위키 구독하기
Share wiki
Bookmark
DeSyn Protocol
0%
DeSyn Protocol
DeSyn 프로토콜은 투자자, 프로젝트, 보안 회사를 위해 협업 투자, 개발 및 관리를 용이하게 하도록 설계된 Web3 기반의 탈중앙화된 유동성 인프라입니다. 이는 개방적이고 투명하며 효율적인 자산 관리 솔루션을 제공하여 풀 관리자가 생성 및 펀드레이징부터 관리 및 종료에 이르기까지 펀드 운영의 모든 단계를 처리할 수 있도록 합니다. [1]
개요
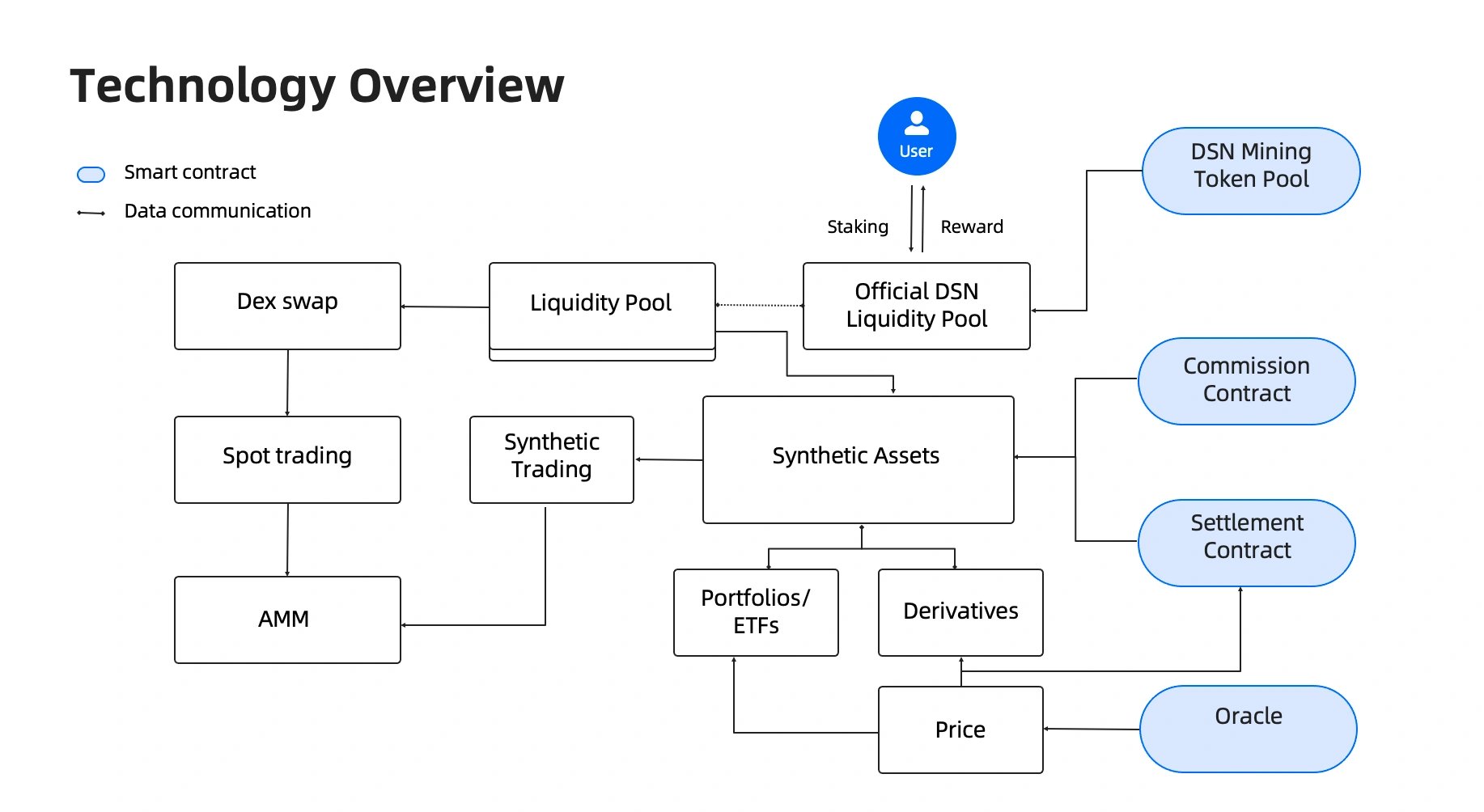
DeSyn 프로토콜은 맞춤형 유동성 풀을 기반으로 하는 스마트 계약을 통해 ETF 및 포트폴리오와 같은 분산형 금융 파생 상품의 생성, 관리 및 거래를 용이하게 합니다. 핵심 구성 요소에는 ETF 및 포트폴리오 관리 도구와 생성, 재조정 및 상환과 같은 기능이 포함됩니다. 거래 기능은 분산형 거래소(DEX) 유동성을 통합하여 유연성을 높이고 2차 시장에서 ETF, 포트폴리오 및 토큰 간의 거래를 지원합니다.
