Subscribe to wiki
Share wiki
Bookmark
Balancer
The Agent Tokenization Platform (ATP):Build autonomous agents with the Agent Development Kit (ADK)
0%
Balancer
Balancer Protocol (established in 2018) is an open-source protocol, automated portfolio manager, and liquidity provider. The protocol allows users to trade tokens, create liquidity pools, and invest in existing pools while earning yields from trades. [1][2][15]
Overview
Balancer is a protocol for multi-token founded by Fernando Martinelli and Mike McDonald in 2018. The name was derived from the platform's self-rebalancing liquidity pools. It enables portfolio owners to create Balancer Pools, and traders to trade against them. Balancer Pools contain two or more tokens, each with an independent weight representing its proportion of the total pool value. The pools provide the Balancer Protocol with liquidity and charge traders a fee for access to it. Pools can be considered automated market-makers, since anyone can swap any two tokens, in any pool. Balancer V2 is live on Ethereum, Polygon, Arbitrum, and specific testnets. [15][31]
In August 2021, Balancer Protocol launched support on the Layer 2 scaling solution Arbitrum to reduce gas costs and scale liquidity. The expansion also allows users to trade on the Balancer app using Arbitrum. [32]
In June 2022, Balancer launched on Layer 2 rollup network Optimism in collaboration with Beethoven X. The benefits for Balancer include additional scaling, smart wallet EOAs (no “approves”, pay gas in any token), and decentralization of the transaction sequencing operation. [33]
“With this launch, Balancer recognizes Optimism as a leading L2 solution. Its distinctive scalability, while inheriting Ethereum’s security, will enhance the user experience and propel DeFi growth. L2s show the promise of reducing transaction fees and network congestion, and we are excited to bring our technology to the Optimism ecosystem.” — Fernando Martinelli, Balancer Labs CEO & Co-Founder. [33]
AMM Protocol
Balancer serves as an automated market maker (AMM). It provides unique liquidity pools that can contain several assets rather than just two, which is standard for most other AMM pools (on exchanges such as Uniswap). The pools can also be programmed via smart contracts, enabling the implementation of custom rules and strategies[8][9].
In October 2020, Balancer partnered with a NEAR protocol. The Balancer team expressed that they will stay primarily focused on the Ethereum implementation of their protocol, however, Balancer Head of Growth Jeremy Musighi said that working with NEAR will give them an idea of how Balancer will perform on a chain with greater scalability. [14]
In addition, Balancer and NEAR are offering two grants worth up to $10,000 to incentivize the development of a Balancer front-end for NEAR, as well as an integration of Balancer into the NEAR wallet. The incentive is designed to drive faster adoption and usability of the NEAR iteration of Balancer, allowing for improved accessibility and user experience. Rewards will be paid in NEAR and BAL tokens. [14]
Balancer Protocol Governance Token (BAL)
The first version of Balancer launched without a native token. On June 1st, 2020, BAL tokens were distributed to users providing liquidity to the Balancer protocol. The Balancer Protocol Governance Token (BAL) allows holders to vote on new features, potential protocol fees, or any other development that takes place around the Balancer protocol[6].
Tokenomics
Out of the initial 100 million BAL tokens, 25 million BAL tokens were allocated to founders, stock options, advisors, and investors, and are all subject to vesting periods. 5 million more were allocated to the Balancer Ecosystem Fund. This fund will be deployed to attract and incentivize strategic partners that will help the Balancer ecosystem grow. Another 5 million was allocated for the Fundraising Fund. [16]
The rest of the tokens will be distributed through a process called liquidity mining. Every week, 145,000 BAL is awarded to users who have liquidity in Balancer pools, totaling 7.5 million BAL per year. [16]
On June 23, 2020, the Balancer protocol governance token (BAL) went live on the mainnet. On its first day of trading, the value of the token rose from $7 to $22 at one point, giving the token a 235% spike in under 12 hours. [6]
veBAL
veBAL (vote-escrow BAL) is a vesting system based on Curve's veCRV mechanism which locks 80/20 BAL/WETH Balancer Pool Tokens for a maximum of 1 year. veBAL went live in March 2022. [21]
veBAL token provides BAL holders and liquidity providers with benefits such as:
- Long-term alignment - By locking BPT, token holders will be encouraged to support Balancer over the long term instead of speculating short-term.
- Protocol revenue distribution: 75% of all fees generated by the protocol are proportionally distributed to veBAL holders.
