignment Node: 15%
- Community Rewards: 13%
- Core Team & Early Backers (44%):
- 0G Team, Contributors & Advisors: 22%
- Backers: 22%
Funding
0G Labs has completed multiple funding rounds to support the development of its decentralized AI infrastructure. In November 2024, the company announced $290 million in new funding, consisting of a $40 million seed round raised by 0G Labs and a $250 million token purchase commitment secured by the 0G Foundation, the governance body for the protocol. The funding involved a range of investors, including Hack VC, Delphi Digital, OKX Ventures, Samsung Next, Bankless Ventures, Animoca Brands and co-founder Yat Siu, Polygon and co-founder Sandeep Nailwal, Stanford Blockchain Fund, Abstract VC, Alchemy, Blockdaemon, and Foresight Ventures. The token commitment is structured to become accessible once the 0G token is launched and traded on exchanges.
In January 2025, the 0G Foundation conducted a large-scale public and private node sale, raising $30.6 million. The sale involved around 85,000 nodes purchased by up to 8,500 participants, making it one of the largest fundraising events in the decentralized AI sector. The process was supported by launchpads such as Second Lane, SwissBorg, and CoinList, and was extended over six weeks to meet demand. This round expanded 0G’s global distributed node operator network and brought the cumulative funding for the project to approximately $400 million across seed, token commitments, and node sales. [11] [12]
Partnerships
- io.net
- Aethir
- ai16z
- Virtuals
- Manta Network
- Arbitrum
- OpenLedger
- Polygon
- Alchemy
- Galxe
- IoTeX
- Netmind AI
- Ankr
- Bitget
- Euclid
- Fog Works
- Hemera
- Movement Labs
- OKX
- Phala Network
See something wrong?
The Agent Tokenization Platform (ATP):Build autonomous agents with the Agent Development Kit (ADK)
