Subscribe to wiki
Share wiki
Bookmark
Ramses
The Agent Tokenization Platform (ATP):Build autonomous agents with the Agent Development Kit (ADK)
0%
Ramses
Ramses is a decentralized exchange based on Arbitrum using an automated market maker model. The protocol utilizes the RAM token and veNFT, and encourages liquidity by allowing token lockers to allocate protocol emissions to specific token pairs. In return, lockers receive an anti-dilution rebase, a portion of the swap fees generated by their selected pairs, and any incentives directed towards these pairs. [1]
Overview
Ramses uses the ve(3,3) model designed by Andre Cronje. The protocol allocates swap fees based on the pools users vote for to receive token emissions, rather than distributing a portion of all protocol fees to token-locking users like other exchanges. [2]
Ramses achieves near-zero slippage through the use of an iterated price determination function designed. Ramses also incorporates a mechanism known as "bribing," allowing users or projects to allocate token emissions to specific pools. This assists in providing initial liquidity support for projects in their early stages. [3]
The exchange has partners including Liquity, The Ennead, Frax Finance, Liquid Driver, fBOMB, Shrapnel DAO, DEUS, Tarot, YFX, Angle, EI-Ramses, Oath, Inverse Finance, QiDAO, xCAD, GND Protocol, GMD Protocol, Gains Network, Firebird, Jarvis Network, Radiant Capital, DAOMaker, Beefy, Yearn, Granary, Vela Exchange, UNIDEX, Root, Ankr Network, Alchemix, Olympus DAO, Gamma, BLOTR Protocol, Arken Finance, SYMM I / O, Gravita Protocol, Muon, Ethos Reserve, PaintSwap, Swell Network, DefiEdge, Ichi, Davos Protocol, 1inch, Paraswap, Odos, Kyberswap, LayerZero, Axelar, Savvy, and others. [4]
Functionalities
Swaps
Slippage and trade prices are calculated according to the total value locked in the liquidity pairs and whether arbitrage activities have equalized the pool to its market rate. Ramses introduces two types of Liquidity Pools with different swap curves: [5]
- Volatile (UniV2-Style): This type of pool employs equal dollar value weighting for token pairs. The volatile swap curve is utilized to execute trades within these pools. [5]
- Correlated (Andre-Style): RAMSES utilizes a stable swap curve known for its efficiency compared to other DEXs. This curve aims to minimize slippage and reflects his innovative approach to stable swaps. [5]
Voting
The veRAM NFT serves to allocate emissions to LP token pairs through a voting process. Emissions are distributed based on the proportion of votes in a given epoch. [6]
Bribing
Two types of bribes are offered within Ramses: [7]
- Vote Bribes: Users and protocols can offer rewards to voters. This encourages voters to choose specific token pairs for emissions. In return for their votes, users offering the reward gets a share of the rewards. [7]
- Gauge Bribes: Apart from emissions, tokens can be provided as bribes directly to LP (liquidity provider) stakers. This encourages the expansion of liquidity in specific token pairs, particularly favoring protocols aiming to efficiently initiate liquidity within the RAMSES AMM. [7]
Vesting (veNFT Management)
In order to manage their veRAM, users can create locks and manage them by increasing lock amount, increasing lock length and merging veRAM positions. [8]
LP Staking
In the RAMSES model, LP providers do not receive swap fees, as all fees are directed to veRAM holders. Instead, staking gauges are utilized to encourage users to supply LP tokens, allowing them to earn competitive APRs. The higher the number of votes allocated to a pair, the greater the amount of RAM that will be distributed to the gauge in the subsequent epoch. A user's gauge boost affects the rate of rewards for each LP position. [9]
Ramses V2
Ramses V2 is based on the ve(3,3) DEX model by incorporating Uniswap V3's concentrated liquidity design alongside the original solid model.
