위키 구독하기
Share wiki
Bookmark
dTRINITY
0%
dTRINITY
dTRINITY는 차입 비용을 줄이고 지속 가능한 이자율을 제공하도록 설계된 스테이블코인 유동성 프로토콜입니다. 이를 통해 sFRAX, sUSDe, sDAI와 같은 수익 창출 자산에 대한 루핑 전략을 개선합니다. [1]
개요
dTRINITY는 분산형 유동성 프로토콜로, 더 낮은 차입 비용, 지속 가능한 수익률, 그리고 새로운 이더리움 레이어 2 및 레이어 3 생태계에 필수적인 DeFi 인프라를 제공합니다. 2024년 3분기에 출시될 예정이며, 기본 블록 공간 인센티브를 제공하는 레이어 2 네트워크인 Fraxtal에서 처음 운영됩니다. dTRINITY는 dUSD 스테이블코인, dLEND 머니 마켓, 그리고 dSWAP 거래소, 그리고 TRIN 거버넌스 토큰의 세 가지 핵심 구성 요소로 이루어져 있습니다. dUSD는 Fraxtal L2 네트워크의 커뮤니티 중심적인 미국 달러 스테이블코인으로, USDC 또는 법정화폐 담보로 상환 가능하며, 온체인 거래 및 법정화폐 온/오프 램프 활동을 용이하게 하며, 담보 준비금에서 발생하는 수익으로 차용자 이자율을 보조합니다. dLEND는 Aave v3의 포크로, dUSD 및 기타 디지털 자산의 담보 대출/차입을 지원하며, dSWAP은 Uniswap v3의 포크로, 효율적인 거래 및 담보 청산을 가능하게 하며, dUSD를 기본 페어로 사용합니다. [2]
Fraxtal
Fraxtal은 "프랙탈 스케일링"을 특징으로 하는 Optimism (OP) 스택 모듈형 롤업 Layer 2 블록체인입니다. 이는 스마트 계약 플랫폼을 위해 OP 스택을 사용하는 EVM과 동등한 롤업으로, Optimism 및 Base와 같은 Ethereum 롤업과 유사하게 안전하고 비용 효율적인 애플리케이션 배포를 가능하게 합니다. Fraxtal은 모듈형으로, 다른 체인 및 네트워크를 위한 여러 구성 요소와 미들웨어를 통합하며, 현재 Frax Core Team에서 개발한 데이터 가용성 모듈을 사용합니다. 