이 프로토콜은 또한 Chainlink 및 주요 DEX와 같은 소스의 데이터를 사용하여 가격 오라클을 통합하여 가격 책정 및 결제 서비스를 제공합니다. 결제 기능은 Ethereum 네트워크의 계약을 통해 인출 및 수수료를 관리합니다. DSN 토큰은 플랫폼 거버넌스 및 거래 결제를 지원하여 프로토콜 내에서 유동성 및 채굴 작업을 지원합니다. [2]
특징
스마트 풀
DeSyn은 스마트 풀을 통합합니다. 스마트 풀은 스마트 계약으로 제어되는 풀로서 잔액, 가중치 및 수수료를 동적으로 조정하면서 완료된 풀을 에뮬레이트할 수 있습니다. 이러한 풀은 팩토리 계약을 사용하여 생성되므로 사용자는 팩토리에서 생성 메서드를 호출하여 새로운 풀 계약을 배포할 수 있습니다. 코어 풀을 직접 배포하면 해당 풀에 대한 사용자 제어가 가능하지만, 스마트 풀을 배포하려면 팩토리 주소에 연결해야 합니다. 이 설정에서 사용자는 스마트 풀을 제어하고 스마트 풀은 코어 풀을 관리하여 고급의 유연한 풀 관리를 가능하게 합니다. [2]
제품
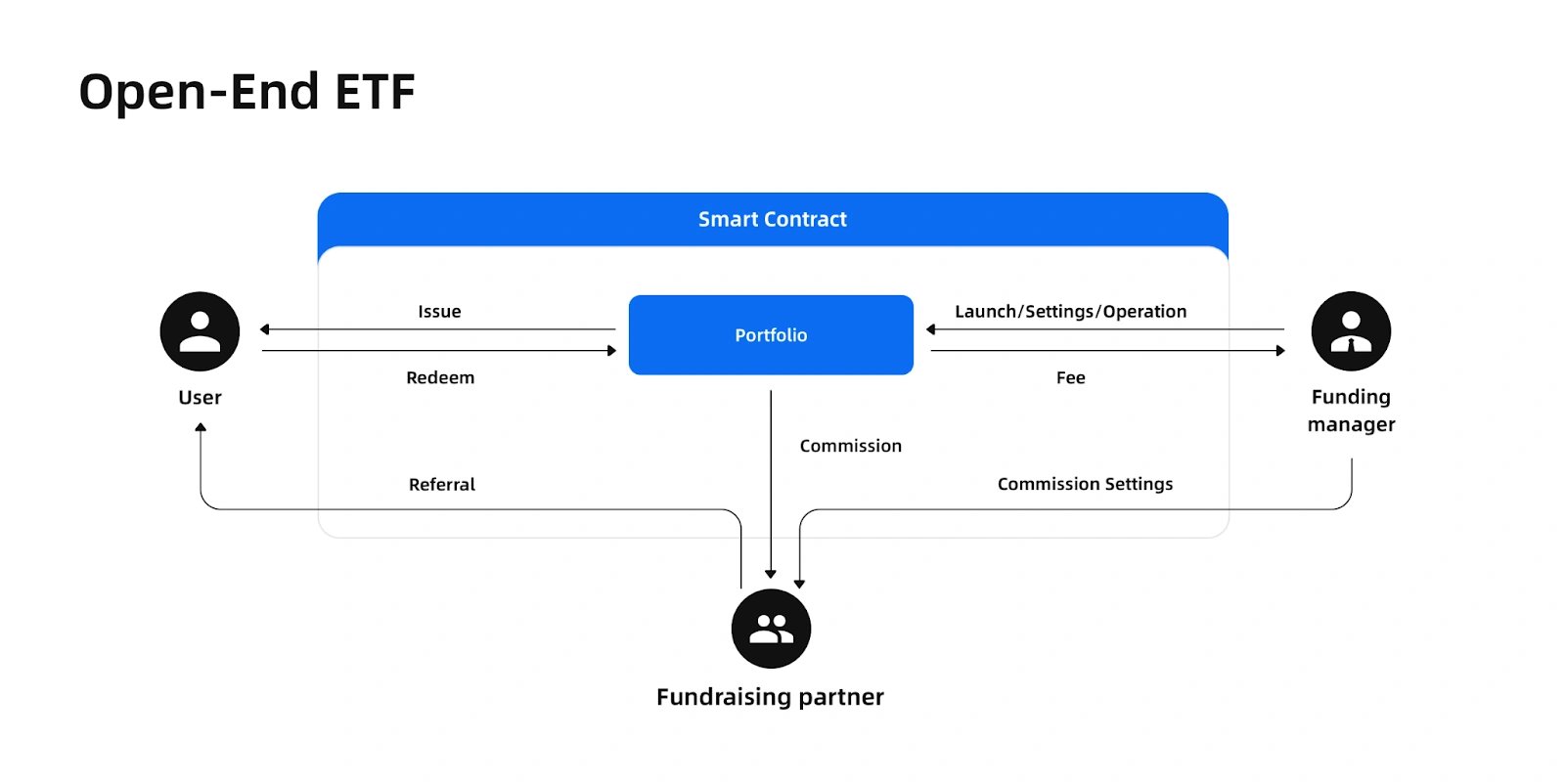
개방형 ETF