- Plug&play compatibility with Curve’s ecosystem
- Predictability[21]
BAL’s Inflation Schedule Update
According to BAL’s inflation schedule introduced with the migration to veBAL tokenomics in early 2022, every four years, the inflation of BAL should be halved. Starting one year after the launch of the tokenomics model, there are gradual steps every year for reducing the BAL inflation. A detailed schedule can be seen in the following figure;
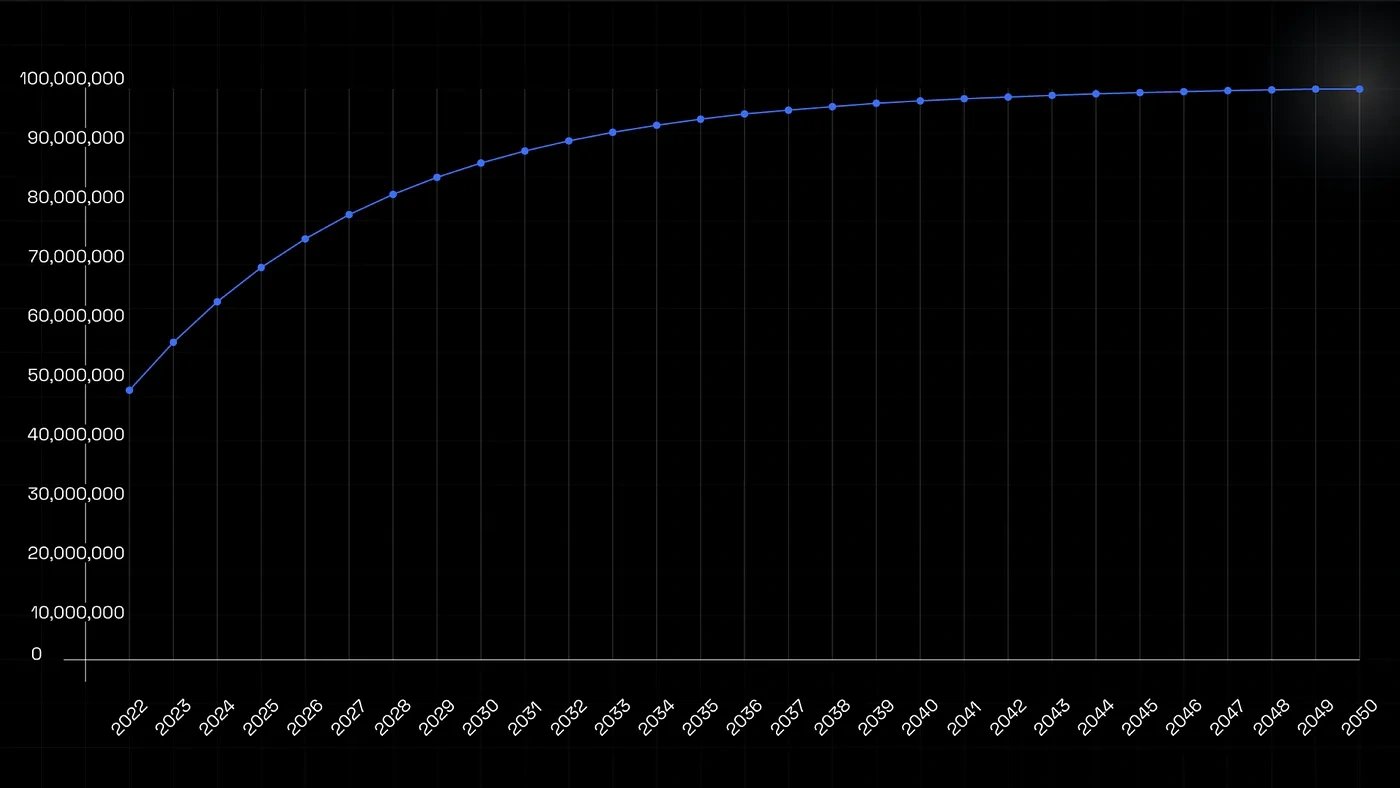
Therefore, the first halving installment scheduled for March 28, 2023, brought about the first annual 15.9% emissions drop, lowering the number of BAL issued weekly to around 122,000. [41]
Liquidity Pools and Rebalancing
Users can create or contribute to liquidity pools, which consist of their weighted assets and a trading fee set by the creator. This allows anyone to own a self-balancing index fund or invest in someone else’s and earn fees as other users trade against their portfolio. Smart Order Routing (SOR) trades to the pools at the best rate possible. [8]
The creator of the liquidity pool defines the % weight of each asset in the portfolio. When an asset from the pool is traded (ETH for BAT) the % weight of the BAT decreases. However, the price adjusts upwards so that BAT maintains its % weight in the portfolio.