이는 사용자와 개발자에게 가스 소비 및 스마트 계약 상호 작용에 대해 FXTL 포인트를 보상하는 블록 공간 인센티브(Flox)를 제공하며, 이는 토큰으로 전환할 수 있습니다. 기본 가스 토큰은 Frax Finance의 Frax Ether (frxETH)이며, 사용자와 dTRINITY와 같은 스마트 계약이 추가 인센티브를 위해 FXTL 포인트를 얻을 수 있도록 합니다. [3]
특징
dUSD 스테이블코인
dTRINITY USD (dUSD)는 탈중앙화된 완전 준비금 스테이블코인으로, USD로 표시된 스테이블코인과 수익 창출 자산의 온체인 준비금으로 뒷받침됩니다. Fraxtal L2에서 발행되며, dUSD는 가스 비용 외에 수수료 없이 스마트 계약을 통해 담보를 유지합니다. 준비 자산은 품질, 실적, 위험 프로필과 같은 요소를 기반으로 선택되며, 최소 90%는 차용자를 위한 수익을 창출하는 수익 코인에 할당됩니다. 가격 안정성은 API3 오라클을 사용하여 유지되며, 이는 시장 거래 가격이 아닌 기본 보유 자산을 기반으로 자산 가치를 결정합니다. 거버넌스는 준비 자산 조정, 필요한 경우 발행 중단, 유동성 변동으로 인한 디페깅 위험 완화를 통해 위험 관리를 감독합니다. [4]
유틸리티
dUSD는 dTRINITY의 기본 스테이블코인이자 통합 유동성 레이어로서, dLEND와 dSWAP의 기본 페어로 사용됩니다. 준비금에서 발생하는 플로트 수입을 외부화하지 않는 중앙화된 스테이블코인과 달리, dUSD는 플로트 수입의 대부분을 이자율 보조금으로 공유하여 프로토콜의 성장과 채택을 장려함으로써 dTRINITY 커뮤니티를 우선시합니다. [4]
이러한 접근 방식은 프로토콜의 성공이 dTRINITY와 dUSD가 계속 확장됨에 따라 커뮤니티 구성원의 가치 향상으로 직접 이어지는 커뮤니티 중심 모델을 강화합니다. [4]
안정성 메커니즘
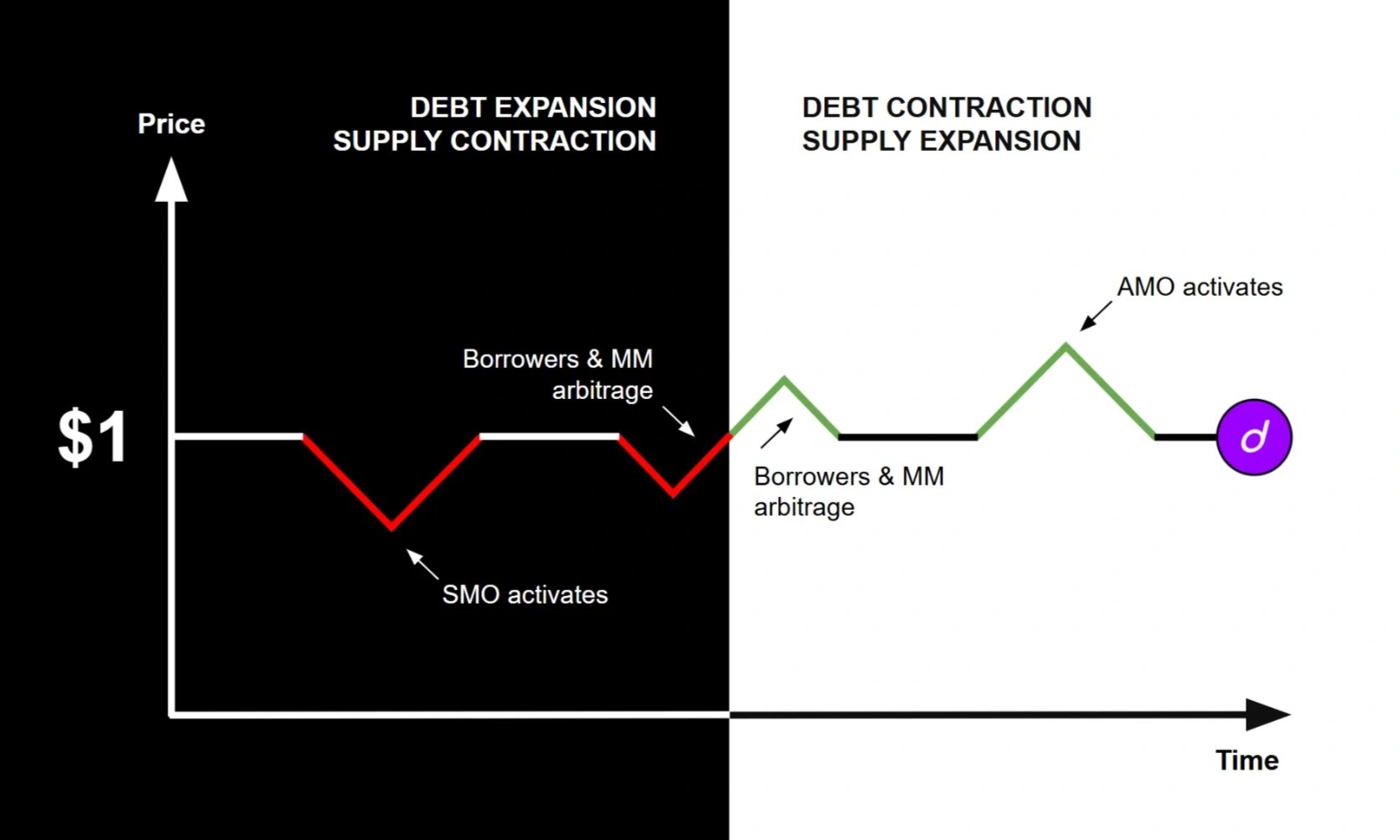
- 비상환성: dUSD는 준비금에 대한 직접적인 상환을 허용하지 않고, 대신 차용인, 트레이더 및 유동성 공급자의 차익 거래와 공개 시장 운영에 의존하여 탈중앙화 거래소에서 1달러에 대한 소프트 페그를 유지합니다.
