订阅 wiki
Share wiki
Bookmark
Stable
0%
Stable
Stable 是一个高吞吐量的 Layer 1 区块链,被称为“稳定链”,旨在作为 USDT 稳定币 的专用发行和结算层。该网络被描述为“以稳定币为中心的链”和 USDT 生态系统的编排层,旨在通过优化其整个架构来实现更快、更便宜和更高效的 稳定币 交易。它以 USDT 作为其原生记账单位和 gas 代币,其既定目标是使 USDT 能够即时且可编程,以用于全球商业和支付。 [7] [4] [11]
历史
Stable于2025年7月21日推出,旨在创建一个专门构建的区块链,以解决现有稳定币交易基础设施的效率低下问题,例如不可预测的费用、缓慢的结算时间和复杂的用户体验。该项目将自己定位为第一个针对使用USDT进行支付而优化的“稳定链”。 [7]
2025年7月31日,该项目宣布已完成2800万美元的种子轮融资。公告强调,此次融资和开发恰逢美国GENIUS法案的通过,该法案为稳定币提供了更高的监管清晰度,并被视为机构采用的催化剂。Paolo Ardoino, Tether首席执行官,评论说:“现在,主要的金融机构和银行将能够充分释放USDT等资产背后的力量,这是Stable团队从根本上理解并特别准备利用的。他们在基础设施和路线图方面非常先进,这使他们能够很好地将USDT带入主流。” [8]
2025年11月4日,Stable公共测试网上线,向开发人员开放了与EVM兼容的执行层。此次发布得到了包括USDT0和LayerZero在内的基础设施合作伙伴的支持,以使USDT成为原生gas代币并提供互操作性。 [12]
11月晚些时候,Stable宣布与全球支付应用程序Oobit和支付编排平台Orbital建立合作伙伴关系,以集成StableChain,实现快速、低费用的USDT结算。 [13] 该项目还进行了一项多阶段的预存款活动,该活动于2025年11月15日结束,吸引了来自10,000多个钱包的超过11亿美元的存款。该活动的第一阶段因涉嫌内部人员抢先交易而受到批评,这促使团队为第二阶段实施了每个钱包的存款限额,以鼓励更广泛的参与。 [14]
2025年12月2日,Stable公布了其原生治理代币STABLE的代币经济学,并宣布其主网将于2025年12月8日启动。 [14] [15]
概述
Stable是一个高吞吐量的Layer 1稳定链,旨在支持USDT作为其主要资产,以满足对更快、更便宜、更高效的稳定币交易日益增长的需求。它被设计为USDT的专用发行和结算层,提供免gas转账、亚秒级最终性和优化的基础设施,用于大规模转移稳定币。该平台旨在通过创建一个具有完全EVM兼容性、专用SDK和强大的API的开发者友好环境,来释放稳定币的潜力。截至2025年11月下旬,该项目的公共测试网已处理超过497,000个账户的交易,并实现了0.73秒的平均区块时间。 [7] [13]
对于日常使用,Stable提供了一个简化的钱包,名为StablePay,可以快速发送和接收资金,与借记卡和信用卡集成,以及在一秒内完成的低成本交易。对于企业,该平台包括高级功能,如保证的区块空间分配、用于大交易量的转账聚合和增强的安全措施。它还支持保密转账,在满足监管合规要求的同时保护隐私。 [5] [11]