If the price of assets in a portfolio drifts too far from market prices, arbitrators eliminate price differences. There is no outside price oracle so asset prices in Balancer’s liquidity pools remain stagnant unless a trade is made.
Balancer pools aren't limited to only a couple of tokens, they support up to 8 tokens with custom % weight distributions. For example, a pool could be 30% BAT, 30% DAI, 30% USDC, and 10% LINK while another pool is 80% WETH and 20% ZRX.
Pool Types
- Weighted Pools[24]
- Composable Pools[25]
- Boosted Pools[26]
- Linear Pools[28]
- Liquidity Bootstrapping [27]
- Managed Pools[29]
- Protocol Pools[30]
Funding Rounds
In March 2020, Balancer Labs secured $3 million in funding through a seed round led by Accomplice and Placeholder, with participation from CoinFund and Inflection[11].
On November 9, 2020, Balancer Labs announced that both Pantera Capital and Alameda Research invested in Balancer Labs through the direct purchase of BAL tokens from the company's treasury. Beyond just providing capital as BAL token holders, both of these organizations provide additional value by being end-users of the protocol. [7]
In February 2021, Balancer Labs raised $5 million in their Series A funding from unknown investors. In May 2021, Balancer Labs raised $24.3 million in a Venture Round through Blockchain Capital, Continue Capital, Fenbushi Capital, FinTech Collective, Kain Warwick, and LongHash Ventures. [18]
Balancer Pool Hack
At least two Balancer multi-token pools lost over $500,000 on June 28th, 2020 when a hacker exploited a vulnerability involving AMM and the deflationary token model[13].
The attacker deployed a smart contract to automate multiple actions in a single transaction. It started with a FlashLoan of 104,000 WETH from dYdX. That FlashLoan was used to swap WETH to STATERA (STA) token back and forth 24 times which drained the STA balance from the pool and it became 1 weiSTA, (0.000000000000000001 STA). [13]
This worked because token balances are tracked in the Balancer Pool and STA token had a deflationary model with a transfer fee of 1% charged from a recipient, which resulted in transfer() and transferFrom() misbehavior. Every time the attacker swapped WETH to STA, the Balancer Pool received 1% less STA than was expected. The attacker then swapped 1 weiSTA to WETH multiple times. Due to STA token transfer fee implementation, WETH was released even though the pool never received STA. The attacker then did the same thing to drain Wrapped Bitcoin (WBTC), SNX, and Link token balances from the pool. [13]
To finish the attack, the hacker repaid their FlashLoan of 104,000 WETH to dYdX and rapidly increased their share in the Balancer Pool by depositing a few weiSTAs. Finally, the attacker swapped their Balancer Pool token to 136,000 STA through Uniswap V2, they then swapped 136,000 STA to 109 WETH again. The attacker had extensive knowledge of smart contracts and used Tornado Cash to get initial funds and obscure the source of their Ethereum. [13]
Balancer V2
In February 2021, the Balancer team shared an upgrade to the protocol - Balancer V2. The core tenets of Balancer V2 are security, flexibility, capital efficiency, and gas efficiency. These highlights include Protocol Vault for all Balancer pool assets, improved gas efficiency, permissionless, customizable AMM logic, capital efficiency through asset managers, low gas cost and resilient oracles, and community-governed protocol fees[7][8].
Protocol Vault
The main architectural change between Balancer V1 and Balancer V2 is the transition to a single vault that holds and manages all the assets added by all Balancer pools. Balancer V2 separates the Automated Market Maker (AMM) logic from the token management and accounting. Token management/accounting is done by the vault while the AMM logic is individual to each pool. Because pools are contracts external to the vault, they can implement any arbitrary, customized AMM logic. [8]
Gas Efficiency
In Balancer V1, trading with two or more pools is gas inefficient because users have to send and receive ERC20 tokens from all pools. With Balancer's new Protocol Vault, even though trades are carried out in batches against multiple pools, only the final net token amounts are transferred from and to the vault, saving a significant amount of gas in the process. Since only final net amounts are transferred, arbitrage trades are also significantly easier. An arber who has no tokens but detects a price asymmetry between Balancer pools could trade DAI for MKR in pool 1, MKR for BAL in pool 2 then BAL for DAI in pool 3 and end up making a profit in DAI[15].
