Subscribe to wiki
Share wiki
Bookmark
Core Chain
The Agent Tokenization Platform (ATP):Build autonomous agents with the Agent Development Kit (ADK)
0%
Core Chain
The Core Blockchain (Core Chain) is a Layer 1 blockchain powered by Bitcoin and compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). Its notable feature is a novel consensus mechanism called Satoshi Plus, which combines Delegated Proof of Work (DPoW) and Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS). [1]
Overview
Launched on January 14th, 2023, the Core Blockchain (Core Chain) is a layer one blockchain powered by Bitcoin and compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). Its distinguishing feature is the Satoshi Plus consensus mechanism, amalgamating Delegated Proof of Work (DPoW) and Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS). This mechanism addresses the blockchain trilemma, which posits that a blockchain cannot simultaneously achieve decentralization, security, and scalability. By leveraging the Bitcoin hash rate and DPoS consensus, Core seeks to enhance security, scalability, and decentralization. As the first to implement Satoshi Plus, Core DAO seeks to catalyze broader adoption of Web3 by fostering necessary network effects. [2]
Core DAO
The Core team oversees the Core blockchain via control of the DAO. However, future plans entail gradually decentralizing governance, with CORE token holders entrusted to foster and uphold a community aligned with the project's vision. The DAO envisions three developmental stages for decentralization: Off-chain governance, wherein resolutions are passed with a majority of DAO voters; Limited on-chain governance, facilitating changes to fixed parameters through on-chain voting; and ultimately, Full on-chain governance. [2]
Technology
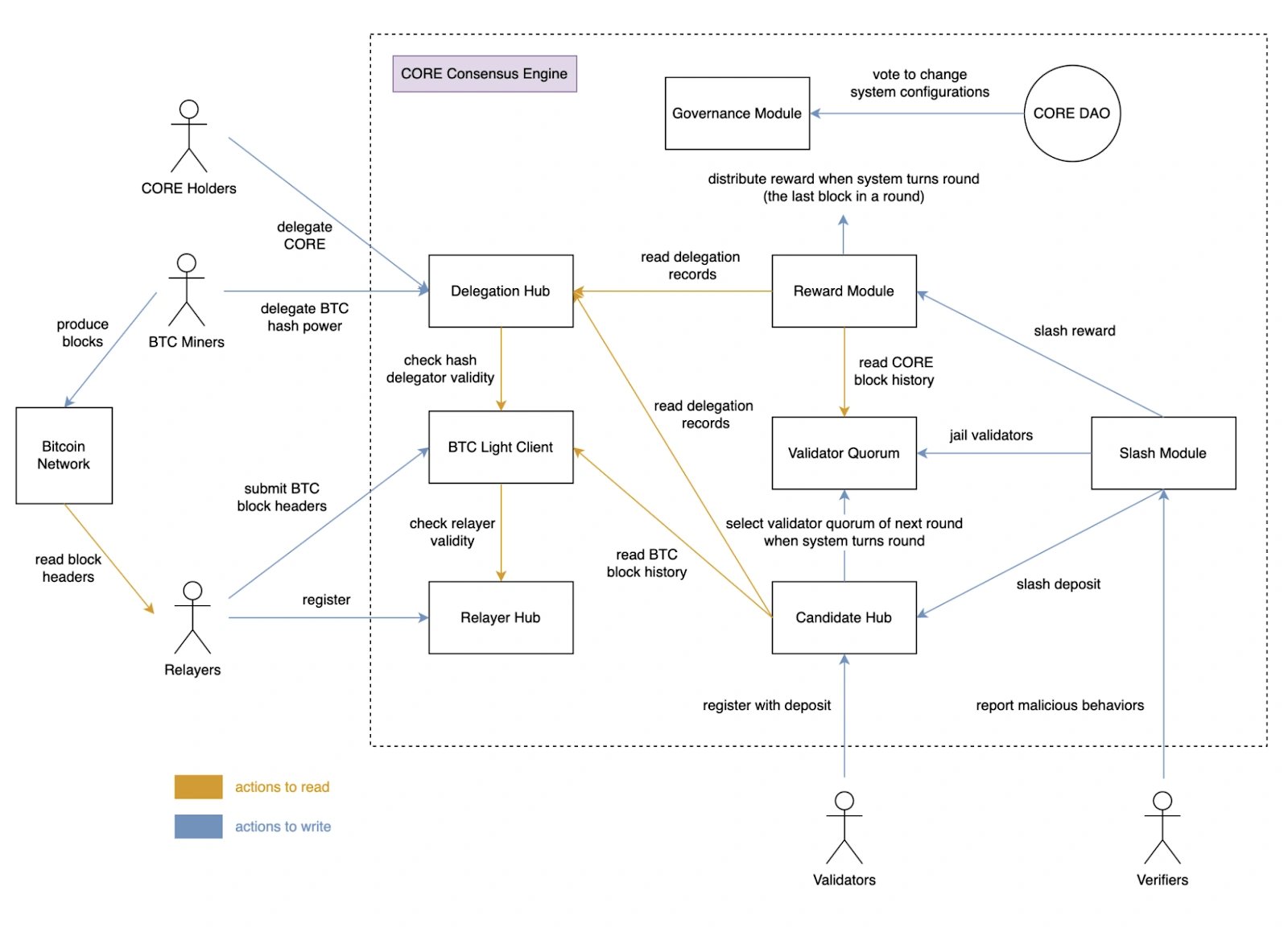
Satoshi Plus
The Satoshi Plus mechanism integrates the hash power of Bitcoin miners with Core validators to synchronize blocks between the BTC miner and Core network. Alongside, DPoS consensus enables token holders to vote and select validators, fostering small holders' participation in network governance. Validator selection involves a complex formula encompassing PoW and DPoS mechanisms, with the top 21 validators elected for 200 blocks. Misbehavior leads to slashing and jailing mechanisms. Blocks are mined every 10 minutes, akin to the Bitcoin network. Rewards are distributed among validators and the System Reward Contract, with 90% allocated to validators and the remainder to relayers and verifiers. [2]
CoreScan
CoreScan is the CORE blockchain's official blockchain explorer, API, and analytics platform. The CoreScan Open APIs have been created to ensure fair access to Core's blockchain data. They enable developers to directly utilize CoreScan's block explorer data and services through standard GET and POST requests. These APIs are offered as a community service without warranty, allowing users to access what they require without unnecessary limitations. [3]
Non-Custodial BTC Staking
Non-Custodial BTC Staking offers a secure and decentralized approach for Bitcoin holders to earn rewards. Users can lock their Bitcoin holdings through a time-bound mechanism within the original Bitcoin network, enabling active participation in the Core blockchain's consensus mechanism while staking. This mechanism is called CLTV timelocks, a Bitcoin-native cryptographic feature setting conditions for transaction outputs. Rather than relinquishing custody of their bitcoins, stakers on Core DAO place their bitcoins in CLTV timelocks within a transaction, which can be configured to return the output after a specified time. Stakers include a script in the transaction with details such as the Core Validator address and the address for receiving CORE token rewards. By delegating their Bitcoin to vote for Validators on Core Chain, Bitcoin stakers earn CORE token rewards, making their otherwise passive Bitcoin holdings productive. This non-custodial implementation of BTC Native Staking enables users to keep their BTC assets on the Bitcoin network while staking, thereby expanding Bitcoin's utility and incentivizing stakers. [4]
Core Bridge