- 안정성 시장 운영 (SMO): dUSD가 1달러 미만으로 거래될 때 프로토콜은 거래소에서 토큰을 다시 구매하여 공급을 줄이고 페그를 안정화합니다. 이 과정은 또한 차익 거래 이익을 생성하여 과잉 담보화를 증가시킵니다.
- 알고리즘 시장 운영 (AMO): dUSD가 1달러 이상으로 거래될 때 프로토콜은 추가 토큰을 지정된 유동성 풀에 공급하여 공급을 확장하고 차익 거래를 통해 준비금을 축적하면서 페그를 안정화합니다.
- 차용인 차익 거래: 차용인은 dUSD가 1달러 미만으로 거래될 때 할인가로 부채를 상환할 수 있으며, 1달러로 빌려 프리미엄으로 판매하여 이익을 얻을 수 있습니다. 이러한 조치는 가격 안정성을 강화합니다.
- 마켓 메이커 (MM) 차익 거래: 마켓 메이커는 dUSD를 할인가로 구매하거나 1달러로 민팅하여 프리미엄으로 판매하여 가격 변동을 활용하여 유동성을 추가하고 프로토콜 기반 안정화 메커니즘에 대한 의존도를 줄입니다.
- 담보 비율 (CR): 프로토콜 운영으로 인한 초과 준비금은 dUSD의 담보 비율을 100% 이상으로 밀어 올려 신뢰를 강화하고 가격 변동을 안정화하며 준비금 평가 절하에 대한 완충 장치를 만들 수 있습니다. 거버넌스는 임계값을 초과할 때 잉여 준비금을 할당하는 방법을 결정할 수 있습니다. [4]
동적 이자
dUSD는 준비금 수익의 최소 90%를 사용하여 매주 새로운 토큰을 발행하고, 미결제 부채를 기준으로 차용인에게 리베이트로 분배하여 차입 비용을 보조합니다. 리베이트율은 준비금의 수익률과 총 부채에 대한 dUSD 유통량 비율에 따라 달라집니다. 또한 dUSD는 여러 번 재대출될 수 있으며, 총 차입 및 공급 가치가 본원 통화 공급량을 초과할 수 있는 전통적인 은행과 유사한 승수 효과를 생성합니다. [4]