Concentrated Liquidity
Ramses CL combines Bribes with Concentrated Liquidity in a custom implementation, where the majority of the platform's revenue is directed towards veRAM voters. [10]
Liquidity providers who provide liquidity in concentrated ranges receive a larger share of emissions or rewards compared to those who provide liquidity in broader price ranges. This model encourages competitive liquidity provisioning and market making that aligns with the highest concentration of utilized liquidity. The veRAM gauge boosting mechanism complements this by rewarding users for actively contributing liquidity to the Ramses system, thereby increasing the utility of veRAM. [10]
veRAM voters have additional opportunities such as claiming of vote bribes and trading fees. Trading fees within CL gauges are distributed among Voters, NFPs, and ecosystem incentives. All of the bribe rewards are allocated to the voters. [10]
Fee Tier
RAMSES V2 introduces a selection of fee tiers for users to consider when establishing a concentrated liquidity position. These tiers are designed to cater to various types of asset pairs. The options include: [11]
- 0.01%: This tier is well-suited for highly correlated and pegged assets like USDC and USDT, offering advantageous rates.
- 0.05%: Ideal for competitive asset classes such as USDC/WETH, known for generating substantial trading volume.
- 0.3%: Standard for pairs that don't fall into the aforementioned categories.
- 1.0%: Tailored for highly volatile assets, providing sufficient fee generation to offset associated risks.
Additionally, RAMSES V2 provides extra fee tier options:
- 0.005%: Specifically designed for ultra-stable token pairs like USDC-DAI, USDC-USDC.e, and USDC-USDT.
- 0.025%: Customized for competitive blue-chip pairs.
Competitive Farming
Competitive farming is a method of rewarding LP providers based on the productivity and competitiveness of their provided liquidity. In concentrated liquidity models, users have the flexibility to select the specific ranges of liquidity they wish to provide for LP. This allows users to choose from a wide range of tick values, providing a high degree of customization. [12]
RAM Token
RAM is the native token of Ramses. When users lock RAM on the platform, they receive veRAM, which can be utilized for voting on the allocation of token emissions and, consequently, determining which pools receive liquidity. User positions can be administered through the use of veNFTs (vote-escrowed non-fungible tokens). [13][10]