개방형 ETF는 인덱스 기반 전략을 위해 설계되었으며, 풀 관리자가 디지털 자산을 비례적으로 할당하여 특정 인덱스나 섹터를 구축하거나 추적할 수 있도록 합니다. 사용자는 제한 없이 풀 지분을 발행하고 상환할 수 있습니다. 필요한 자산이 없는 경우, USDC 또는 WBTC와 같은 토큰을 사용하여 지능형 발행을 할 수 있으며, 계약은 Uni V2, V3 또는 1inch와 같은 플랫폼을 통해 환율을 최적화하여 목표 자산을 획득합니다.
펀드레이징 파트너는 시간 제약 없이 추천 프로그램을 통해 수수료를 얻을 수 있으며, "원클릭 전달"과 같은 도구를 사용하여 추천 링크를 공유할 수 있습니다. 수수료는 언제든지 추적하고 청구할 수 있습니다. 풀을 시작할 때 풀 관리자는 수수료, 커미션 및 액세스 권한과 같은 매개변수를 설정합니다. 수수료 및 커미션 분배는 스마트 계약을 통해 자동화되며, 관리자는 프로토콜에서 직접 자산을 이전할 수 없습니다. [3]
soETH
Semi Open-end 3x ETH 스테이킹 ETF (soETH)는 레버리지 유동성 스테이킹 전략을 사용하여 ETH 스테이킹 수익률을 높이는 동시에 매달 3일(5일, 15일, 25일) 동안 자금에 대한 제한적인 접근을 제공합니다. 이 접근 방식은 수익 잠재력과 유동성 관리를 균형 있게 유지합니다.