금리 주기
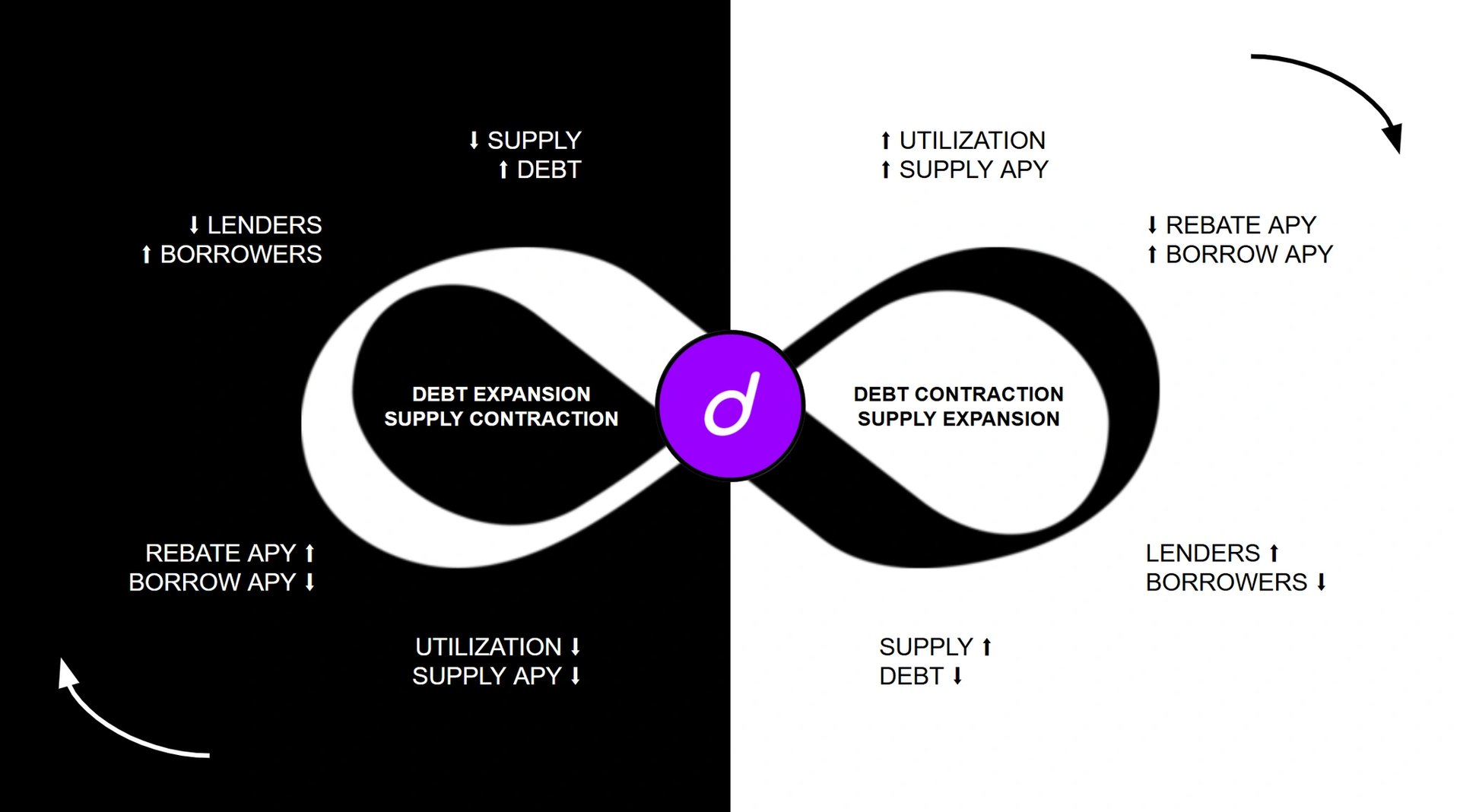
dUSD의 금리 주기는 시장 수요와 공급에 따라 차입 금리가 동적으로 조정되므로 전통적인 연방 준비 제도 이사회 주기와 반대로 작동합니다. 차입 수요가 낮으면 금리가 하락하여 부채 발행이 증가하고 안정성 시장 운영(SMO)을 통해 dUSD 공급이 감소합니다. 반대로 차입 수요가 증가하면 금리가 인상되어 대출 기관은 더 많은 dUSD를 공급하고 차용인은 대출을 상환하여 알고리즘 시장 운영(AMO)을 통해 dUSD 공급이 확대됩니다. 프로토콜은 차용인에게 보조금을 지급하여 활용률을 유지하고 대출 기관의 인센티브가 매력적으로 유지되도록 보장하며 지속적인 생태계 참여를 촉진합니다. [4]
dLEND 머니 마켓
dLEND는 Fraxtal에서 Aave V3를 포크한 담보 대출 시장으로, 사용자가 담보를 사용하여 대출을 받고 유동성 공급자에게 지속적인 이자 지급을 대가로 유동성을 제공할 수 있습니다. 레버리지, 숏 포지션, 헤징 등 다양한 금융 전략을 지원하며, 수익률 루핑 전략에 중점을 둡니다. [5]
이 프로토콜은 Fraxtal에서 dUSD 및 기타 디지털 자산의 담보 대출 및 차입을 용이하게 합니다. dLEND의 dUSD 대출 금리는 수요와 활용을 촉진하기 위해 정기적으로 보조금을 지급하여 dUSD 대출자에게 다른 프로토콜 및 네트워크 인센티브와 함께 지속 가능한 스테이블코인 수익률을 제공합니다. [5]