Balancer V2 allows users to hold internal token balances. For example, if a user trades token A for token B but knows that they will trade back B for A in a few hours, then they probably don’t need to take delivery of B after the first trade. Balancer can keep both tokens in the vault which may be used for the next trades, avoiding any ERC20 transactions altogether. [8]
Customizable AMM Logic
Balancer V2 pioneers customizable AMM logic by creating a launchpad for teams to innovate with different AMM strategies without thinking about low-level token transfers, balance accounting, security checks, and smart order routing. At launch, Balancer V2 will offer weighted pools (constant weight, index fund style pools like in Balancer v1) and stable pools which are suitable for tokens that are soft pegged to each other (building on the work by the Curve Finance team). Shortly after launch, they will have smart pools that allow for ongoing parameter changes and many other types of pools being built by partners. All pools provide trading liquidity due to the smart order router. [8]
Balancer V2 Asset Manager
In Balancer V2, asset managers are external smart contracts nominated by pools that have full power over the underlying tokens the pool has deposited in the vault. The asset manager can lend tokens to a lending protocol to improve the pool’s yield. A buffer must always be kept in the vault, or else trades could fail: the vault cannot trade out assets it does not currently hold on behalf of a pool[9][10].
On February 23, 2021, the Balancer announced its partnership with Aave ($AAVE) to build the first Balancer V2 Asset Manager, allowing idle assets in V2 pools to earn a yield on Aave. This partnership will bring more capital efficiency to Balancer, allowing liquidity providers to earn an additional yield on top of swap fees and BAL from liquidity mining.
As a natural consequence of Automated Market Makers, if prices start to shift in one direction, the token that’s getting more expensive will become more scarce in the pool (i.e. its balance will decrease as users buy it). This means that the cash amount of that token will run out until it hits zero. At that point, any swap attempts to buy this token would fail. This is when the Aave-Balancer Asset Manager comes into play by replenishing the cash amount of that token by redeeming a portion of the invested tokens on Aave and sending them back to the Balancer vault to prevent swaps from failing. The Asset Manager also increases the invested amount of the token that’s becoming more abundant in the pool by sending some more of it to Aave to maximize its yield. [10]
Low Gas Cost and Resilient Oracles
Balancer V2 includes oracles that are resistant to sandwich attacks using accumulators. In addition, dApps will be able to query prices with minimal gas costs and without having to store past accumulator states. The Balancer team plans on offering two types of prices that can be queried with low gas costs: instant (a more up-to-date price but less resilient to manipulation) and resilient (a less up-to-date price but more resilient to manipulation). Choosing a price type will vary depending on each use case. For example, lending protocols will likely rely on the resilient price while prediction markets could use the instant price. [9]
Governable Protocol Fees
As Balancer transitions towards a community-driven protocol, Balancer V2 implements three different types of protocol-level fees that are controlled by governance (BAL token holders):
- Trading fees: a small percentage of the trading fees paid by traders to pool LPs.
- Withdrawal fees: a small percentage of any tokens that are withdrawn from the Balancer Protocol Vault (trades not included). Moving liquidity between Balancer pools does not incur this fee.
- Flash Loan fees: a small percentage of assets that are used for flash loans from Balancer’s vault.
Trading fees and withdrawal fees will be turned off at inception, while the Flash Loan fee will start at a small value to ensure there is always a cost of capital to create a flash loan on Balancer. At first, all protocol fees will be kept in the vault. It will be up to Balancer’s governance to decide if and how these fees are used.
Liquidity Mining
Shortly after the V2 announcement, a post on Balancer’s governance forums from Balancer co-founder and CO Mike Ray McDonald invited users to “brainstorm” the V2 liquidity mining parameters. The objectives for the new liquidity mining program will center on being agile enough to quickly provide pools for “hot tokens” and the trading fees they’ll bring in, while also ensuring sustainability and simplicity, as opposed to V1's focus on "long tail" assets. McDonald also wrote that improvements to the liquidity mining program and the community incentives it provides are both parts of a long-term vision for fully decentralized governance:
“The goal is to have the widest distribution possible across users and time in order to achieve a decentralized ownership and therefore governance of the protocol.”