特性
Stable 是一个委托权益证明 区块链,专为支持大规模 USDT 活动而设计,它结合了亚秒级 区块 时间和单时隙最终性,以实现高效可靠的结算。该网络完全 EVM 兼容,允许开发人员部署 以太坊 智能合约 并使用熟悉的工具,同时受益于 Stable 优化的基础设施。一个核心特性是将 USDT 集成作为原生记账单位。用户可以通过账户抽象和 EIP-7702 标准执行无 gas 费的 USDT 转账。相比之下,非 USDT 转账使用 USDT 支付 gas 费,这些费用由捆绑器和支付系统自动转换为 gasUSDT。这种方法简化了用户体验,只需持有 USDT0 即可无缝参与。
其他功能包括一个由 LayerZero 支持构建的跨链桥,用于在 以太坊、Arbitrum、HyperEVM、Tron 和其他支持的生态系统之间转移 USDT0,以及一个专用的 Stable 钱包,它提供 Web2.5 风格的界面,以简化发送、接收和管理资产。展望未来,Stable 计划推出 USDT 转账聚合器,将多个转账合并到一个捆绑包中,从而提高吞吐量,并提供有保证的区块空间,使企业能够可预测地访问资源,以实现大批量 USDT 使用。总而言之,这些特性使 Stable 成为一个专为零售和机构环境中的 稳定币 交易而构建的 区块链 环境。 [1] [12]
技术
StableBFT
网络的共识由StableBFT管理,它是一种基于CometBFT(Tendermint Core的分支)的定制委托权益证明(dPoS)协议。它专为低延迟和高吞吐量而设计,实现了亚秒级区块时间和单时隙最终性。该协议的设计包括优化,例如将数据传播过程与共识机制本身分离,并允许直接向区块提议者广播交易,这有助于减少瓶颈并提高整体网络速度。
共识层计划进行的一项重大未来升级是过渡到名为“Autobahn”的基于有向无环图(DAG)的模型。该模型旨在通过允许并行处理交易提案来消除许多传统区块链架构中发现的单领导者瓶颈。通过将数据传播与交易的最终排序分离,Autobahn模型旨在实现更快的最终性,并提供增强的拜占庭容错(BFT),使网络更能抵抗某些类型的攻击。 [2]
Stable EVM
Stable 具有 Stable EVM,这是一个与 以太坊虚拟机 完全兼容的执行环境。这种兼容性允许开发者将现有的基于 以太坊 的 智能合约 和 去中心化应用程序 (dApps) 迁移和部署到 Stable 网络上,而无需进行重大修改。它还确保开发者可以使用来自 以太坊 生态系统的熟悉工具、编程语言(如 Solidity)和钱包。Stable EVM 包含一组预编译合约,使 智能合约 能够通过 StableSDK 安全且原子地与链的核心逻辑进行交互。
为了进一步提高性能,该项目计划将执行层升级到 "StableVM++"。这个未来的迭代将集成另一种高性能 EVM 实现,例如 EVMONE,并结合基于 Block-STM 模型的乐观并行执行引擎。并行执行使网络能够同时处理多个交易,前提是它们彼此不冲突,这可以显著提高链的交易吞吐量和效率。 [2]
StableDB