이 펀드는 DeSyn의 분산형 자산 관리 프레임워크를 활용하여 레버리지 전략을 구현하고, stETH 수익률을 최적화하는 동시에 거래 비용을 줄이고 AAVE 담보 부채와 관련된 위험을 최소화합니다. 이는 스테이킹과 ETH 차입 간의 금리 차이에 의존하여 체계적인 레버리지 위험을 관리합니다.
저렴하게 설계된 soETH는 낮은 관리 및 거래 수수료를 특징으로 합니다. 이는 체계적인 모니터링 및 운영 관리를 통해 지원되는 직접적인 Ethereum 스테이킹보다 훨씬 높은 수익률을 제공하는 것을 목표로 합니다. [4]
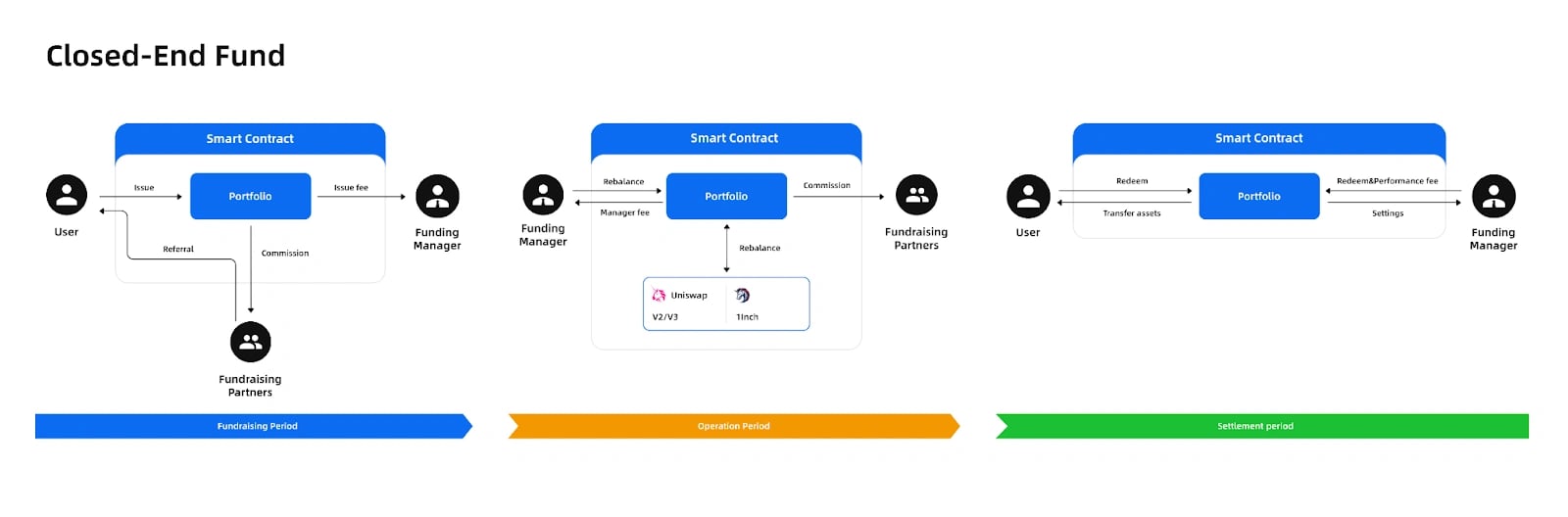
폐쇄형 펀드
폐쇄형 펀드는 모금, 운영, 청산의 3단계 과정을 통해 복잡한 투자 전략을 실행하도록 설계되었습니다. 사용자는 모금 기간 동안 풀 지분을 발행할 수 있지만 인출할 수는 없습니다. 풀 관리자는 발행 수수료를 징수하고, 모금 파트너는 스마트 계약에 미리 정의된 수수료를 받으면서 모금 목표 달성을 돕기 위해 추천 프로그램에 참여합니다.