Stable Pools
In July 2021, Balancer launched Stable Pools on Balancer V2. Stable Pools are designed specifically for assets that trade at a similar price which vastly increases capital efficiency for like-kind swaps. Traders enjoy tighter spreads and lower slippage while liquidity providers earn a competitive yield with very little impermanent loss. [22]
MetaStable Pools Launch | Lido Partnership
In August 2021, Balancer announced the launch of MetaStable Pools alongside a partnership with Lido with joint pool incentives. MetaStable Pools are well suited to handle pegged tokens that gradually accumulate fees. [23]
A use case for MetaStable Pools is “nesting” other pools by holding their Balancer Pool Tokens (BPTs), thereby facilitating cheap swaps between their constituent tokens and those of the nested pool — as though all the component tokens were in a single pool. While Stable Pools are well suited for tokens with 1:1 exchange rates, MetaStable Pools work well for tokens that gradually diverge in value. [23]
With the MetaStable Pool launch, liquid staking protocol Lido launched a pool to facilitate trades between Ether and Staked Ether to offer liquidity for stakers securing the Ethereum Network. The number of liquidity pools was also increased for the Ethereum staking community and to support growing liquidity conditions for Lido’s stETH token. [23]
Partnerships
Balancer x Gnosis
In April 2021, Balancer partnered with Gnosis to develop a new decentralized exchange (DEX). The new Balancer-Gnosis-Protocol (BGP), as it’s dubbed, is to combine the improved vault system inherent to Balancer v2 with the price-finding mechanism devised by Gnosis. BGP will set new standards for UX, pricing, and transparency. It will use Miner Extractable Value (MEV), which utilizes an auction system to obtain better pricing. The DEX is scheduled to launch in mid-June 2021 but a PoC is already up and running, CowSwap (an acronym for “Coincidence of Wants). Its primary USP is the ability to support gasless transactions, with trades settled off-chain and zero network fees attached. [19]
Balancer x Certora
In October 2022, Balancer partnered with security auditor Certora by launching the Balancer Certora Security Accelerator to help projects building on Balancer increase their code security. The Security Accelerator will provide code reviews and grant access to Certora’s formal verification Prover. This alignment will strengthen the soundness of the code base and streamline the go-to-market process for upcoming projects. [20]
“The launch of the Balancer and Certora Security Accelerator aims to strengthen the security of Balancer’s growing builder ecosystem through its Smart Contract tooling. The Security Accelerator gives projects additional access to security reviews and software tools which makes building on Balancer a more viable option” — Fernando Martinelli, Balancer Labs CEO & Co-founder [20]
Balancer x Polygon zkEVM
In June 2023, Polygon Labs launched its zkEVM Mainnet Beta in its first step to exponentially improve the scalability and finality of Ethereum with an EVM equivalent Layer-2 ZK scaling solution. Balancer is deploying its technology onto the network to bootstrap liquidity growth and accelerate development across the ecosystem. [40]
zkEVM combines Zero Knowledge Proof Computation into an EVM equivalent Layer 2 to offer users and developers a seamless cryptographically prooved scaling solution. Polygon Labs believes this technology is primed to offer the same code and apps but with better performance, higher throughput, lower latency, and lower cost than alt-L1s, optimistic, and other ZK-Rollups. [40]
Balancer x Avalanche
On August 1, 2023, Balancer launched on Avalanche to enhance the liquid staked-token market and provide users with a flexible technology stack for DeFi. Balancer will deploy its technology on the chain to offer participants a tech stack that is tailor-made to fuel the growth of LST. [42]
Balancer and 4 LST protocols collaborate to unite the Liquid Staked Token market. Balancer will provide liquidity for sAVAX by BenQi, ankrAVAX by Ankr, yyAVAX by Yield Yak, and ggAVAX by GoGoPool to boost the Avalanche LST market. [43][45]

Balancer x Base
On August 3, 2023, Balancer announced its partnership with Base, an Ethereum Layer-2 platform solution powered by Coinbase. The launch of Balancer on Base aims to accelerate the expansion of DeFi on the Base ecosystem across a number of key areas; Boosted Pools, LSTs, ve8020, lending markets, and more. [44][45][46]
The Balancer Ecosystem LaunchPad
The 8020 Initiative
Introduced on July 6, 2023, 8020 refers to a two-asset pool with 80% of one asset and 20% of another. The 8020 initiative proposes using an 8020 pool BPT token as the governance token instead of a single token, with a pool configuration of 80% of the protocol’s native token paired with their chain’s base token or a highly liquid stablecoin. [34][35]
This model hosts a range of benefits including Deep Liquidity, Asymmetric upside and reduced impermanent loss (IL), Efficient incentive programs, and Hedging/price appreciation. [35]

LST Liquidity Hub
On May 3, 2023, Balancer tweeted that its tech has helped facilitate a 20x growth in $rETH liquidity on Ethereum.