为了解决可能影响区块链可扩展性的与存储相关的性能问题,Stable 采用了一种名为 StableDB 的自定义数据管理系统。该系统旨在通过将状态提交过程与物理磁盘存储操作分离来加速区块处理。这种分离允许在无需等待缓慢的磁盘 I/O 写入完成的情况下处理区块。
StableDB 利用 MemDB 和 VersionDB 的组合,后者由 mmap 提供支持,mmap 是一种将文件或设备映射到内存中的系统调用。这种方法允许直接在内存中管理最近和经常访问的数据,以实现更快的访问,而较旧、较少使用的数据则更有效地存储在磁盘上。这种分层数据管理策略有助于缓解存储瓶颈,并有助于网络的整体性能和高吞吐量能力。 [2]
USDT 集成
Stable 区块链 从根本上是围绕 USDT 构建的,USDT 是网络的主要资产和原生记账单位。这种集成旨在创建一个以 稳定币 实用性为中心的无缝经济环境。
USDT 作为原生 Gas
在 Stable 网络上,USDT 是支付交易费用的唯一代币。对于任何需要 gas 的链上操作,例如 智能合约 交互或非 USDT0 资产的转移,费用都以 USDT0 计价和支付。为了方便这一点,网络采用捆绑器和支付方系统,该系统自动将所需的费用金额转换为专用的内部 gas 代币 gasUSDT。这种设计为用户简化了 gas 管理的复杂性,用户只需持有 USDT0 即可与网络交互。 [6]
Gas-Free Transfers
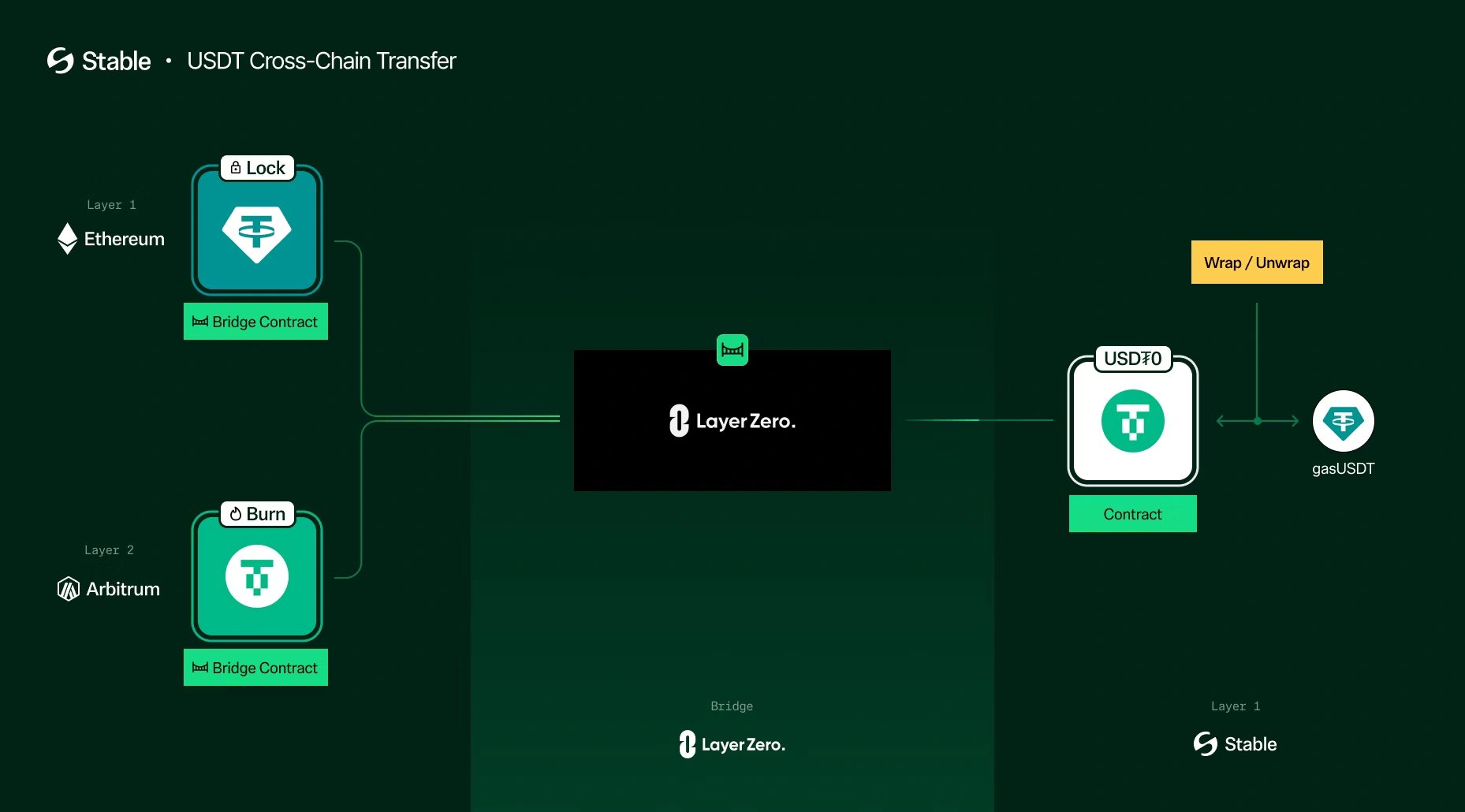
Stable网络的一个关键特性是为其原生USDT0代币实施gas免费转移。USDT0的标准点对点转移不需要发送者在协议层面支付gas费。这是通过账户抽象的实现来实现的,特别是利用EIP-7702等标准。账户抽象允许更灵活的交易验证规则,使协议能够赞助特定类型交易的gas成本,从而改善简单支付和汇款的用户体验。 [6]
这种gas免费模型旨在消除“双代币摩擦点”,这是主流采用的一个重大障碍,用户必须同时持有稳定币和单独的、不稳定的原生代币来支付gas费。对于零售用户来说,这种双代币要求增加了认知负担和复杂性。对于企业来说,它使审计、对账和合规报告变得复杂,因为传统框架是为单币种流动而构建的。通过使用USDT作为原生gas代币并使点对点转移免费,Stable旨在创建一种类似于传统金融的用户体验,将数字资产定位为传统支付方式的可行替代方案。 [9]
面向企业的功能
为了支持机构和高交易量用例,Stable 正在开发一套企业级功能:
- 保证区块空间: 此功能将允许企业和其他高交易量用户预留网络 区块 容量的固定部分。通过购买此预留空间,企业可以确保可预测的交易成本和一致的延迟,即使在全网络需求量大的时期也是如此。
- USDT 转移聚合器: 一种即将推出的机制,旨在通过将多个 USDT0 转移捆绑到单个链上交易中来提高网络吞吐量。这对于需要有效处理大量付款的交易所、支付处理商和其他实体特别有用。
- 机密转移: 此功能将利用零知识密码学为交易提供隐私。它旨在隐藏交易金额,同时保持发送者和接收者地址在链上可见。这种混合方法旨在提供商业隐私,同时保持监管合规和审计所需的透明度。 [1]