모금 목표가 달성되면 운영 단계가 시작됩니다. 사용자는 지분을 발행하거나 인출할 수 없으며, 모금 파트너는 홍보를 중단하지만 계속해서 수수료를 받습니다. 풀 관리자는 자산을 이전하거나 인출하지 않고 풀의 포지션만 조정할 수 있습니다. 사용자는 청산 단계에서 원금과 이자를 받으면서 풀 지분을 인출할 수 있습니다. 프로토콜은 스마트 계약에 미리 결정된 비율에 따라 풀 관리자와 모금 파트너 간에 상환 수수료를 자동으로 할당합니다. [5]
erETH 펀드
erETH 펀드는 Eigenlayer, Ether.fi 및 DeSyn을 포함한 여러 계층화된 재스테이킹 토큰(LRT) 프로토콜을 통합하여 Ethereum 재스테이킹 수익률을 향상시킵니다. 스테이킹 및 재스테이킹 수익률, 에어드랍 및 프로토콜별 보상을 결합하여 포괄적인 수익 전략을 제공합니다. 이 펀드는 개방형 모델로 운영되어 유연한 발행 및 상환을 가능하게 하며 DeSyn의 분산 관리 인프라를 통해 자산 보안을 보장합니다. [6]
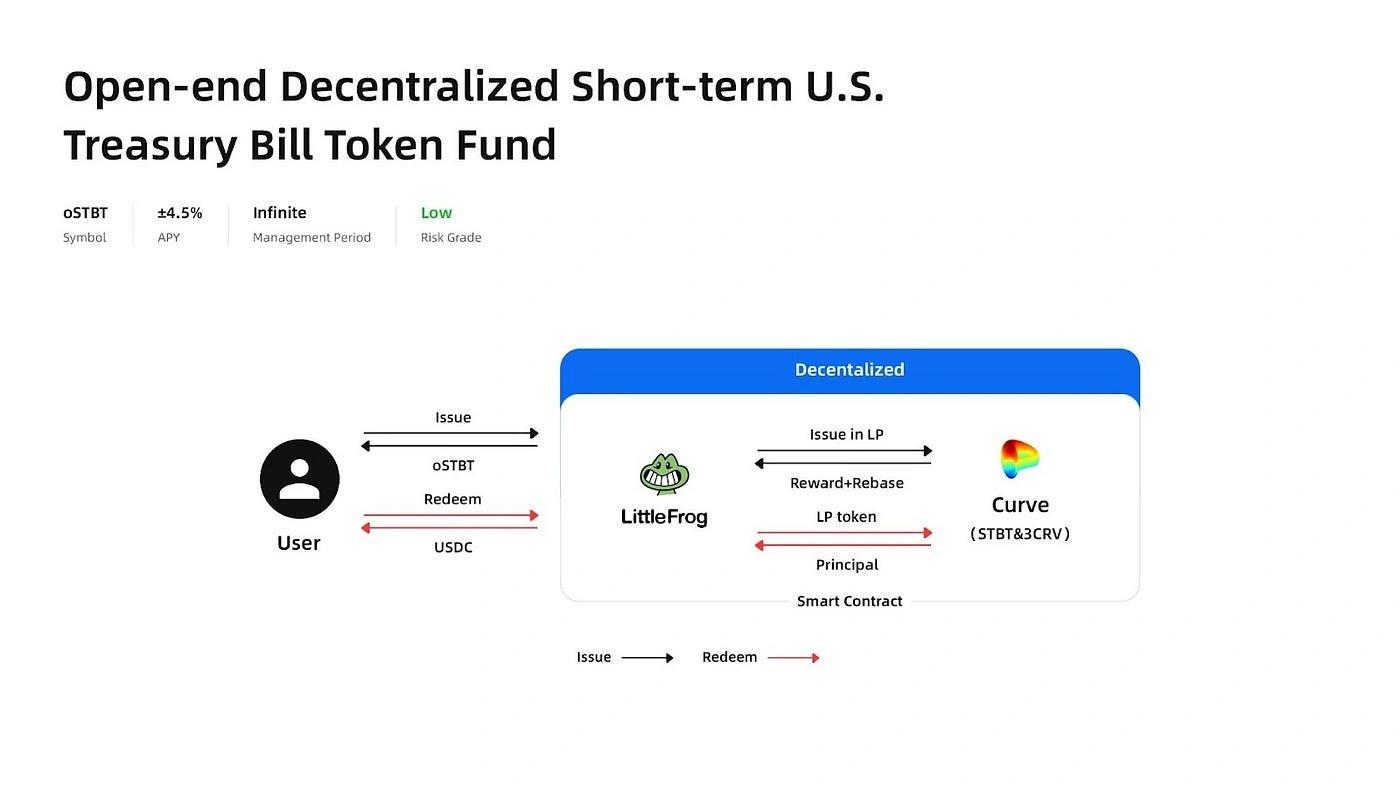
oSTBT
RWA 펀드 oSTBT는 단기 미국 국채 토큰(STBT)을 기반으로 한 개방형 분산 펀드로, 투자자들이 언제든지 입출금할 수 있습니다. 안정적이고 안전한 투자 기회를 제공하도록 설계되었으며, 낮은 위험, 4.5% 이상의 예상되는 일관된 수익률(APR), 높은 유동성으로 미국 국채에 접근할 수 있도록 하며, 펀드 관리의 투명성과 효율성을 우선시합니다. [7]
dSTBT
탈중앙화 단기 미국 국채 토큰 펀드(dSTBT)는 탈중앙화 자산 관리 DAO인 Little Frog가 관리하는 폐쇄형 펀드입니다. 이는 단기 국채 토큰(STBT)을 기반으로 하며, STBT는 ERC 1400 표준을 준수하고 낮은 위험의 수익률을 가진 미국 국채를 나타냅니다. 각 STBT 토큰은 페깅되어 있으며, 스테이블코인으로 미국 달러와 1:1로 교환 가능하며, 6개월 이하 만기의 국채와 미국 정부가 보증하는 증권으로 완전히 담보된 환매 조건부 채권으로 뒷받침됩니다.