Token Distribution
There is a total terminal supply of 500,000,000 RAM tokens. Out of this, the initial distribution consists of 125,000,000 RAM tokens, with 75,000,000 tokens designated as veRAM. [13]
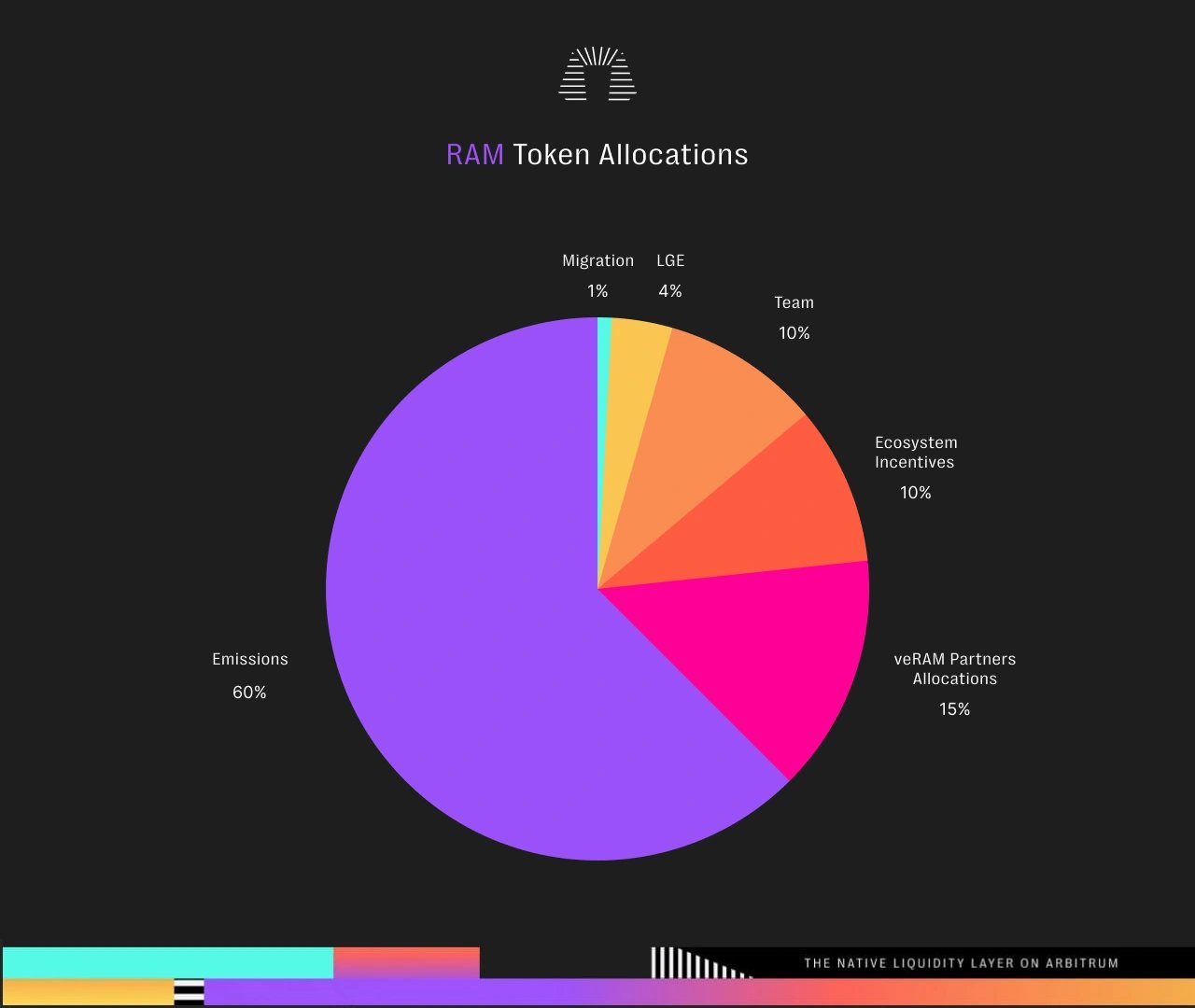
From the total supply, 1% is allocated to moSOLID Migration Bonus, 4% to LGE, 10% to the Team, 10% to Ecosystem Incentives, 15% to Parner veRAM Allocations, and 60% to emissions. [13]
Tokenomics
RAMSES adoption of the (3,3) model includes a mechanism to mitigate dilution. Initially, veRAM holders receive a 50% weekly rebase, which helps offset dilution resulting from the protocol's emissions schedule. Over time, this percentage increases by 1% with each subsequent epoch (week), until reaching a maximum cap of 75% anti-dilution per epoch. [14]
veRAM (veNFT)
veNFTs are specialized ERC-721 tokens that implement the vested-vote escrow (ve) model, representing a user's underlying position. They offer various functionalities within the RAMSES ecosystem, including the ability to vote on gauge emissions, pools for earning Vote Bribes and Swap Fees, as well as the capability to transfer or merge NFT positions. Additionally, veNFTs provide protection against dilution through Rebases. [15]
The RAMSES Bazaar, based PaintSwap, is the marketplace for veRAM trading and bartering activities. [16]
xoRAM
XoRAM is a non-transferable representation of 1 unit of RAM, securely stored within the xoRAM token smart contract. It provides users with different conversion options to both RAM and veRAM, each entailing specific penalties and vesting periods. [17]
Users can obtain xoRAM through vote bribes and emission splits in specific low-impact liquidity pairs. Each gauge can receive a portion of RAM/xoRAM based on the liquidity pair's impact on the DEX's health. Core pair will receive the majority or all of the emissions in liquid RAM. Conversely, pairs with very low trading volume and fee generation will receive a higher percentage of emissions in xoRAM. [18]
Team
The team is composed by the two co-founders DOG and North, front end developer Mali, smart cotnract developer Ren, advisors Lafa and Dudesahn, admin King, and community admin Achi. [19]
See something wrong?
The Agent Tokenization Platform (ATP):Build autonomous agents with the Agent Development Kit (ADK)