dLEND에서 대출자는 대출 자본에 대한 이자를 얻으며, 이는 종종 대출자가 얻는 것보다 더 높은 APR을 지불하는 대출로 이어집니다. 대출 및 차입에 대한 이자율은 활용률에 따라 결정되며, 더 높은 금리는 대출자가 대출금을 상환하도록 장려하고 더 많은 대출자를 유치하여 새로운 대출자를 위한 유동성을 보장합니다. [5]
대출 보조금
dUSD 대출은 보조금 혜택을 받아 담보 대비 가장 비용 효율적인 옵션입니다. dLEND의 프로젝트는 대출자 또는 차용자에게 추가 토큰으로 보상하여 사용량을 더욱 늘릴 수 있습니다. dTRINITY의 거버넌스는 현재 시장에 대한 새로운 보상 토큰을 도입하여 사용자 참여를 장려할 수 있습니다. 이러한 보조금으로 인해 dUSD의 대출 APR은 공급 APY보다 낮아져 보조금을 받지 않는 시장보다 활용률이 높아질 수 있습니다. [5]
dUSD 시장
dUSD는 dLEND에서 차입을 위해 지정된 스테이블코인으로, 차용인이 스테이블코인 간 전환 없이 일관되고 낮은 차입 비용을 제공합니다. 이는 차입 과정을 단순화하고, 대출 기관이 지속적인 활용률과 더 높은 수익률로부터 이익을 얻도록 보장하며, 지속적인 차용인 보조금으로 지원됩니다. [5]
오라클
dLEND는 시장 상황에 따라 혼합된 오라클 접근 방식을 사용합니다. 주로 광범위한 외부 가격 발견 장소를 가진 자산에 대해서는 RedStone 오라클을 사용합니다. Fraxtal에만 있거나 외부 시장에 유동성이 부족한 자산의 경우 dSWAP이 가격 오라클 역할을 합니다. RedStone 가격이 오래된 경우 dSWAP은 대체 오라클 역할도 합니다. [5]