USDT0
Stable生态系统的核心资产是USDT0,它是USDT的全链版本,旨在统一流动性并简化跨链转移。USDT0建立在LayerZero的全链可替代代币(OFT)标准之上,并与传统USDT保持严格的1:1挂钩。它的主要功能是消除与传统跨链桥相关的复杂性和风险,例如流动性碎片化、包装资产和潜在的安全漏洞。
OFT标准不是在不同的区块链上创建单独的、包装版本的USDT,而是允许USDT0作为单个、可互操作的资产存在于多个网络中。当用户希望将USDT0从一个支持的链转移到另一个链(例如,从Stable到Ethereum)时,代币会在源链上被销毁或锁定,并在目标链上铸造等量的代币。这种销毁和铸造机制由LayerZero的安全跨链消息传递协议促进,确保USDT0的总供应量保持一致,并且与USDT的挂钩得以维持。与传统的桥接方法相比,此过程可实现更快的转移、最小的滑点和更低的费用。Stable网络具有原生跨链桥,可实现Ethereum、Arbitrum、HyperEVM和Tron等生态系统之间的无缝转移。 [3] [12]
STABLE 代币和代币经济学
虽然 USDT 用于所有交易和 gas 费用,但 Stable 网络由一个单独的本地实用代币 STABLE 提供安全保障和治理。STABLE 代币于 2025 年 12 月 2 日宣布,旨在作为生态系统的协调工具,旨在协调网络参与者,而不会让最终用户接触到用于支付的波动性资产。 [15] [14]
代币效用
STABLE代币具有三个主要功能:
- 质押: 该代币用于网络委托权益证明 (DPoS)共识机制 StableBFT 中的质押。验证者必须质押 STABLE 才能参与区块生产,代币持有者可以将他们的 STABLE 委托给验证者以帮助保护网络。
- 治理: STABLE 持有者可以参与链上治理,对协议升级、网络参数更改和生态系统资金的分配进行投票。
- 激励: 质押者和委托者可以获得网络交易费用的一部分,这些费用以 USDT 收取并作为真实收益奖励分配。对 STABLE 的需求是由赚取这些奖励以及参与网络安全和治理的愿望驱动的。 [15]
代币分配
STABLE代币的总供应量固定为1000亿,没有计划中的通货膨胀排放。分配如下:
- 生态系统和社区: 40% (40,000,000,000 STABLE)
- 团队: 25% (25,000,000,000 STABLE)
- 投资者和顾问: 25% (25,000,000,000 STABLE)
- 创世分配: 10% (10,000,000,000 STABLE)
团队、投资者和顾问的分配方案需遵守一年的锁仓期,随后是48个月的线性解锁计划,以确保长期一致性。 [14] [15]
路线图和里程碑
Stable 制定了一个多阶段的路线图,并在其开发中实现了几个关键的里程碑。
开发阶段
- 第一阶段:USDT的基础层: 这个初始阶段侧重于建立核心基础设施,包括使用USDT作为原生gas代币,实施StableBFT共识机制以实现亚秒级的区块时间和最终性,以及推出Stable Wallet以改善用户体验。