Little Frog는 DeSyn 플랫폼의 탈중앙화 스마트 계약을 활용하여 펀드를 생성하고 관리하여 투명성, 보안 및 접근성을 보장합니다. 이 펀드는 최소 투자 임계값이 없고 수수료가 저렴하며 실시간 온체인 거래 모니터링이 가능합니다. Matrixport에서 제공하는 기본 자산은 미국 국채로 뒷받침되어 투자자에게 안전하고 투명한 투자 수단을 제공합니다. [8]
DIY 제품
DIY 제품은 고급 전략에 맞춰 전문 개인 또는 자산 관리 기관을 위해 설계되었습니다. 사용자는 DeSyn의 인터페이스 문서를 참조하거나 팀과 상담하여 복잡한 계산을 통해 다양한 DeFi 전략을 통합한 제품을 만들 수 있습니다. 이 플랫폼은 맞춤형 전략 제품 개발을 지원하여 풀 관리자가 특정 거래 전략에 맞춰 상품을 조정할 수 있도록 합니다. [9]
SLP 모델 런치패드
SLP 모델 런치패드는 사용자에게 개방적이고 투명하며 자동화된 플랫폼을 제공하도록 설계되었습니다. 참가자는 중앙 집중식 프레임워크에 참여하면서 여러 DeFi 전략에 액세스하고 관리할 수 있습니다. 이 모델은 다양한 DeFi 전략과 기회를 하나의 시스템에 통합하여 사용자가 다양한 재정적 목표를 효율적으로 추구할 수 있도록 간소화된 접근 방식을 제공합니다. 세 가지 SLP 모델 제품은 다양한 위험 감수성과 투자 전략을 충족합니다: [10]
단순 예금 상품은 DeSyn 플랫폼에 직접 자산을 예치하여 낮은 위험을 감수하는 투자자를 대상으로 하며, 다른 DeFi 프로토콜을 사용하지 않고 DeSyn, 새로운 체인 및 파트너의 Layer-1 보상 토큰 및 에어드랍을 통해 안정적인 수익을 창출하는 데 중점을 둡니다.