청산
dLEND의 차용자는 대출 가치(LTV) 비율이 시장별로 다른 특정 임계값 아래로 떨어지면 청산될 가능성이 있습니다. 청산을 피하려면 차용자는 담보를 더 추가하거나 부채의 일부를 상환할 수 있습니다. 청산이 발생하면 청산인과 프로토콜 모두 수수료를 부과하며, 수수료 금액은 관련된 특정 시장에 따라 달라집니다. [5]
DeFi 플라이휠
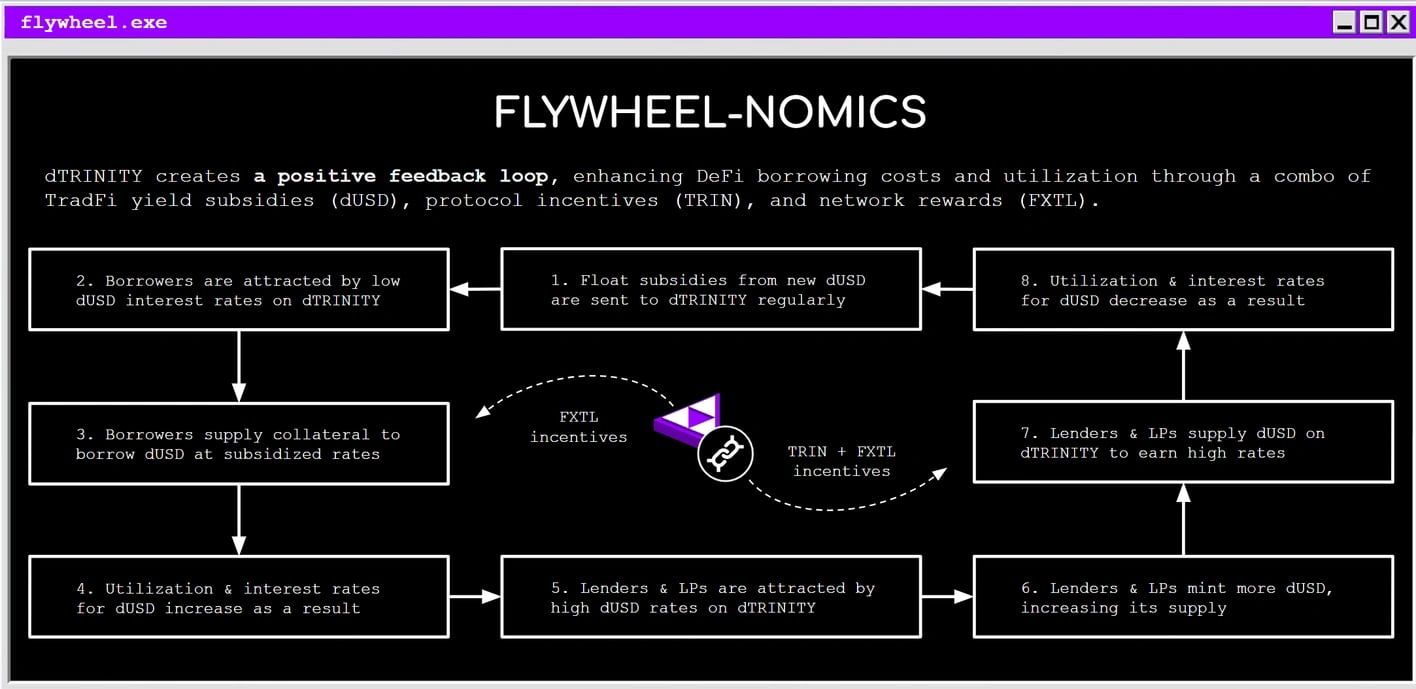
dTRINITY의 플라이휠은 외생적 및 내생적 인센티브를 통해 유동성과 사용자 활동을 유치하도록 설계되었으며, TVL 성장과 함께 지속 가능하게 확장됩니다. 이 프로토콜은 거버넌스 토큰 보유자와 dUSD 유동성을 제공하는 대출 기관 및 LP와 같은 공급 측 참여자 간의 상호 작용을 강화하기 위해 ve(3,3) 프레임워크를 통합합니다. [6] [7]
외생적 인센티브에는 dUSD 보상 및 보조금, FXTL 네트워크 보상, 생태계 파트너의 인센티브가 포함됩니다. 내생적 인센티브에는 TRIN 토큰/포인트 보상 및 TGE 이후 투표 에스크로 TRIN(veTRIN) 토큰 보유자와의 프로토콜 수수료 공유가 포함됩니다. [6]
파트너십
- Stably
- Frax
- Fraxtal
- Cream Labs
- Coin98
- Verichains
- RedStone Oracles [8]
잘못된 내용이 있나요?