- 第二阶段:USDT的体验层: 第二阶段旨在通过采用乐观并行执行来提高交易吞吐量,从而增强网络性能和企业功能。它还将引入USDT转账聚合器和企业专用区块空间,以确保高效处理和一致的性能。
- 第三阶段:USDT的完整堆栈优化层: 最后一个阶段涉及升级到基于DAG的共识模型,以提高速度和弹性。此阶段还将侧重于扩展开发者工具和资源,以促进网络上分散式应用程序的开发。 [7]
主要里程碑
- 2025年7月31日: 宣布了2800万美元的种子轮融资(种子轮融资宣布链接)
- 2025年11月4日: 稳定公共测试网启动,向开发者开放。 [12]
- 2025年11月15日: 结束了预存款活动,吸引了超过11亿美元。 [14]
- 2025年12月2日: 公布了STABLE代币的代币经济学。 [14]
- 2025年12月8日: 计划主网上线。 [14]
领导层
Stable由在金融基础设施、区块链协议、风险投资和监管导航方面经验丰富的团队领导。[10]
- Brian Mehler (首席执行官): 截至2025年11月,Mehler担任Stable的首席执行官,领导公司的整体战略和执行。他之前曾担任首席财务官,负责监督财务运营和战略规划。他之前的经验包括担任Gateway Capital的首席财务官和董事总经理,管理超过10亿美元的区块链基金。[10] [13]
- Sam Kazemian (首席技术官): Kazemian担任Stable的首席技术官,同时继续担任Frax Finance的创始人。在Frax中,他开发了一种稳定币,将抵押品支持与算法稳定相结合,达到了超过14亿美元的市场价值。他还共同创立了IQ.wiki。[10]
- Thibault Reichelt (首席运营官): Reichelt负责管理Stable的运营和战略。他的职业生涯始于Kirkland & Ellis,之后在阿布扎比投资委员会工作,然后转向风险投资。他的投资组合包括Compound、dYdX、StarkWare、Circle、Wintermute和Kraken等公司。[10]
融资
2025年7月31日,Stable宣布已完成2800万美元的种子轮融资,以开发其专注于使用USDT改革传统支付基础设施的区块链。本轮融资由Bitfinex和Hack VC领投,其中包括机构公司和著名的天使投资人。 [8] [16]
机构投资者
- Bitfinex (领投)
- Hack VC (领投)
- Franklin Templeton
- Castle Island Ventures
- KuCoin Ventures
- eGirl Capital
- Mirana
- Susquehanna International Group (SIG)
- Nascent
- Blue Pool Capital
天使投资人和顾问
- Paolo Ardoino (Tether CEO)
- Bryan Johnson (Braintree 创始人)
- Divesh Makan (Iconiq Capital 创始人)
此外,Paolo Ardoino 以其作为 Tether 的 CEO 和 Bitfinex 的 CTO 的身份,自项目开始以来一直是该项目的密切顾问。 [8]
发现错误了吗?