유동성 풀 상품은 중간 위험을 감수하는 투자자에게 적합하며, DEX 및 대출 프로토콜과 같은 DeFi 플랫폼에 자산을 배포하고, 레버리지 스테이킹 및 리스테이킹과 같은 전략을 통합하는 동시에 생태계 및 프로토콜 에어드랍을 통해 보상을 극대화합니다.
기초 거래 상품은 Binance에서 구조화된 기초 거래와 예측 가능하고 낮은 변동성 수익을 위해 온체인 에어드랍을 결합하여 안정성을 강조하며, 위험 회피 참가자에게 적합합니다.
SDT 모델
SDT 모델은 안전, 효율성 및 단순성을 강조하는 분산형 풀 관리 접근 방식을 도입합니다. 이 시스템은 자동화된 관리 프로세스를 통해 사용자의 복잡성을 줄이면서 분산된 감독을 유지합니다. SDT 모델을 활용함으로써 투자자는 자산 보안과 운영 효율성을 우선시하는 자동화된 프레임워크에 의존하여 간소화된 방식으로 풀 관리에 참여할 수 있습니다. [10]
팀 배틀
SLP 모델 내 팀 배틀 기능은 모금 팀, 마케팅 회사, 보안 기관과 같은 다양한 주체들이 협력적인 노력을 통해 파밍 캠페인에 참여할 수 있도록 합니다. 이러한 구조는 공동 참여와 자원 공유를 장려하여 DeFi 생태계 내에서 기회를 향상시킵니다. 협업을 촉진함으로써 팀 배틀은 참가자들이 전문 지식과 자원을 결합하여 탈중앙화 금융에서 상호 목표를 달성하기 위한 보다 역동적이고 상호 연결된 접근 방식을 만들 수 있도록 합니다. [10]
자금 조달
첫 번째 라운드
2022년 7월 자금 조달 라운드에서 DeSyn 프로토콜은 140만 달러의 자금을 확보했습니다. 첫 번째 라운드는 Fenbushi Capital, SNZ Capital, Everest Ventures Group, Incuba Alpha, Bing Ventures, Lancer Capital 및 TKX Capital이 주도했으며, 암호화폐 업계의 저명한 개인 투자자들이 참여했습니다. [11]
두 번째 라운드
DeSyn 프로토콜은 5백만 달러 이상의 자금을 모금하며 두 번째 펀드레이징 라운드를 완료했습니다. 이 프로젝트는 ETF 및 포트폴리오와 같은 금융 상품의 안전하고 투명하며 비용 효율적인 생성 및 거래를 가능하게 하는 차세대 DeFi 파생 상품 프로토콜을 개발하는 것을 목표로 했습니다. 이번 펀드레이징에는 TPS Capital, LD Capital, Spark Digital Capital, Mentha Partners, Kosmos Ventures, Asymmetries Technologies, PAKA, Outliers Fund, CoinSummer, Consensus Lab, AZDAG, LucidBlue Ventures, Westlabs, Chiron Partners, Zonff Partners, TGE Capital, JDAC Capital, Ticker Capital, CatcherVC, EVG, TKX, Lancer Capital, TokenInsight Research, A+CAPITAL을 포함한 다양한 자본 펀드가 참여했습니다. 거래소 펀드에는 OKX Blockdream Ventures, MEXC, Mirana Ventures, BitMart & Cipholio Ventures, Bibox가 포함되었으며, 퍼블릭 체인 펀드에는 TRON 및 NEO ECOFUND가 포함되었습니다. 개인 투자자로는 Joseph Eagan(Acme Crypto Holding의 공동 창립자 겸 CEO, Polychain Capital의 전 사장)과 Jeff Pan이 참여했습니다. [12]
파트너십
AILayer
Avalon
IONIC
UniRouter
B2 Network
zkLink
Allora
Babylon
UXLINK
Eigenpie
Safeheron
Meta Trust Labs
VIP3
Halo Wallet
Realtize
잘못된 내용이 있나요?