The Core Bridge, fueled by LayerZero, facilitates smooth asset transfers between Core and other blockchains. It comprises LayerZero contracts on Core for cross-chain transfers and bridge/token contracts deployed on both Core and connected blockchains, ensuring seamless interoperability across the blockchain ecosystem. [5]
coreBTC
coreBTC is a native wrapped Bitcoin on the Core Chain, maintaining a 1:1 peg with BTC via a secured and trustless mechanism. This enables Bitcoin users to seamlessly engage with the DeFi space on the EVM-compatible Core Chain using their BTC assets, thereby expanding Bitcoin's utility within DeFi while preserving its security features. In contrast to centralized wrapped tokens like WBTC, which require a custodian to hold the underlying Bitcoin, coreBTC operates on a decentralized infrastructure involving permissionless participants such as Lockers, Guardians, and Liquidators. This decentralized model enhances security and integrity, aligning with the blockchain's decentralized ethos and mitigating risks associated with central custodians. [6]

CORE
CORE, the native utility token on the blockchain, plays a crucial role in staking and covering gas fees. With a total supply of 2.1 billion, CORE follows a token model similar to Bitcoin's. Like Ethereum, a portion of block rewards and gas fees will be burned. The emission schedule spans 81 years to attract Bitcoin miners to delegate their hash power to the network after the expected decrease in mining rewards around 2040. [2]
Tokenomics
CORE had the following allocation: [2]
- Node Mining: 839.9 million CORE tokens (39.995% of total supply), distributed over 81 years;
- Users: 525.6 million CORE tokens (25.029% of total supply), with the first airdrop in February 2023;
- Contributors (Existing and Future): 315 million CORE tokens (15% of total supply);
- Reserves: 210 million CORE tokens (10% of total supply);
- Treasury: 199.5 million CORE tokens (9.5% of total supply);
- Relayer Rewards: 10 million CORE tokens (0.476% of total supply).
stCORE
Introduced in January 2024, stCORE aims to improve the functionality of the CORE token and streamline the staking procedure, offering token holders more flexibility and efficiency. While staking CORE assists in network security, it traditionally restricts token holders from engaging with various DeFi protocols due to the inability to transact tokens. However, this limitation has been overcome with Liquidity Staking Tokens, unlocking liquidity for staked tokens and enabling their utilization in diverse interactions within the DeFi ecosystem. Essentially, liquid staking enhances liquidity for staked tokens, building upon existing frameworks. [7]
Partnerships
XLink
On April 29th, 2024, XLink, a Bitcoin bridge from ALEX LAB Foundation, launched on Core Chain. XLink gives users seamless access to various DeFi services on the Core Chain. [8]
Pyth
On November 14th, 2023, Pyth Price Feeds became accessible on Core, marking a notable infrastructure expansion. Recognizing the pivotal role of infrastructure in maintaining a robust blockchain ecosystem, incorporating Pyth into Core's existing oracle networks enables developers to construct more sophisticated protocols. This enhancement instills users with increased confidence in the efficiency of applications running on Core. [9]
Ankr
On November 13th, 2023, Core announced its integration with Ankr, a leading Web3 infrastructure provider, to offer Core-specific Remote Procedure Calls (RPCs). With access to Ankr's reputable RPC endpoints, developers can ensure seamless and high-speed performance for their decentralized applications (dApps). [10]
SushiSwap
On August 2nd, 2023, Core DAO announced the full integration of SushiSwap, a highly regarded decentralized exchange in the crypto space, onto Core. The integration of SushiSwap introduces concentrated liquidity pools, cross-chain swaps, and a DEX aggregator, aiming to provide users with optimal quotes across various token pairs, thereby empowering them within the ecosystem. [11]
OKX
On March 9th, 2023, Core DAO announced its strategic partnership with OKX to broaden product integration and collaborate with the CORE community, including staking agreements and improved compatibility with Core dApps. [12]
See something wrong?
The Agent Tokenization Platform (ATP):Build autonomous agents with the Agent Development Kit (ADK)