"Igniting rapid liquidity growth across the ecosystem, discover why Balancer is primed to become the Liquid Staked Token (LST) hub of DeFi" [36]
Balancer's Composable Stable pools are programmatically tailored to ensure that the full power of Yield Bearing tokens flows to Liquidity providers. Composable Stable Pools harness an inbuilt rate provider that constantly queries the blockchain, updating the token to the correct ratio and feeding the yield accrual back to Liquidity Pools. Without rate provider technology, the two assets trade at 1:1 with any appreciation in staking yield leached out to arbitrage traders. [37]
The integration of Composable Stable pools also unlocks an efficient Liquid Staked Tokens (LST) incentive flywheel. With the benefits of these tokens actually flowing to users, Balancer can take a fee on this otherwise lost advantage. Integrated into a strategically implemented core pool mechanism, this fee is then fed back into the pool as voting incentives igniting a flywheel of efficient and ongoing liquidity growth. [37]
Boosted Pools
Introduced on April 26, 2023, Boosted Pools combine the benefits of Liquidity Pools and single-sided yield markets, creating a dynamic position. While typical Liquidity Pools have less than 20% of liquidity facilitating swaps, Boosted Pools redirect idle liquidity into external yield-generating protocols. This unlocks an additional source of sustainable Liquidity Mining incentives for users. [37][38]
An example of this unique pool type is Balancer Boosted Aave V3 USD on Ethereum. This Tri-Stable Boosted USDC/USDT/DAI pool offers protocols instant access to efficient swap paths for multiple USD tokens at the onset of pairing alongside an additional boost in efficiency for users. [38]
A Base Layer to Build
Balancer is encouraging coding less and building more via its base layer that allows other protocols and developers to simplify their work, saving time and resources. [37] For example, the Gyroscope protocol built a unique E-CLP concentrated Liquidity model with the optimized Balancer tech stack that led to the pool facilitating $4,100,262 in concentrated swaps in the first two weeks. [39]
Vulnerability Attack
On August 22, 2023, Balancer Labs received a report of a critical vulnerability affecting a number of pools representing about 4% of Balancer TVL. The Balancer team advised users to "withdraw affected LPs immediately". Users can determine whether their connected wallets are associated with affected pools via the Balancer personalized UI. [48]
In response, the Emergency SubDAO[47] acted to enable proportional exit from all affected pools and pause any pools still within the pause window. [48]
A few hours later on August 23, 2023, the team announced on Twitter (now called X) that over 97% of the vulnerability had been resolved and 0.89% of the total TVL remained at risk and although nothing had been exploited, users were advised to withdraw their funds ASAP:
"Due to the swift action of Balancer LPs, over 97% of liquidity initially deemed vulnerable is now SAFE. The vulnerability has not been exploited, however, 0.89% of total TVL ($5.6 million) remains at risk, with users advised to withdraw ASAP using the UI."[49]
Suspected Exploit on Balancer
On 3 November 2025, Balancer v2 was hit by a suspected exploit resulting in approximately USD 70.9 million worth of liquid staked Ether tokens being transferred to a newly created wallet across three transactions. [50]
The stolen tokens included: 6,850 StakeWise Staked ETH (OSETH), 6,590 Wrapped Ether (WETH) and 4,260 Lido wstETH. Analytics firm Cyvers estimated that suspicious activity related to the incident could total up to USD 84 million across multiple chains.
Balancer’s team posted publicly that a potential exploit was impacting v2 pools, and that engineering and security teams were investigating.
"We’re aware of a potential exploit impacting Balancer v2 pools. Our engineering and security teams are investigating with high priority. We’ll share verified updates and next steps as soon as we have more information.We’re aware of a potential exploit impacting Balancer v2 pools." - the team tweeted [51]
The protocol offered a white-hat bounty of up to 20% of the stolen funds if the assets were returned immediately. This event marked Balancer’s third major security incident since 2020, following a flash-loan attack in 2020 (~USD 500 K loss) and a DNS-related phishing attack in September 2023 (~USD 238 K loss). [50]
In response to the exploit, the governance token BAL dropped by over 5% as investor confidence was shaken. [50]
See something wrong?
The Agent Tokenization Platform (ATP):Build autonomous agents with the Agent Development Kit (ADK)
